[1] Davenport AP, et al. Endothelin. Pharmacol Rev. 2016;68(3):357-418.
[2] Zeng Y, et al. Associations of EDNRA and EDNRB polymorphisms with intracerebral hemorrhage. World Neurosurg. 2019;130:e804-e814.
[3] Braasch I, et al. The endothelin system: evolution of vertebrate-specific ligand-receptor interactions by three rounds of genome duplication. Mol Biol Evol. 2009;26(4):783-799.
[4] Yanagisawa M, et al. A novel potent vasoconstrictor peptide produced by vascular endothelial cells. Nature. 1988;332(6163):411-415.
[5] Li X, et al. The EDN1/EDNRA/β-arrestin axis promotes colorectal cancer progression by regulating STAT3 phosphorylation. Oncogene. 2023; doi:10.1038/s41388-023-02620-5.
[6] Wei W, et al. EDNRA Gene rs1878406 Polymorphism is Associated With Susceptibility to Large Artery Atherosclerotic Stroke. Front Genet. 2022;12:783074.
[7] Zhang L, Sui R. Effect of SNP polymorphisms of EDN1, EDNRA, and EDNRB gene on ischemic stroke. Cell Biochem Biophys. 2014;70(2):233-239.
[8] Menzi F, et al. Genomic amplification of the caprine EDNRA locus might lead to a dose dependent loss of pigmentation. Sci Rep. 2016;6:28438.
[9] Pan Z, et al. MicroRNA-342-3p Loaded by Human Umbilical Cord Mesenchymal Stem Cells-derived Exosomes Attenuates Deep Vein Thrombosis by Downregulating EDNRA. Preprints. 2021; doi:10.21203/rs.3.rs-764341/v1.
[10] Zhou W, et al. MicroRNA-1929-3p participates in murine cytomegalovirus-induced hypertensive vascular remodeling through Ednra/NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int J Mol Med. 2021;47(2):719-731.
[11] Lampmann T, et al. Experimental Induction of Intracranial Aneurysms in Rats: A New Model Utilizing a Genetic Modification within the EDNRA Gene. Brain Sci. 2022;12(9):1239.
[12] Mercier O, et al. Endothelin A receptor blockade improves regression of flow-induced pulmonary vasculopathy in piglets. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg. 2010;140(3):677-683.
[13] Zhou W, et al. MicroRNA-1929-3p participates in murine cytomegalovirus-induced hypertensive vascular remodeling through Ednra/NLRP3 inflammasome activation. Int J Mol Med. 2022;49(1):27.
[14] Zhang Y, et al. miR-1929-3p Overexpression Alleviates Murine Cytomegalovirus-Induced Hypertensive Myocardial Remodeling by Suppressing Ednra/NLRP3 Inflammasome Activation. 2022; doi:10.3390/ijms23158409.
[15] Yasuno K, et al. Common variant near the endothelin receptor type A (EDNRA) gene is associated with intracranial aneurysm risk. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011;108(49):19707-19712.


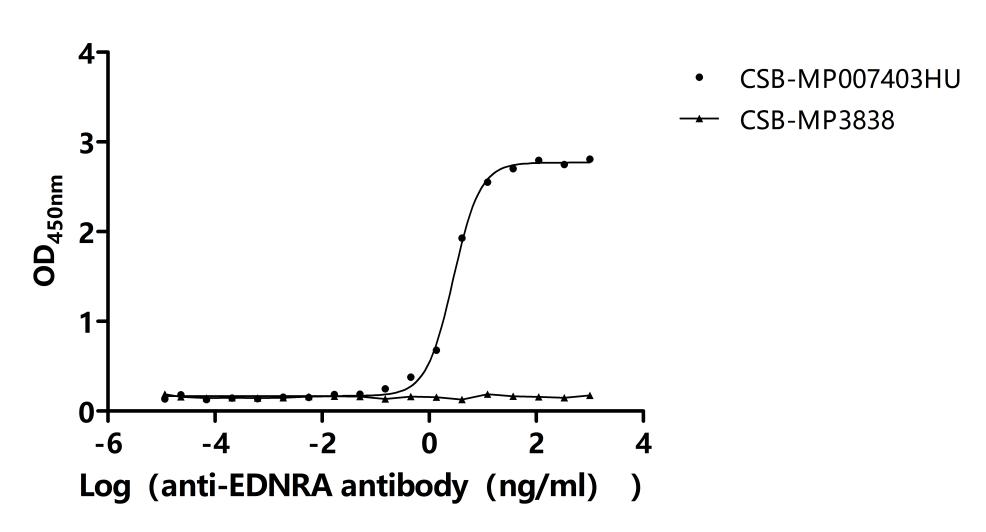
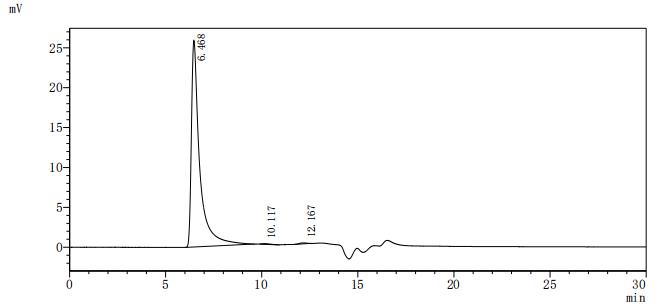
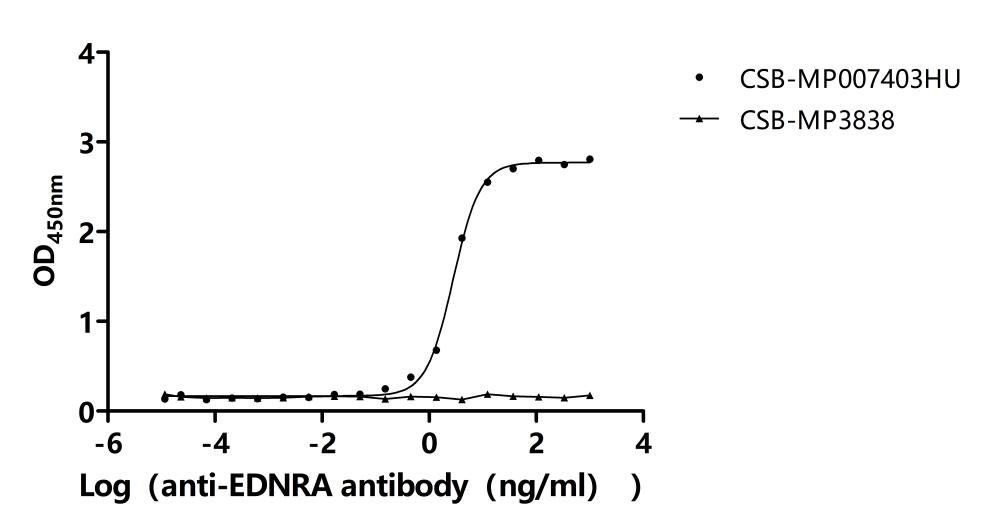
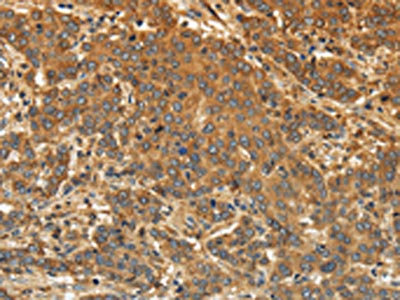




Comments
Leave a Comment