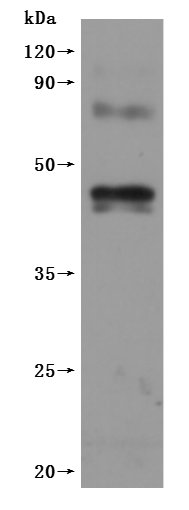
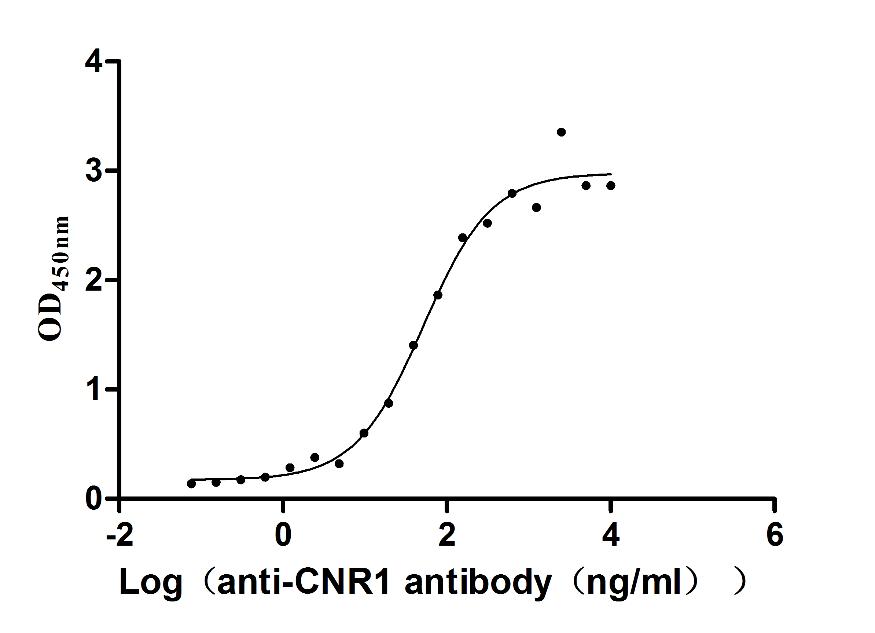
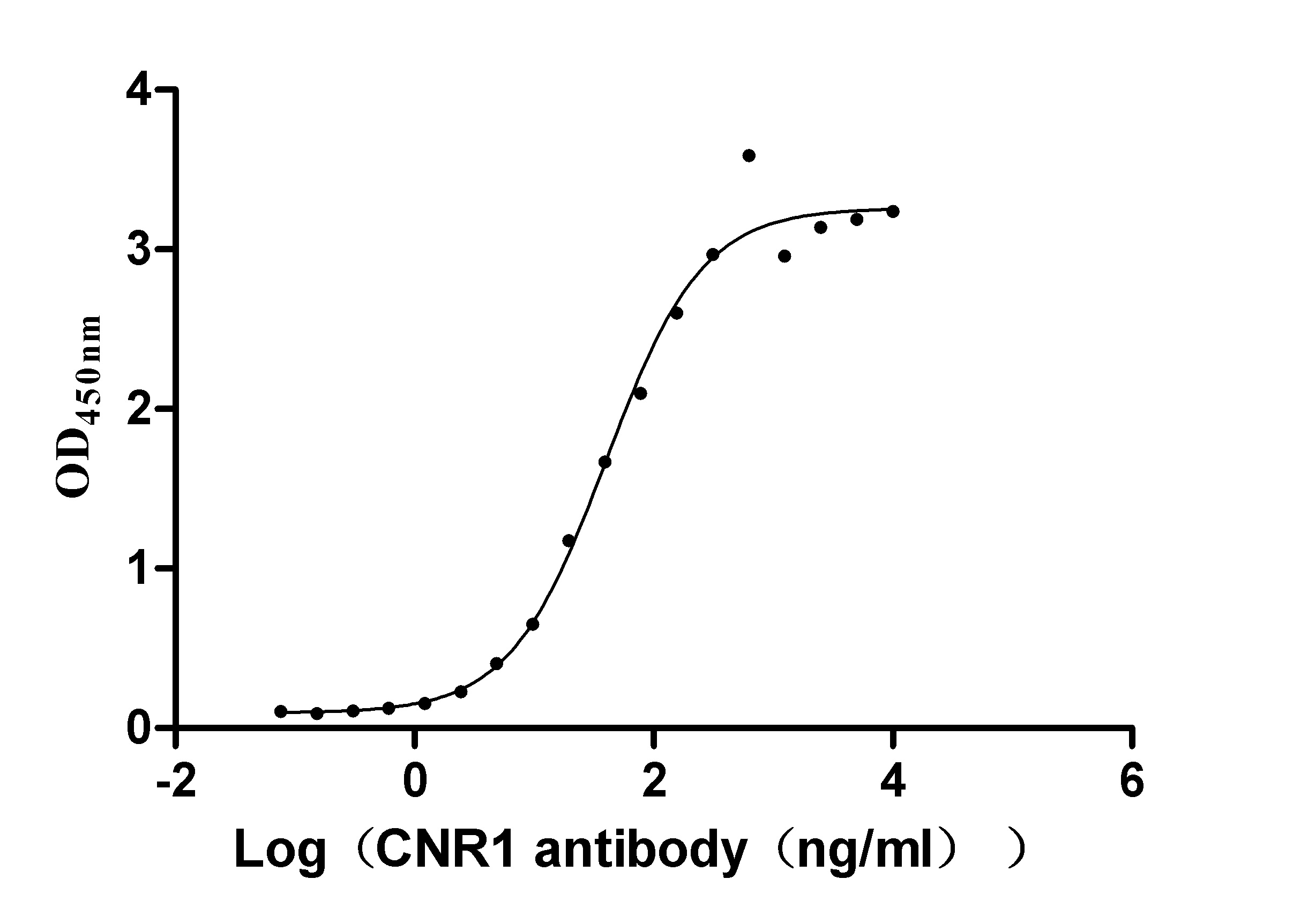
This recombinant human CNR1 (amino acids 1-472) is expressed as a virus-like particle (VLP) in mammalian cells with C-terminal 10×His tagging. The VLP formulation maintains the CNR1's native conformation while exhibiting low endotoxin levels (<1.0 EU/μg, LAL method). Functional analysis demonstrates specific binding to anti-CNR1 antibody (CSB-RA005678MA01HU) in ELISA (EC50: 41.72-63.54 ng/mL at 10 μg/mL immobilization), validating its structural integrity. The mammalian expression system ensures proper post-translational modifications critical for CNR1 functionality, while the VLP presentation mimics natural membrane association. This lyophilized preparation offers enhanced stability and represents an advanced tool for studying endocannabinoid signaling, drug discovery, and neurological research applications.
