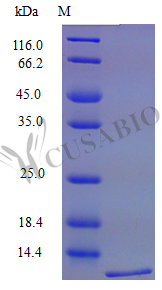
Recombinant Mouse C-X-C motif chemokine 16 protein (Cxcl16) is produced in E. coli and spans amino acids 27-114, representing a partial-length, tag-free protein. SDS-PAGE analysis shows purity exceeding 98%. The protein demonstrates full biological activity, which was confirmed through chemotaxis bioassays using murine lymphocytes at concentrations ranging from 20-1000 ng/ml. Endotoxin levels remain below 1.0 EU/µg according to LAL methodology.
Cxcl16 functions as a chemokine that appears to play a significant role in immune response regulation. The protein primarily attracts T cells and natural killer cells through its chemotactic activity. Research suggests Cxcl16 may also participate in various signaling pathways linked to inflammation and immune surveillance. Its research value stems largely from studies examining immune system dynamics and inflammatory mechanisms.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. Lymphocyte Chemotaxis Assays
This recombinant mouse Cxcl16 is confirmed to be biologically active in murine lymphocyte chemotaxis (active at 20-1000 ng/ml) and suitable for studying lymphocyte migration. However, the wide activity concentration range suggests variable potency, requiring careful dose optimization for different lymphocyte subsets. The high purity (>98%) supports reliable results, but researchers should establish precise dose-response curves for each specific cell type, as different lymphocyte populations may exhibit varying sensitivity to Cxcl16.
2. Receptor Binding and Interaction Studies
The protein is appropriate for CXCR6 binding studies, but the partial sequence (27-114aa) may lack important structural elements present in full-length Cxcl16. While the chemokine domain is contained within this region, researchers should validate that binding kinetics match those of the full-length protein, particularly since native Cxcl16 exists as a transmembrane protein with complex structure-function relationships.
3. Antibody Development and Validation
This protein serves as a good immunogen for antibody development, but the partial sequence will generate antibodies with limited epitope coverage, potentially missing epitopes in the mucin-like stalk or cytoplasmic domain of full-length Cxcl16. Antibodies should be validated for recognition of native, membrane-bound Cxcl16 in addition to the soluble chemokine domain.
4. Inflammatory Response Modeling
The biologically active Cxcl16 can be used in inflammation models, but researchers should note that the partial sequence represents only the soluble chemokine domain, lacking the transmembrane and cytoplasmic regions that contribute to Cxcl16's full biological functions as both a chemokine and a scavenger receptor. Results may not fully recapitulate native Cxcl16 behavior in inflammatory contexts.
5. Protein Structure-Function Analysis
This partial Cxcl16 (27-114aa) is suitable for studying the chemokine domain structure, but it cannot inform about the full-length protein's structural properties. The tag-free design is advantageous for structural studies, but findings should be contextualized as representing only the soluble chemokine domain rather than the complete transmembrane protein.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This recombinant mouse Cxcl16 partial protein (27-114aa) represents the soluble chemokine domain and shows confirmed biological activity in lymphocyte chemotaxis, though with a relatively wide effective concentration range. Researchers should: 1) Perform careful dose optimization for each specific application, as the 20-1000 ng/ml range indicates variable potency; 2) Acknowledge that this truncated form lacks the transmembrane and mucin-like domains of full-length Cxcl16, limiting direct comparisons with native membrane-bound Cxcl16 functions; 3) For binding studies, focus on CXCR6 interactions while recognizing that the soluble domain may exhibit different binding characteristics than the full-length protein; 4) When developing antibodies, validate against full-length Cxcl16 to ensure comprehensive epitope recognition. The high purity and low endotoxin content make this protein valuable for controlled studies of the chemokine domain's functions, but researchers should supplement key findings with full-length Cxcl16 validation when studying complex biological contexts involving membrane presentation or scavenger receptor functions.