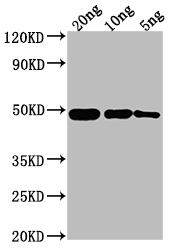
Generation of the OMPF polyclonal antibody starts with the choice of a recombinant Escherichia coli (strain K12) OMPF protein (23-362aa) as the immunogen. This protein is used for immunizing a rabbit, which induces the production of antibodies. The serum is collected from the rabbit to obtain polyclonal antibodies, which are then purified through protein G affinity chromatography. The OMPF antibody is recommended for detecting Escherichia coli (strain K12) OMPF protein through ELISA and WB assays.
The OMPF protein in Escherichia coli (strain K12) is an outer membrane porin that plays a crucial role in regulating the transport of molecules across the bacterial outer membrane. It forms a channel that allows small molecules, such as nutrients and waste products, to pass through the outer membrane and into the periplasmic space. OMPF also plays a role in protecting the bacterial cell from various environmental stresses, such as osmotic shock and antibiotics.