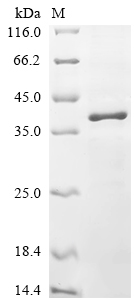
Recombinant Mouse 5-AMP-activated protein kinase catalytic subunit alpha-1 (Prkaa1) is produced in E. coli and includes an N-terminal 6xHis tag that makes purification more straightforward. This partial protein spans amino acids 1-312 and comes with purity levels above 85%, as confirmed through SDS-PAGE analysis. The protein is intended for research purposes only and appears to meet strict quality standards for experimental work.
5-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) acts as a central regulator of cellular energy homeostasis. It functions as an energy sensor within cells and likely plays a critical role in metabolic pathways through its ability to modulate enzyme activity in glucose and lipid metabolism. These characteristics make AMPK an important target for researchers studying metabolic disorders and energy regulation mechanisms.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
AMPK is a heterotrimeric complex whose catalytic α-subunit requires correct folding, activation loop phosphorylation (at Thr172), and interaction with regulatory β/γ subunits for full bioactivity. The expressed fragment (1-312aa) contains the kinase domain but lacks critical C-terminal regions needed for regulatory subunit binding and complex assembly. E. coli cannot perform eukaryotic-specific phosphorylation, and the His tag may sterically hinder proper folding. While the kinase domain might fold independently, its enzymatic activity depends on upstream kinase phosphorylation (e.g., LKB1). Without co-expression of activating kinases or in vitro phosphorylation, the protein will likely be inactive. High purity does not guarantee correct folding or post-translational modification. Thus, this protein is probably misfolded/inactive without experimental validation.
1. In Vitro Kinase Activity Assays
This application is only feasible if the recombinant Prkaa1 is phosphorylated at Thr172 and correctly folded. Without activation, kinase assays will yield false-negative results. If activity is confirmed (e.g., via phosphorylation of substrates like SAMS peptide), the His tag facilitates immobilization for kinetic studies. However, the partial sequence lacks regulatory domains, limiting physiological relevance. Always include a positive control (e.g., commercially active AMPK).
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This recombinant Prkaa1 fragment is suitable as an immunogen for antibody production, as antibodies can target linear epitopes. The His tag simplifies purification for immunization. However, antibodies generated may not recognize native, full-length AMPK complexes due to conformational epitope differences or truncated sequence. Validate antibodies against full-length Prkaa1 from eukaryotic sources.
3. Structural and Biophysical Characterization
The protein is suitable for basic biophysical analyses (e.g., circular dichroism to assess secondary structure, dynamic light scattering to check aggregation). However, for structural studies (e.g., crystallography), the partial sequence and lack of phosphorylation may yield non-native conformations. The His tag could interfere with crystallization. Use tag-free, phosphorylated full-length protein for meaningful insights.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Before using this recombinant Prkaa1 fragment, validate its folding and phosphorylation status. First, check phosphorylation at Thr172 via Western blot with anti-pT172 antibodies. If unphosphorylated, perform in vitro phosphorylation using an upstream kinase (e.g., LKB1). Next, test kinase activity with a standard substrate (e.g., SAMS peptide). If inactive, limit use to non-functional applications like antibody production, but validate antibodies against native AMPK. For intraction studies, the partial Prkaa1 fragment cannot bind regulatory β/γ subunits (missing C-terminal domains), making interactions non-physiological. Misfolding may cause artifactual binding. Validate any interactions with full-length AMPK complexes from mammalian cells.