Human CNR1 is a G protein-coupled receptor primarily found in the brain but also localized in other tissues throughout the body, including the gastrointestinal system and adipose tissues. It plays a crucial role in mediating the effects of endocannabinoids, which are endogenous lipid-based signaling molecules. The CNR1 gene is located on chromosome 6 in humans (not chromosome 1) and exhibits polymorphic variations that can influence individual responses to cannabinoids and susceptibility to various neurological and psychiatric conditions.
The receptor is critically involved in numerous physiological processes, including appetite regulation, pain perception, mood, and memory. It is the primary receptor that mediates the psychoactive effects of Δ9-tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), the principal compound derived from cannabis [1][2]. Studies have shown that activation of CNR1 can lead to varied behavioral responses, with genetic polymorphisms in the receptor being linked to alterations in psychological phenomena such as fear extinction mechanisms [3]. For instance, homozygotes of a specific single nucleotide polymorphism (SNP) associated with CNR1 demonstrated significant differences in fear-potentiated startle responses, highlighting its role in emotional regulation [4].
Furthermore, CNR1's involvement in the endocannabinoid system suggests its significance in neuropsychological disorders. Genetic studies indicate that individuals carrying certain CNR1 variants may exhibit heightened vulnerability to substance use disorders and mood disorders, such as depression [1][5][6]. Preclinical and clinical findings have associated CNR1 activity with the development of conditions like chronic pain, anxiety, and depression, reinforcing its potential as a target for therapeutic interventions aimed at these ailments [7][8].
Additionally, the CNR1's pharmacological profile provides a basis for its application in various treatment paradigms, including the management of appetite and metabolism, evidenced by the effects of CNR1 antagonists like rimonabant that reduce food intake and weight gain [2][7]. In rodent models, CNR1 deficiency has been linked to maladaptive stress responses, further underscoring its relevance in understanding mood disorders [8].
References:
[1] P. Zhang, H. Ishiguro, et al. Human cannabinoid receptor 1: 5′ exons, candidate regulatory regions, polymorphisms, haplotypes and association with polysubstance abuse. Molecular Psychiatry, vol. 9, no. 10, p. 916-931, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1038/sj.mp.4001560
[2] Z. Tang, J. Xu, et al. Genome-wide association study reveals candidate genes for growth relevant traits in pigs. Frontiers in Genetics, vol. 10, 2019. https://doi.org/10.3389/fgene.2019.00302
[3] E. Russo. Clinical endocannabinoid deficiency reconsidered: current research supports the theory in migraine, fibromyalgia, irritable bowel, and other treatment-resistant syndromes. Cannabis and Cannabinoid Research, vol. 1, no. 1, p. 154-165, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1089/can.2016.0009
[4] D. Smith, C. Stanley, T. Foss, R. Boles, & K. McKernan. Rare genetic variants in the endocannabinoid system genes cnr1 and dagla are associated with neurological phenotypes in humans. Plos One, vol. 12, no. 11, p. e0187926, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0187926
[5] G. Juhász, D. Chase, et al. Cnr1 gene is associated with high neuroticism and low agreeableness and interacts with recent negative life events to predict current depressive symptoms. Neuropsychopharmacology, vol. 34, no. 8, p. 2019-2027, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1038/npp.2009.19
[6] M. Şengül, C. Şengül, et al. Association of the drd2 taqia, 5-ht1b a-161t, and cnr1 1359 g/a polymorphisms with alcohol dependence. Klinik Psikofarmakoloji Bülteni-Bulletin of Clinical Psychopharmacology, vol. 24, no. 2, p. 115-121, 2014. https://doi.org/10.5455/bcp.20131229022915
[7] M. Dao and A. François. Cannabinoid receptor 1 inhibition in chronic kidney disease: a new therapeutic toolbox. Frontiers in Endocrinology, vol. 12, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fendo.2021.720734
[8] Q. Zhang, A. Shao, Z. Jiang, H. Tsai, & W. Liu. The exploration of mechanisms of comorbidity between migraine and depression. Journal of Cellular and Molecular Medicine, vol. 23, no. 7, p. 4505-4513, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/jcmm.14390