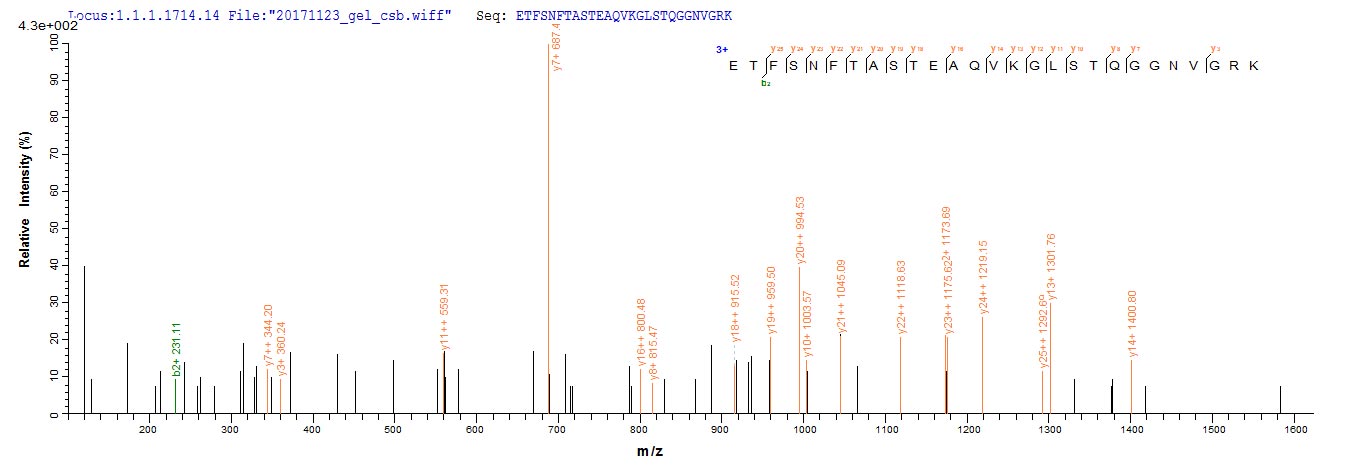
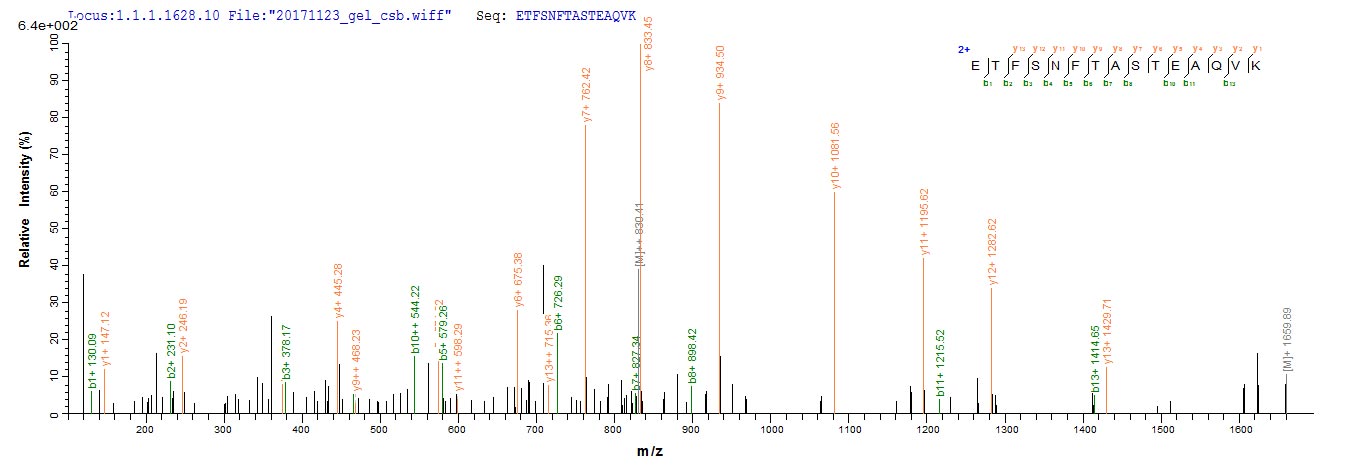
The generation of the recombinant human ASGR1 protein begins by cloning the ASGR1 gene fragment (68-291aa) with the N-terminal 6xHis-tag gene into an expression vector. The recombinant vectors are then transformed into E. coli cells, which are cultured for protein expression upon induction with IPTG. The cells are lysed to release the expressed ASGR1 protein, which is subsequently purified using Ni-NTA affinity chromatography, capitalizing on the 6xHis tag's affinity for nickel ions. The eluted ASGR1 protein is then analyzed for purity using SDS-PAGE, which demonstrates a purity exceeding 90%.
