Call us
301-363-4651 (Available 9 a.m. to 5 p.m. CST from Monday to Friday)
| Code | CSB-E04541m |
| Size | 96T,5×96T,10×96T |
| Price | Request a Quote |
| Trial Size |
24T ELISA Kit Trial Size (Only USD$150/ kit) * Sample kit cost can be deducted as a $30 credit for each 96-assay kit of the same analyte and brand you subsequently purchase within six months until depleted. More details >> Interested in a trial size? Please leave a message below.
|
| Have Questions? | Leave a Message or Start an on-line Chat |
| Intra-assay Precision (Precision within an assay): CV%<8% | |||||||
| Three samples of known concentration were tested twenty times on one plate to assess. | |||||||
| Inter-assay Precision (Precision between assays): CV%<10% | |||||||
| Three samples of known concentration were tested in twenty assays to assess. | |||||||
| To assess the linearity of the assay, samples were spiked with high concentrations of mouse E-Selectin in various matrices and diluted with the Sample Diluent to produce samples with values within the dynamic range of the assay. | |||||||
| Sample | Serum(n=4) | ||||||
| 1:1 | Average % | 93 | |||||
| Range % | 90-96 | ||||||
| 1:2 | Average % | 85 | |||||
| Range % | 81-90 | ||||||
| 1:4 | Average % | 104 | |||||
| Range % | 100-108 | ||||||
| 1:8 | Average % | 86 | |||||
| Range % | 82-90 | ||||||
| The recovery of mouse E-Selectin spiked to levels throughout the range of the assay in various matrices was evaluated. Samples were diluted prior to assay as directed in the Sample Preparation section. | |||||||
| Sample Type | Average % Recovery | Range | |||||
| Serum (n=5) | 102 | 98-106 | |||||
| EDTA plasma (n=4) | 89 | 85-94 | |||||
| These standard curves are provided for demonstration only. A standard curve should be generated for each set of samples assayed. | ||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
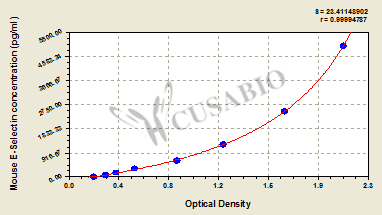
|
||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||||
This Mouse SELE ELISA Kit was designed for the quantitative measurement of Mouse SELE protein in serum, plasma, tissue homogenates. It is a Sandwich ELISA kit, its detection range is 78 pg/mL-5000 pg/mL and the sensitivity is 19.5 pg/mL.
There are currently no reviews for this product.