The mouse cTnI ELISA Kit quantitates mouse cTnI levels in serum and plasma. cTnI (TNNI3) is uniquely expressed in cardiac sarcomeres. It is the inhibitory component of the heterotrimeric troponin complex (cTn) that controls calcium ion-dependent activation of sarcomeres. cTnI functions as a key modulatory protein in cardiac muscle contraction and relaxation, combining calcium ion-troponin C (TnC) binding with activation of cross-bridge reactions with the thin filament. Increased serum levels of cTnI are identified as highly sensitive and specific indicators of myocardial injury. Serial determination of cTnI is routinely applied in the evaluation of patients with the acute coronary syndrome (ACS) for diagnosis and prognosis.
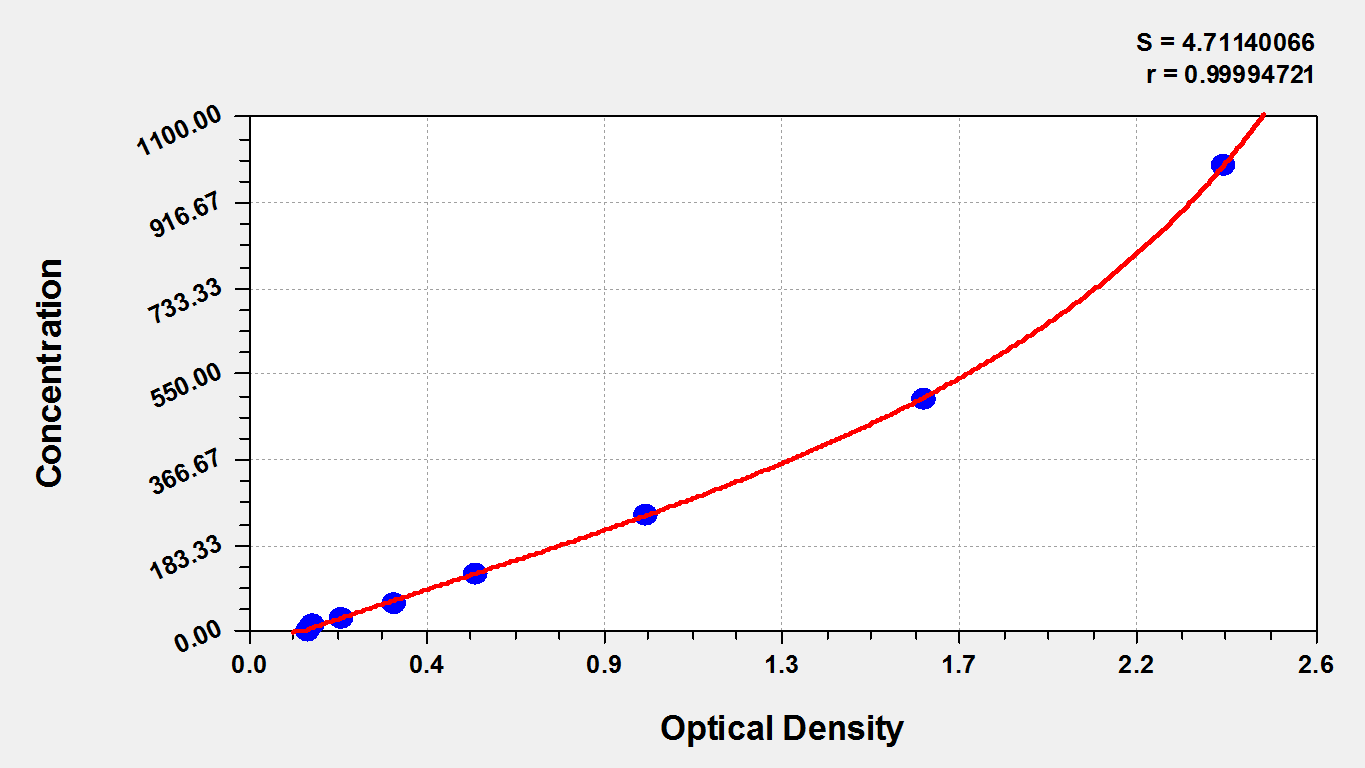
This kit employs the sandwich-ELISA mechanism in conjugation with cTnI antibody-cTnI antigen-specific binding as well as HRP-TMB chromogenic reaction to measure the concentration of cTnI in the samples. The kit is characterized by high sensitivity, strong specificity, good linearity, high recovery, and a precision of less than 10%.