S100 calcium binding protein B (S100B) is a small acidic protein belonging to the S100 family of calcium-binding proteins. Glial cells and Schwann cells of the nervous system primarily express S100B, where it plays important roles in intracellular calcium homeostasis, cell cycle regulation, and cytoskeletal dynamics. Under pathological conditions, S100B is released into extracellular spaces and can serve as a biomarker for neuronal damage. This makes it valuable in research examining brain injury, neurodegenerative diseases, and neuroinflammation.
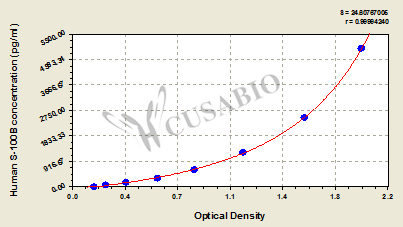
The Human Soluble protein-100B,S-100B ELISA Kit (CSB-E08065h) is designed for quantitative measurement of S100B in human samples. This sandwich ELISA accommodates serum, plasma, tissue homogenates, and cerebrospinal fluid with a detection range of 78 pg/mL to 5000 pg/mL and sensitivity of 19.5 pg/mL. The assay requires 50-100 μL sample volume, measures absorbance at 450 nm, and can be completed within 1-5 hours.
Application Examples
Note: The following application examples are drawn from a selection of publications citing this product. For additional applications, please refer to the full list of references in the "Citations" section.
This ELISA kit has been used in clinical research studies to measure S100 calcium binding protein B levels in human biological samples. The applications span neurological research contexts, including studies of brain injury biomarkers and complement system activation following cardiac arrest resuscitation.
• Neurological biomarker research: Measuring brain-specific protein levels in serum samples from patients undergoing surgical procedures, as part of comprehensive biochemical parameter panels
• Cardiac arrest studies: Measuring neurological damage markers in serum samples collected at multiple time points following return of spontaneous circulation, alongside complement system and inflammatory biomarkers
• Brain injury research: Analysis of plasma levels in conjunction with other neurological biomarkers including amyloid beta proteins and tau protein for comprehensive neurological profiling
• Multi-biomarker panels: Integration into broader biochemical screening approaches that simultaneously evaluate multiple neurological and inflammatory markers in clinical research settings