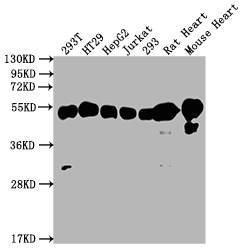
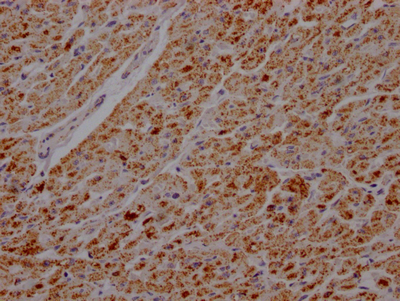
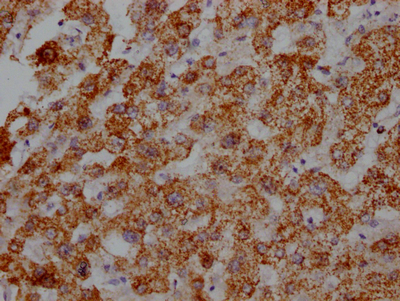
The ATP5B recombinant monoclonal antibody is produced using recombinant DNA technology and is ideal for identifying ATP5B protein from human, mouse, and rat samples in ELISA, WB, and IHC assays. The cDNA of ATP5B antibody-producing hybridomas is sequenced, and the gene coding for the ATP5B monoclonal antibody is synthesized. Myeloma cells are fused with B cells from an animal that was immunized with a synthesized peptide derived from human ATP5B to produce the hybridomas. The synthesized gene is then cloned into a vector and then transfected into cells for cultivation. The resulting ATP5B recombinant monoclonal antibody is purified through affinity chromatography from the cell culture supernatant.
The ATP5B protein is a component of the ATP synthase complex, which is responsible for generating ATP in the mitochondrial inner membrane by utilizing the energy from the proton gradient created by the electron transport chain. Specifically, ATP5B forms a catalytic core of the complex along with four other subunits, and it provides the binding sites for ADP and phosphate to produce ATP. The ATP5B protein is essential for oxidative phosphorylation, which is the main source of ATP production in cells.