Recent advancements in CDH6-targeted drug research include First Three's initiation of the international multicenter Phase II/III clinical trial for its CDH6-targeted antibody-drug conjugate (ADC), R-DXd, marking it as the first such drug to enter this phase in China. R-DXd has shown promising clinical efficacy, particularly for platinum-resistant ovarian cancer. Additionally, Puzhong Discovery has entered a billion-dollar partnership with Adcendo ApS for the innovative ADC ADCE-T02 (AMT-754), which demonstrates potential to enhance clinical efficacy and safety. Furthermore, Simcere Pharmaceutical's CDH6 ADC drug SIM0505 has been approved by China's National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) for clinical trials, becoming the second domestically produced CDH6 ADC to enter the clinical phase after Aukang Pharma's offering. These developments highlight CDH6 as a critical target in cancer treatment and offer new therapeutic options for patients.
1. The Background of CDH6
CDH6, also known as Cadherin-6 or K-Cadherin, is a Type II classical cadherin protein made up of 790 amino acids. It includes an extracellular domain, a transmembrane region, and an intracellular tail. Located on the fifth human chromosome, CDH6 is vital for mediating calcium-dependent cell adhesion in epithelial cell membranes, maintaining tissue integrity. While it normally interacts with adjacent cells' CDH6 or other cadherins, its expression is notably increased in cancers like ovarian and renal cell carcinoma, correlating with poor outcomes. CDH6 dysfunction can impact tumor cell infiltration, metastasis, and recurrence, making it a key target in cancer research. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) targeting CDH6, such as Daiichi Sankyo's DS-6000a and Aukang Pharma's CUSP06, are in development and have shown promise in clinical trials, offering new hope for cancer treatment [1].
2. The Mechanisms of CDH6 in Tumors
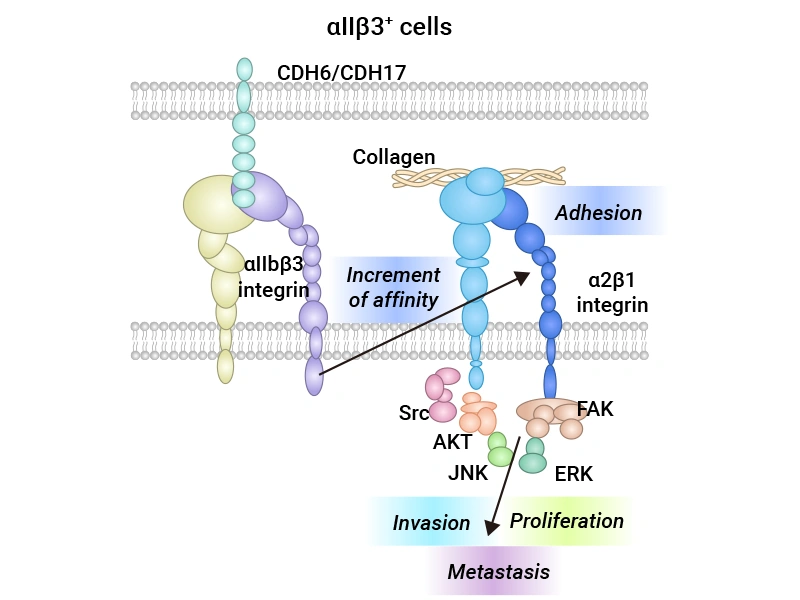
CDH6's regulatory mechanisms in tumors involve its roles in cell adhesion and signal transmission. It activates critical pathways such as SRC, FAK, AKT, and ERK by interacting with integrins αIIbβ3 and α2β1. These pathways boost tumor cell migration, survival, and proliferation. For example, SRC and FAK enhance cell adhesion and migration, while AKT inhibits apoptosis, promoting cell survival. The ERK pathway is linked to cell proliferation, which CDH6 further stimulates. Additionally, CDH6 may affect immune cell function in the tumor microenvironment, potentially fostering an immunosuppressive environment that helps tumors evade immune detection. CDH6 can also modulate the polarization of tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs), shifting them to a tumor-promoting phenotype. This makes CDH6 not only a crucial player in tumor cell behavior but also a significant target for cancer treatment strategies (Figure 1) [2-3].
