AGE and RAGE
Advanced glycation end products (AGEs) are the non-enzymatic glycation products of the aldehyde group of reducing sugars and the free amino groups of macromolecular substances such as proteins, amino acids, lipids or nucleic acids in the body under the condition of hyperglycemia. This process is also known as the browning reaction. AGE receptors include RAGE, oligosaccharide transferase -48(OST48, also known as AGE-R1), 80K-H (also known as AGE-R2), galectin-3(AGE-R3) and other AGE-binding proteins such as scavenger receptors. RAGE is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. It is mainly responsible for signal transduction and ligand-induced up-regulation after ligand binding.
The Function of AGE-RAGE Signaling Pathway
Excessive deposition of advanced glycation end products (AGEs) can damage the structure of the extracellular matrix, alter its biochemical properties and metabolism, and cause covalent cross-linking of proteins.
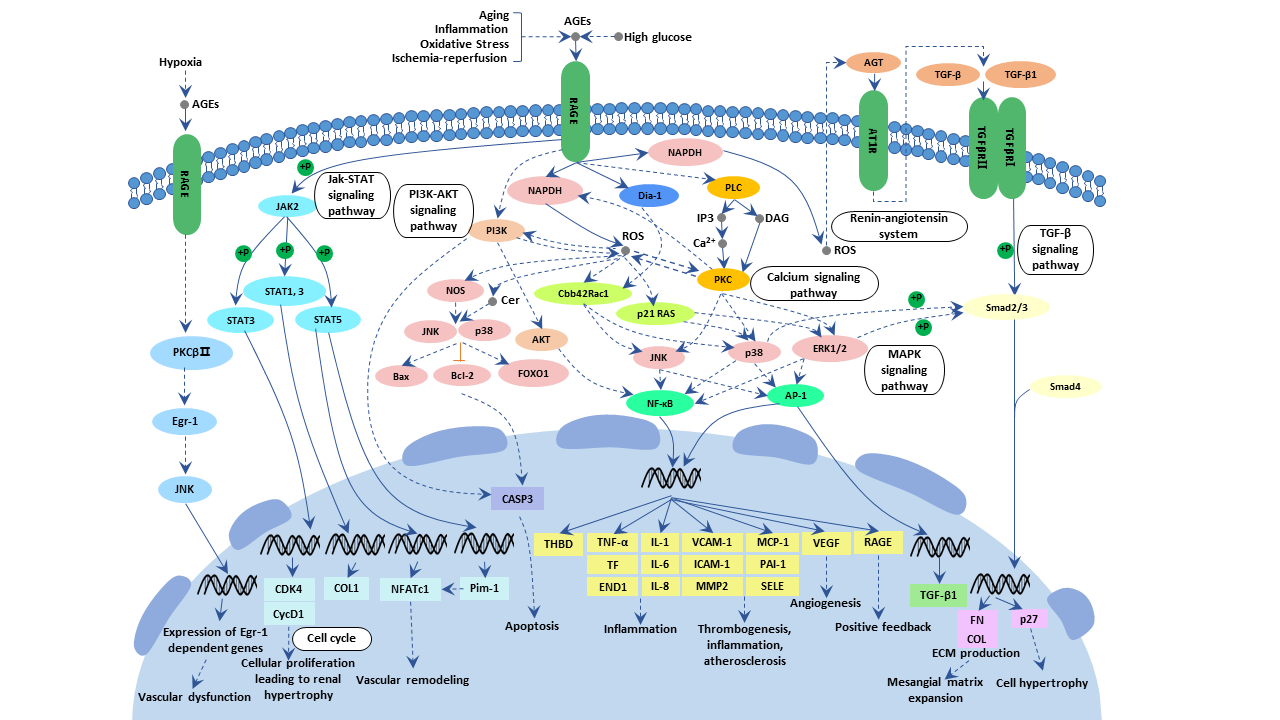
The binding of AGE to its receptor RAGE products NAPDH and enhances oxidative stress, activates the NF-κB signaling pathway, and further stimulates the production of cytokines and growth factors, thereby causing damage to cells and tissues. Therefore, this signaling pathway plays an important role in the pathogenesis of diabetic complications.
AGE-RAGE Signaling Pathway
Binding of AGEs to their receptor RAGE activates a range of signaling pathways, including activation of protein kinase C (PKC), tyrosine phosphorylation of JAK-STAT, PI3K-Akt, MAPK and Calcium signaling pathways. By activating MAPK and PI3K-Akt signaling pathways, NAPDH can be further activated to promote the formation of reactive oxygen species, activation of caspase-3 and degradation of nuclear DNA, leading to nerve cell damage and even apoptosis.
Activation of MAPK signaling pathways, PI3K-Akt signaling pathways and NAPDH promotes the formation of reactive oxygen species, and ultimately leads to the activation of caspase-3 and the degradation of nuclear DNA, thereby causing damage and even apoptosis of nerve cells.
Binding of AGEs to RAGE leads to the production of oxygen free radicals (ROS), which lead to increased transcription of NF-κB and transcription factor activator protein-1 (AP-1). NF-κB and AP-1 further regulate the expression of cytokines, growth factors (such as TNF, IGF-1, IFN-γ) and adhesion molecules (such as ICAM-1, VCAM-1), resulting in disorder of cell function.
AGE-RAGE Signaling Pathway and Disease
AGE-RAGE signaling-mediated diabetic complications include diabetic neuropathy, diabetic nephropathy, diabetic vascular complications, and diabetic foot syndrome. In addition, AGEs also play an important role in most age-related diseases such as Alzheimer's, cancer, cardiovascular disease, kidney disease, high blood pressure, stroke, visual impairment and skin diseases.





