TAR DNA-binding protein 43 (TARDBP/TDP-43) is a highly conserved nuclear protein that plays essential roles in RNA metabolism, including transcriptional regulation, RNA splicing, and mRNA transport. Under normal physiological conditions, TDP-43 predominantly localizes to the nucleus where it binds to TAR DNA sequences and regulates gene expression. This protein has attracted considerable research attention due to its involvement in neurodegenerative diseases. Pathological aggregation and mislocalization of TDP-43 from the nucleus to the cytoplasm represents a hallmark feature of several proteinopathies, making it an important biomarker for neurological research.
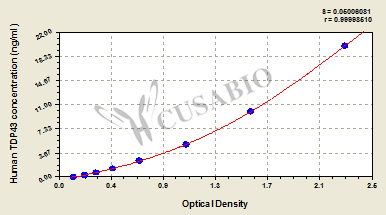
The Human TAR DNA-binding protein 43 ELISA kit (CSB-E17007h) uses a quantitative sandwich measurement principle for detecting TARDBP in human samples. This assay accommodates multiple sample types including serum, plasma, cell culture supernatants, and cerebrospinal fluid. The detection range spans 0.312 ng/mL to 20 ng/mL with sensitivity of 0.078 ng/mL. The protocol requires 50-100 μL sample volume and can be completed within 1-5 hours, with detection performed at 450 nm wavelength.
Application Examples
Note: The following application examples are drawn from a selection of publications citing this product. For additional applications, please refer to the full list of references in the "Citations" section.
Based on the provided information, no citation excerpts were available to document specific research applications for this ELISA kit targeting TAR DNA binding protein in human samples.
Without published research citations, it is not possible to provide a summary of validated applications or research contexts where this kit has been used in scientific studies.