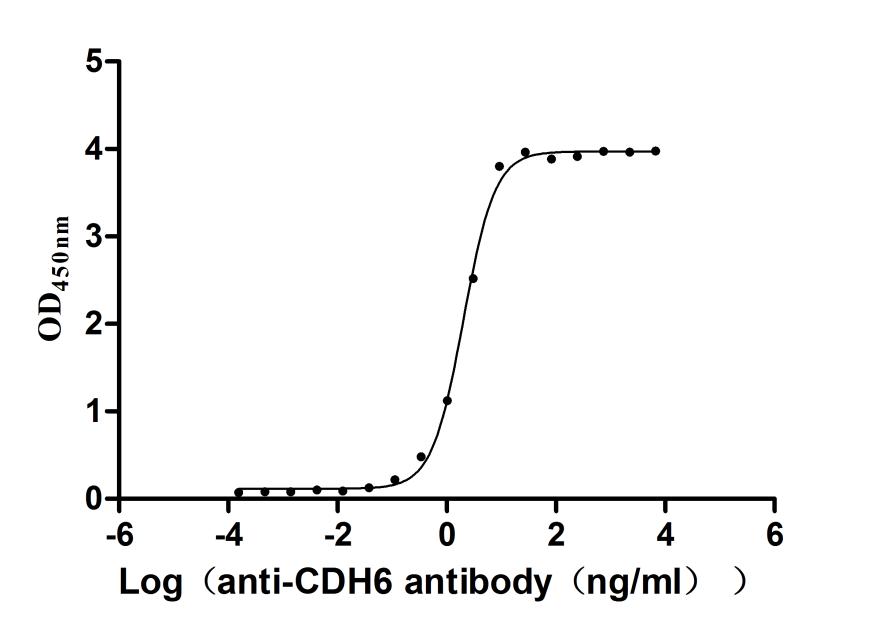
This recombinant mouse Cdh6 protein is an active form expressed in a mammalian system to ensure proper folding and native-like functionality. It consists of amino acids 54 to 615 from the mouse Cdh6 sequence and includes a C-terminal 10xHis tag for convenient purification and detection. The recombinant Cdh6 protein exhibits high purity—over 95% as confirmed by SDS-PAGE analysis. Endotoxin content is controlled to be less than 1.0 EU/μg by LAL testing standards. The Cdh6 protein's activity has been validated in a functional ELISA. When coated at 2 μg/mL, it binds specifically to the anti-CDH6 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA005055MA1HU), with an EC50 between 1.884 and 2.164 ng/mL. These features confirm its suitability for applications involving antibody interaction or cadherin-related research.
The mouse Cdh6 protein, a type II cadherin, plays a significant role in various biological processes, particularly in neural development and kidney formation. Its primary functions encompass mediating cell-cell adhesion, contributing to neuronal circuitry, and influencing nephrogenesis.
In the context of the nervous system, Cdh6 is crucial for axon-target matching in retinal ganglion cells (RGCs). Specifically, Cdh6 is expressed by RGCs and their target cells in the visual pathway, facilitating the correct targeting of these axons during development. Studies have demonstrated that Cdh6 acts as a guiding signal that ensures RGCs project appropriately to their synaptic targets [1][2]. Deletion of Cdh6 leads to aberrant projections by RGCs, causing them to target incorrect areas, which could significantly disrupt visual processing [2][3].
Cdh6's involvement is not restricted to neural functions; it also plays a critical role in kidney development. Research has indicated that Cdh6 is vital for the proper formation of nephron structures during embryonic development. Mice lacking this protein exhibit a reduced number of nephrons, attributable to improper epithelial polarization and nephron fusion to ureteric buds [4][5]. This function highlights its essential role in transforming mesenchymal precursors into epithelial cells crucial for nephrogenesis [6].
Additionally, Cdh6 is implicated in various aspects of cellular signaling, particularly during epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT), a process critical in both development and cancer metastasis. Cdh6 contributes to regulating intracellular signaling pathways essential for cell adhesion and motility [7][8]. Notably, its expression has been connected to advanced stages of EMT in various cancer types, signifying a dual role in both normal developmental processes and pathological states [9][8].
The interplay of Cdh6 with other cadherins and their associated proteins suggests a complex network of interactions essential for maintaining tissue architecture and function [10]. Cdh6's ability to interact with β-catenin and other cytoplasmic signaling proteins underscores its multifaceted role as both a structural and signaling molecule [11].
References:
[1] J. Osterhout, N. Josten, et al. Cadherin-6 mediates axon-target matching in a non-image-forming visual circuit. Neuron, vol. 71, no. 4, p. 632-639, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuron.2011.07.006
[2] J. Osterhout, R. El‐Danaf, P. Nguyen, & A. Huberman. Birthdate and outgrowth timing predict cellular mechanisms of axon target matching in the developing visual pathway. Cell Reports, vol. 8, no. 4, p. 1006-1017, 2014. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.celrep.2014.06.063
[3] J. Kay, I. Huerta, et al. Retinal ganglion cells with distinct directional preferences differ in molecular identity, structure, and central projections. Journal of Neuroscience, vol. 31, no. 21, p. 7753-7762, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1523/jneurosci.0907-11.2011
[4] N. Treacy, S. Clerkin, et al. Growth and differentiation of human induced pluripotent stem cell (hipsc)-derived kidney organoids using fully synthetic peptide hydrogels. Bioactive Materials, vol. 21, p. 142-156, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.bioactmat.2022.08.003
[5] U. Dahl, A. Sjödin, et al. Genetic dissection of cadherin function during nephrogenesis. Molecular and Cellular Biology, vol. 22, no. 5, p. 1474-1487, 2002. https://doi.org/10.1128/mcb.22.5.1474-1487.2002
[6] V. Sancisi, G. Gandolfi, et al. Cadherin 6 is a new runx2 target in tgf-β signalling pathway. Plos One, vol. 8, no. 9, p. e75489, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0075489
[7] I. Huerta, I. Kim, P. Voinescu, & J. Sanes. Direction-selective retinal ganglion cells arise from molecularly specified multipotential progenitors. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 109, no. 43, p. 17663-17668, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.1215806109
[8] M. Gugnoni, V. Sancisi, et al. Cadherin-6 promotes emt and cancer metastasis by restraining autophagy. Oncogene, vol. 36, no. 5, p. 667-677, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2016.237
[9] C. Ma, J. Zhao, et al. Combined overexpression of cadherin 6, cadherin 11 and cluster of differentiation 44 is associated with lymph node metastasis and poor prognosis in oral squamous cell carcinoma. Oncology Letters, 2018. https://doi.org/10.3892/ol.2018.8509
[10] E. Epifanova, В. Салина, et al. Adhesion dynamics in the neocortex determine the start of migration and the post-migratory orientation of neurons. Science Advances, vol. 7, no. 27, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1126/sciadv.abf1973
[11] Q. Liu, M. Dalman, et al. Cell adhesion molecule cadherin‐6 function in zebrafish cranial and lateral line ganglia development. Developmental Dynamics, vol. 240, no. 7, p. 1716-1726, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1002/dvdy.22665