Figure 1. The regulatory mechanisms of CDH6 in tumors [3]
3. CDH6 is Closely Associated with Different Cancers
3.1 Renal Cancer
Research on CDH6 in renal cancer is gaining increasing attention. Studies indicate that CDH6 is highly expressed in renal cell carcinoma (RCC), with this expression linked to tumor growth and metastasis. The overexpression of CDH6 is considered one of the key factors enhancing the invasiveness of renal cancer cells. Research by Rubén A. Bartolomé et al. suggests that CDH6 promotes cell adhesion, migration, and proliferation through interactions with integrins (such as αIIbβ3 and α2β1), potentially leading to the metastatic spread of cancer cells. Antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs) targeting CDH6 are under development, including Raludotatug Deruxtecan (DS-6000a), an ADC drug that has shown efficacy in preclinical studies on ovarian and renal cancer models. Additionally, another CDH6 ADC named CUSP06 is in development, demonstrating strong antiproliferative activity against various CDH6-positive cancer cell lines in vitro. CDH6 is not only an important molecule for understanding the biology of renal cancer but also offers new opportunities for future targeted therapies [4-6].
3.2 Ovarian Cancer
CDH6 exhibits high expression in ovarian cancer, associated with disease progression and lower survival rates. Preliminary studies show that DS-6000a has shown good safety and efficacy in treating platinum-resistant advanced ovarian cancer. In a Phase I clinical trial, the objective response rate was 46%, with a disease control rate of 98%. Data presented at the 2023 European Society for Medical Oncology (ESMO) conference indicate that DS-6000a demonstrates sustained clinical efficacy in ovarian cancer patients who have received multiple prior treatments. The median duration of response was 11.2 months, further supporting CDH6 as a therapeutic target. Currently, ADC drugs targeting CDH6 are undergoing additional clinical trials to confirm their long-term efficacy and safety. These studies not only offer new hope for ovarian cancer patients but also pave the way for treating other tumor types with high CDH6 expression [7-8].
3.3 Other Cancers
CDH6 shows abnormal expression in various cancers, particularly with higher expression levels in ovarian and renal cancers, associated with poor prognosis. In addition to these two types of cancer, increased expression of CDH6 has also been found in various malignant tumors such as cholangiocarcinoma, gastric cancer, thyroid cancer, hepatocellular carcinoma, and small cell lung cancer. The high expression of CDH6 is closely related to the growth and proliferation of tumor cells, participating in key biological processes such as cell adhesion, organ development, and epithelial-mesenchymal transition. Given the difference between high expression in tumor tissues and low expression in normal tissues, CDH6 is considered a potential therapeutic target, especially showing great potential in the development of antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs). The importance of CDH6 as a therapeutic target is growing, with expectations that it will provide new treatment options for patients with various types of cancer in the future [9-11].
4. The Advances of CDH6 in Drug Research
CDH6 is becoming a focal point in clinical drug research for its potential in cancer treatment. The primary drugs under investigation are antibody-drug conjugates (ADCs), including DS-6000, AMT-707 (CUSP06), and SIM0505, which target specific types of renal and ovarian cancers. These ADCs function by blocking CDH6-mediated cell adhesion and signaling pathways, thereby inhibiting tumor cell proliferation, migration, and invasion. DS-6000 (Raludotatug deruxtecan, R-DXd), developed by Daiichi Sankyo, is an ADC based on the DXd technology platform and is currently in Phase 2/3 clinical trials following a $22 billion partnership with Merck & Co. for global development and commercialization rights. AMT-707 (CUSP06), co-developed by Multitude Therapeutics and Oncusp Therapeutics, is in Phase 1 clinical trials. SIM0505, the first CDH6 ADC from Simcere Pharmaceutical, is in the clinical application stage with its trial application accepted by the NMPA. While CDH6 drug development is still in its early stages, the ongoing research is anticipated to yield breakthroughs in precision oncology, providing innovative solutions for cancer treatment.
|
Drug
|
target
|
Drug type
|
Indications
|
Institutions
|
Highest clinical phase
|
|
Raludotatug deruxtecan
|
CDH6 x TOP1
|
ADC
|
Fallopian tube carcinoma | platinum resistant fallopian tube carcinoma | platinum resistant ovarian carcinoma | primary peritoneal carcinoma | locally advanced malignant solid tumor | metastatic solid tumor | advanced renal cell carcinoma | ovarian carcinoma | advanced malignant solid tumor | platinum resistant primary peritoneal carcinoma | epithelial ovarian carcinoma
|
Daiichi Sankyo Co., Ltd. | First Three Co. (China) Investment Co., Ltd. | Daiichi Sankyo Pro Pharma Co., Ltd. | Mercksharp & Dohme LLC | Daiichi Sankyo, Inc. | Merck & Co., Inc.
