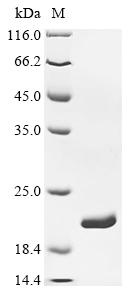
Recombinant Escherichia coli Dihydrofolate reductase (folA) is expressed in E.coli, covering the full-length sequence from amino acids 1-159. This product features a C-terminal 6xHis-tag, which helps with purification and detection. The protein appears to be of high purity, greater than 90% as assessed by SDS-PAGE, suggesting it may be reliable for experimental use. It seems suitable for research applications where a high-quality, recombinant source of dihydrofolate reductase is required.
Dihydrofolate reductase (DHFR) from Escherichia coli plays a critical role in folate metabolism by catalyzing the reduction of dihydrofolate to tetrahydrofolate. This reaction is essential for nucleotide biosynthesis. DHFR appears to be a key enzyme in folic acid's metabolic pathway, and its involvement in cellular growth and division likely makes it a significant target in antimicrobial research and drug development studies.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
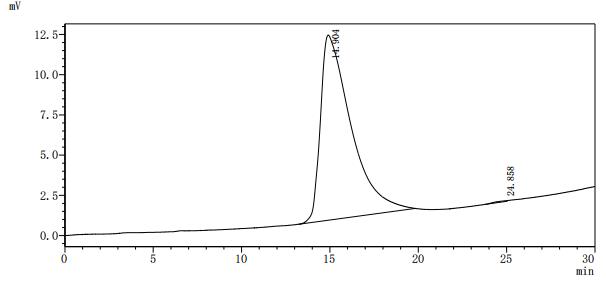
Based on the provided information, the recombinant E. coli Dihydrofolate Reductase (folA) is expressed in its native E. coli system, which is a homologous expression environment. This significantly increases the probability of correct folding since the host possesses the appropriate cellular machinery for this bacterial protein. The protein is full-length (1-159aa) with a C-terminal 6xHis tag, which typically has minimal impact on folding. The high purity (>95% by both SDS-PAGE and SEC-HPLC) is particularly noteworthy - SEC-HPLC showing a single peak suggests the protein is monodisperse, which often correlates with proper folding. However, since enzymatic activity is unverified, the protein cannot be guaranteed to be bioactive without functional validation (e.g., activity assays with dihydrofolate and NADPH).
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using His-Tag Affinity Purification
This application is well-supported. The C-terminal 6xHis tag enables effective pull-down assays to identify physiological binding partners within E. coli lysates. The homologous expression system and evidence of monodispersity (from SEC-HPLC) suggest a correctly folded protein is likely, which should preserve native interaction interfaces.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is appropriate. The high-purity, full-length protein is an excellent immunogen for generating E. coli folA-specific antibodies. Even if the protein were misfolded (unlikely in this case), it would still be useful for generating linear epitope antibodies.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Enzyme Kinetics Analysis
This application description requires significant modification. The protein is suitable for basic biochemical characterization (stability, pH sensitivity). Binding studies and especially enzyme kinetics analysis are only valid if the protein is enzymatically active. It should be stated that preliminary activity assays must confirm functionality before any binding or kinetic studies are performed. If inactive, such studies would be invalid.
4. Comparative Structural and Functional Studies
This application is highly suitable. The consistent homologous expression system and high purity make this recombinant folA an ideal reference for comparative studies with homologs from other species or engineered variants.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Given the high probability of correct folding due to homologous expression in E. coli and the strong indication of a monodisperse, pure protein from SEC-HPLC, this recombinant folA is suitable for all described applications. However, the critical first step is to perform a functional enzyme activity assay to confirm bioactivity. Once activity is verified, it can be confidently used for interaction studies, detailed enzyme kinetics, and comparative functional analyses. For antibody development, it can be used immediately. The SEC-HPLC data is a very positive indicator, but functional validation remains essential for quantitative kinetic and binding studies.