Full Product Name
Rabbit anti-Escherichia coli(strain K12) ompF Polyclonal antibody
Alternative Names
Outer membrane protein F (Outer membrane protein 1A) (Outer membrane protein B) (Outer membrane protein IA) (Porin OmpF), ompF, cmlB coa cry tolF
Species Reactivity
Escherichia coli
Immunogen
Recombinant Escherichia coli Outer membrane protein F protein (23-362aa)
Immunogen Species
Escherichia coli(strain K12)
Purification Method
>95%, Protein G purified
Concentration
It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
Buffer
Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4
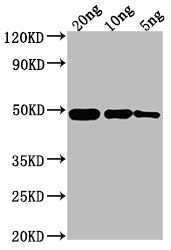
Tested Applications
ELISA, WB
Recommended Dilution
| Application |
Recommended Dilution |
| WB |
1:1000-1:5000 |
Storage
Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
Lead Time
Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
Description
Polyclonal rabbit anti-ompF antibody raised against a recombinant protein containing the 23-362 amino acids of the Escherichia coli ompF is recommended to detect the Escherichia coli ompF protein. This ompF antibody was subjected to protein G purification and reached up to 95% in purity. Two applications ELISA and WB have been used in assays to test for the specificity of this ompF antibody.
ompF plays an important role in regulating the permeability of the bacterial cell envelope as a porin in the outer membrane of E. coli. It has been shown to be involved in the uptake of nutrients and antibiotics, as well as in the efflux of toxins and metabolic waste products. It is also involved in the maintenance of the structural integrity of the bacterial cell envelope and the attachment and invasion of host cells, as well as in the regulation of the host immune response.
Usage
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.