|
Clinical stage 2/3
|
|
CUSP06
|
CDH6 x TOP1
|
ADC
|
Advanced malignant solid tumor | platinum-resistant ovarian cancer | solid tumor
|
OnCusp Therapeutics | Puzhong Discovery Pharmaceutical Technology (Shanghai) Co., Ltd.
|
Clinical stage 1
|
|
SIM-0505
|
CDH6 x TOP1
|
ADC
|
Solid tumor
|
Simcere Group Co., Ltd. | Shanghai Xianxiang Pharmaceutical Technology Co., Ltd.
|
Clinical application
|
|
ATG-106
|
CD3 x CDH6
|
Bispecific antibody
|
Hematological tumor
|
Deqi (zhejiang) pharmaceutical technology co ., ltd
|
Preclinical
|
|
SY2023
|
CDH6
|
antibody
|
tumour
|
Shanghai Xiangyao Biotechnology Co., Ltd.
|
Preclinical
|
|
CDH6-RGD (Protein Alternatives)
|
CDH6
|
monoclonal antibody
|
Renal tumor
|
Protein Alternatives SL
|
Drug discovery
|
|
WO2024165049
|
CDH6
|
monoclonal antibody
|
tumour
|
Shandong xiansheng biopharmaceuticals co., ltd
|
Drug discovery
|
|
Raludotatug
|
CDH6
|
monoclonal antibody
|
tumour
|
/
|
Unknown clinical stage
|
Table 1. Part of CDH6 clinical development drug
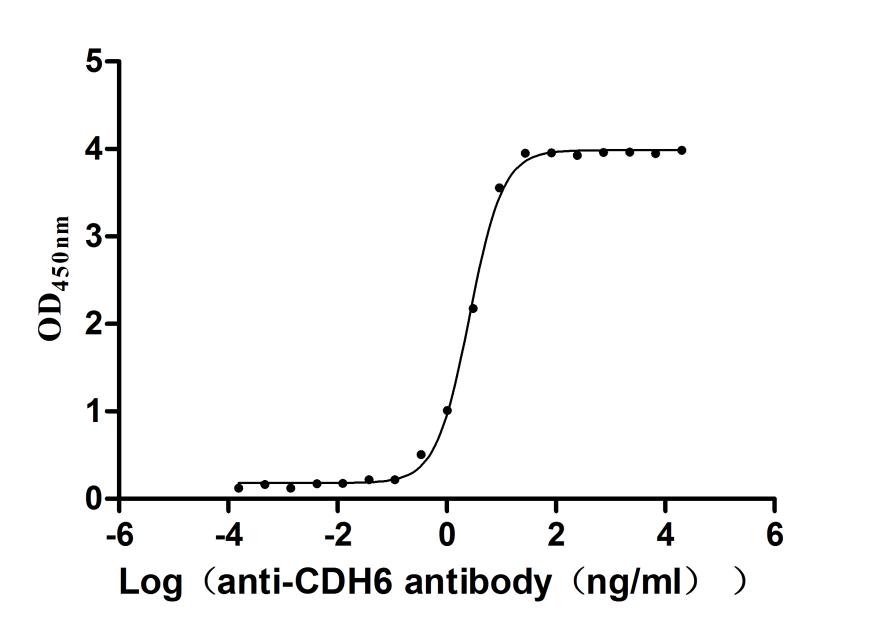
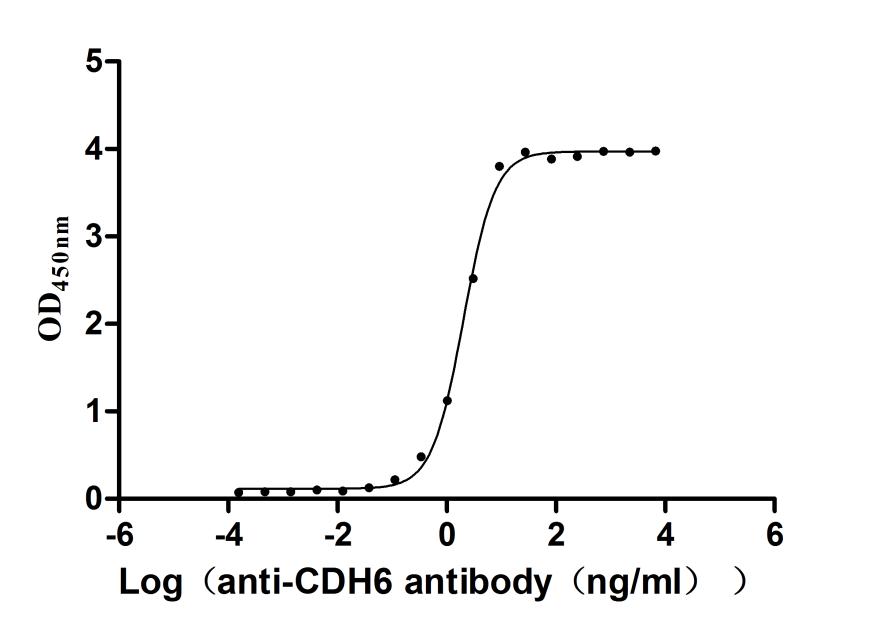
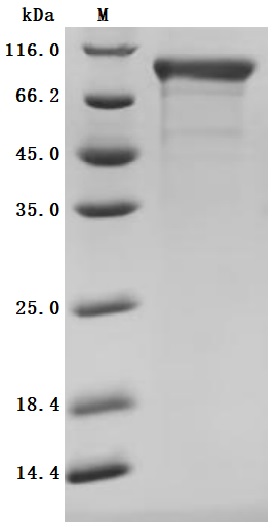
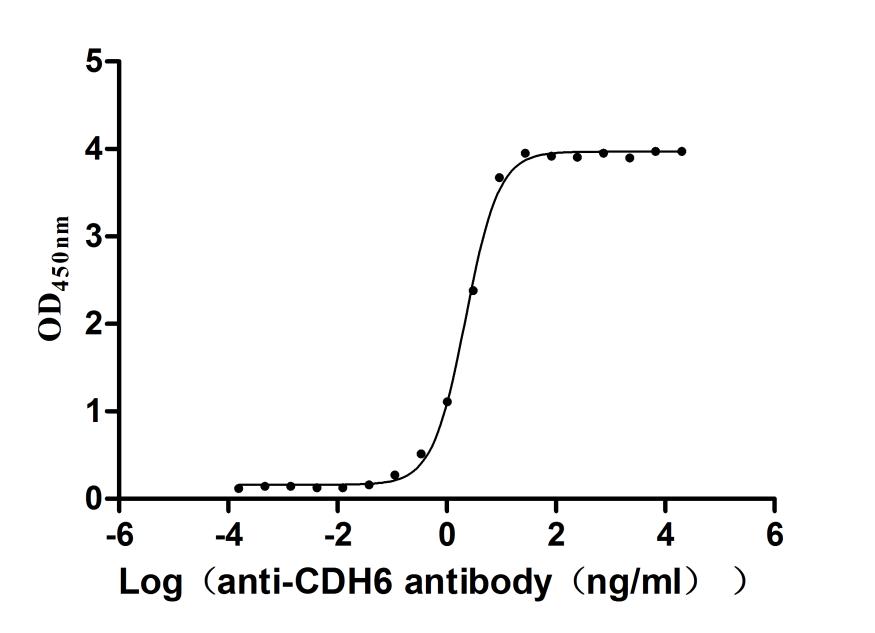
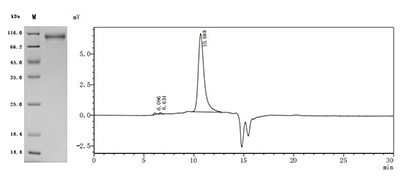
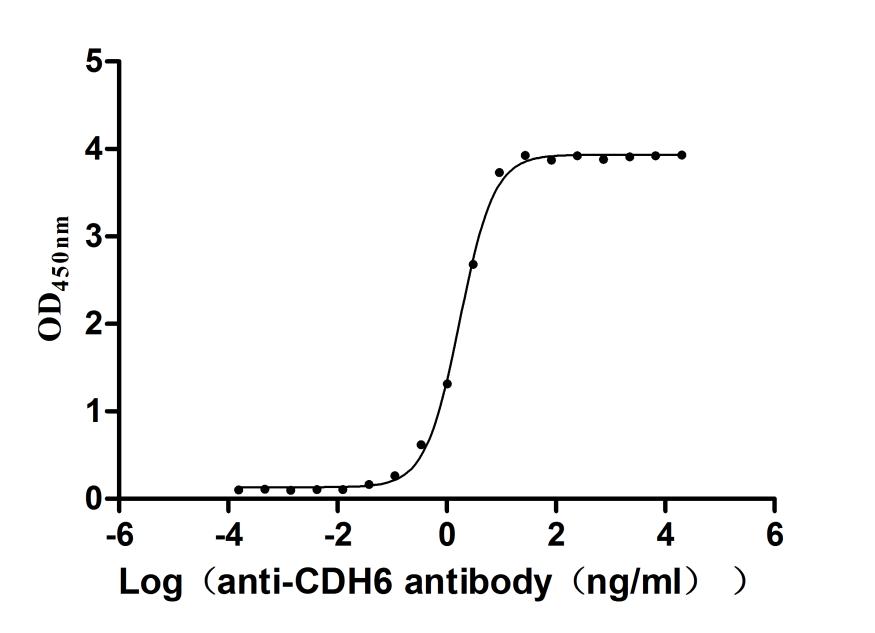
5. CUSABIO CDH6 Recombinant Protein and Antibody for Research Use