The Human ASGR1 is a critical component of the hepatic system, primarily expressed on the surface of hepatocytes [5]. It functions as a lectin that specifically recognizes and binds to asialoglycoproteins, which are glycoproteins lacking sialic acid residues. This receptor plays a significant role in the clearance of these glycoproteins from the bloodstream, facilitating their internalization through clathrin-mediated endocytosis [1][2]. The ASGR1 is part of a larger family of receptors, which includes ASGPR2, and together they are essential for maintaining the homeostasis of glycoproteins in the liver [3][4].
ASGR1's expression is not only crucial for normal liver function but also has implications in various pathological conditions, including liver diseases and cancers. Studies have shown that ASGR1 expression can be downregulated in hepatocellular carcinoma (HCC), suggesting its potential utility as a biomarker for tumor progression [6][7].
ASGR1 has been implicated in the uptake of HBV, indicating its role in viral pathogenesis [8][9]. The receptor's interaction with HBV suggests that targeting ASGR1 could be a viable strategy for developing antiviral therapies.
References:
[1] M. Tanowitz, L. Hettrick, A. Revenko, G. Kinberger, T. Prakash, & P. Seth, Asialoglycoprotein receptor 1 mediates productive uptake of n-acetylgalactosamine-conjugated and unconjugated phosphorothioate antisense oligonucleotides into liver hepatocytes, Nucleic Acids Research, vol. 45, no. 21, p. 12388-12400, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkx960
[2] W. Xu, L. Cao, L. Chen, J. Li, X. Zhang, H. Qian, et al. Isolation of circulating tumor cells in patients with hepatocellular carcinoma using a novel cell separation strategy, Clinical Cancer Research, vol. 17, no. 11, p. 3783-3793, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-10-0498
[3] L. Swystun and D. Lillicrap, Current understanding of inherited modifiers of fviii pharmacokinetic variation, Pharmacogenomics and Personalized Medicine, vol. Volume 16, p. 239-252, 2023. https://doi.org/10.2147/pgpm.s383221
[4] R. Harris, C. Berg, & D. Bowen, asgr1andasgr2, the genes that encode the asialoglycoprotein receptor (ashwell receptor), are expressed in peripheral blood monocytes and show interindividual differences in transcript profile, Molecular Biology International, vol. 2012, p. 1-10, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1155/2012/283974
[5] T. Kaden, K. Graf, K. Rennert, R. Li, A. Mosig, & M. Raasch, Evaluation of drug-induced liver toxicity of trovafloxacin and levofloxacin in a human microphysiological liver model, Scientific Reports, vol. 13, no. 1, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-40004-z
[6] B. Shu, M. Abrams, & L. Sepp‐Lorenzino, Expression of asialoglycoprotein receptor 1 in human hepatocellular carcinoma, Journal of Histochemistry & Cytochemistry, vol. 61, no. 12, p. 901-909, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1369/0022155413503662
[7] M. Hamaoka, T. Kobayashi, Y. Tanaka, H. Mashima, & H. Ohdan, Clinical significance of glypican-3-positive circulating tumor cells of hepatocellular carcinoma patients: a prospective study, Plos One, vol. 14, no. 5, p. e0217586, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0217586
[8] J. Yang, X. Bo, X. Ding, J. Dai, M. Zhang, X. Wang, et al. Antisense oligonucleotides targeted against asialoglycoprotein receptor 1 block human hepatitis b virus replication, Journal of Viral Hepatitis, vol. 13, no. 3, p. 158-165, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2893.2005.00666.x
[9] J. Yang, X. Bo, J. Yao, N. Yang, & S. Wang, Differentially expressed cellular genes following hbv: potential targets of anti‐hbv drugs?, Journal of Viral Hepatitis, vol. 12, no. 4, p. 357-363, 2005. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2893.2005.00611.x