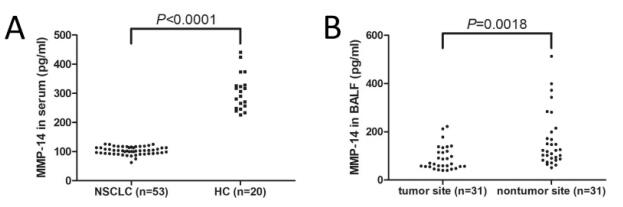
To make this Recombinant Human MMP14 protein, the MMP14 gene was isolated at first and cloned into an expression vector. CUSABIO has built a mature recombinant protein platform. This Recombinant Human MMP14 protein was developed in the platform. It was expressed in E.coli at the region of 112-582aa of the Human MMP14 protein. N-terminal 6xHis-SUMO tag was fused with the expression vector for affinity and purification purposes. The purity is 90%+ determined by SDS-PAGE.
MMP14 was first described by Sato et al. as a transmembrane protein which activates pro-MMP2 to induce tumor cell invasion. Most MMPs are secreted as inactive pro-proteinases that are activated by proteolytic cleavage. Active MMP14 binds to the metallopeptidase inhibitor, tissue inhibitor of metalloproteinases 2 (TIMP2), to form a receptor for proMMP2 activation. MMP14 knockout mice exhibit defects in skeletal development and angiogenesis, fibrosis of soft tissues, and premature death. This phenotype has been attributed largely to the importance of MMP14 in collagen turnover and bone remodeling. MMP14 is up-regulated in several types of cancer, promoting angiogenesis, inflammation, cancer cell invasion, and metastasis. In genetically-modified mouse models, MMP14 overexpression induces mammary gland adenocarcinoma formation and pancreatic cancer development. Other mouse models of epithelial cancers have also identified MMP14 expression, particularly in tumor-associated cells of the TME, to be involved in cancer progression. An MMP14-deficient breast cancer mouse model showed reduced metastasis; an effect attributed to the reduced collagen I degradation by stromal fibroblasts. Yet, the MMP14 gene expression across a variety of cancer types is highest in sarcomas, with the childhood rhabdomyosarcomas and Ewing sarcoma representing intriguing exceptions, suggesting that it may be a particularly important player in sarcoma biology.