To assist pharmaceutical companies in their research on CDH6 in clinical cancer, especially in the fields of renal cancer and ovarian cancer immunotherapy, CUSABIO has launched high-activity CDH6 protein products to facilitate your research on CDH6 mechanisms or exploration of its potential clinical value.
References
[1] Schöffski, Patrick, et al. "A phase 1 study of a CDH6-targeting antibody-drug conjugate in patients with advanced solid tumors with evaluation of inflammatory and neurological adverse events." Oncology research and treatment 44.10 (2021): 547-556.
[2] Gugnoni, M., et al. "Cadherin-6 promotes EMT and cancer metastasis by restraining autophagy." Oncogene 36.5 (2017): 667-677.
[3] Bartolomé, Rubén A., et al. "CDH6‐activated αIIbβ3 crosstalks with α2β1 to trigger cellular adhesion and invasion in metastatic ovarian and renal cancers." Molecular Oncology 15.7 (2021): 1849-1865.
[4] Collins, Scott D., et al. "Targeting cadherin-6 (CDH6) with an antibody-drug conjugate for the treatment of ovarian and renal cancer." Cancer Research 76.14_Supplement (2016): 2974-2974.
[5] Suzuki, Hirokazu, et al. "Raludotatug Deruxtecan, a CDH6-Targeting Antibody–Drug Conjugate with a DNA Topoisomerase I Inhibitor DXd, Is Efficacious in Human Ovarian and Kidney Cancer Models." Molecular cancer therapeutics 23.3 (2024): 257-271.
