Alternative Names
Dihydrofolate reductase (EC 1.5.1.3) folA tmrA b0048 JW0047
Species Reactivity
Escherichia coli (strain K12)
Immunogen
Recombinant Escherichia coli (strain K12) folA protein (1-159aa)
Immunogen Species
Escherichia coli (strain K12)
Purification Method
Affinity-chromatography
Concentration
It differs from different batches. Please contact us to confirm it.
Buffer
Preservative: 0.03% Proclin 300
Constituents: 50% Glycerol, 0.01M PBS, pH 7.4
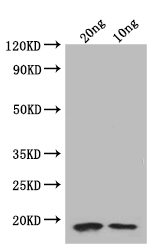
Tested Applications
ELISA, WB
Storage
Upon receipt, store at -20°C or -80°C. Avoid repeated freeze.
Lead Time
Basically, we can dispatch the products out in 1-3 working days after receiving your orders. Delivery time maybe differs from different purchasing way or location, please kindly consult your local distributors for specific delivery time.
Description
The folA polyclonal antibody production involves the repeated immunization of a rabbit with a recombinant Escherichia coli (strain K12) folA protein (1-159aa). When a sufficient titer (antibody concentration) is obtained, the rabbit is bled and the antibodies are purified from the serum through affinity chromatography. The functionality of the resulting folA antibody is tested in ELISA and WB applications. And it can react with Escherichia coli (strain K12) folA protein.
The Escherichia coli (strain K12) folA protein is a bifunctional enzyme that catalyzes two reactions: the reduction of dihydrofolate (DHF) to THF, and the conversion of 5,10-methylenetetrahydrofolate (5,10-methylene-THF) to 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (5-methyl-THF). This enzymatic reaction is a crucial step in the folate (vitamin B9) metabolic pathway. The activity of the folA protein is pivotal for providing the reduced form of folate needed for various biosynthetic processes within the cell.
Usage
For Research Use Only. Not for use in diagnostic or therapeutic procedures.