[6] Marable, Sierra S., Eunah Chung, and Joo-Seop Park. "Page Title: Hnf4a is required for the development of Cdh6-expressing progenitors into proximal tubules in the mouse kidney."
[7] Suzuki, H., et al. "10P DS-6000a, a novel CDH6-targeting antibody-drug conjugate with a novel DNA topoisomerase I inhibitor DXd, demonstrates potent antitumor activity in preclinical models." Annals of Oncology 32 (2021): S363-S364.
[8] Hamilton, Erika P., et al. "Phase I, two-part, multicenter, first-in-human (FIH) study of DS-6000a in subjects with advanced renal cell carcinoma (RCC) and ovarian tumors (OVC)." (2022): 3002-3002.
[9] Meng, Ming, et al. "CDH6 as a prognostic indicator and marker for chemotherapy in gliomas." Frontiers in genetics 13 (2022): 949552.
[10] Zhao, Zongxian, et al. "High expression of oncogene cadherin-6 correlates with tumor progression and a poor prognosis in gastric cancer." Cancer Cell International 21 (2021): 1-9.
[11] Gugnoni, M., et al. "Cadherin-6 promotes EMT and cancer metastasis by restraining autophagy." Oncogene 36.5 (2017): 667-677.
CUSABIO team. Advancements in CDH6-Targeted Drug Research for Cancer Treatment. https://www.cusabio.com/c-21203.html



Comments
Leave a Comment