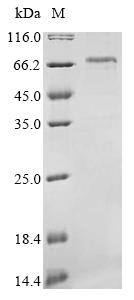
This recombinant mouse Neurofilament light polypeptide (Nefl) comes from an E.coli expression system, which appears to produce the full-length mature protein quite efficiently across amino acids 2-543. The protein carries an N-terminal 6xHis-tag that makes purification and identification more straightforward. SDS-PAGE analysis suggests the purity reaches over 85%, which should work well for most research applications that demand high-quality reagents.
Neurofilament light polypeptide (Nefl) seems to be crucial for neuronal cytoskeleton structure and function. It's one of the key building blocks of neurofilaments, helping neurons keep their shape while supporting axonal transport processes. Nefl contributes to intermediate filament assembly, which likely provides stability and structural support to nerve cells. Given its importance in neurological research, it has become an attractive target for investigating nerve cell function and disease mechanisms.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
The mouse Nefl is a neuronal intermediate filament protein that requires proper folding and coiled-coil domain formation for its structural function in neurofilament assembly. While E. coli can express soluble proteins, it lacks the eukaryotic chaperones and post-translational modification machinery that may be important for the correct folding of complex structural proteins like Nefl. The small His tag is unlikely to significantly interfere with folding. However, without experimental validation (e.g., circular dichroism for secondary structure or filament assembly assays), the protein cannot be assumed to be correctly folded. The high purity indicates low impurities, but does not guarantee native conformation.
1. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is suitable. The recombinant Nefl can serve as an immunogen for generating antibodies against linear epitopes. The high purity supports consistent immunization. However, antibodies generated may not recognize conformational epitopes important for neurofilament assembly. Validate antibody specificity against native neurofilaments from mouse neural tissue.
2. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
Use with caution. The His-tag enables pull-down assays to identify binding partners with other neurofilament subunits (NF-M, NF-H) or cytoskeletal proteins. However, if Nefl is misfolded, interactions may be non-physiological. Validate any identified interactions using co-immunoprecipitation from neural tissue extracts.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Biophysical Analysis
This recombinant mouse Nefl is suitable for basic biophysical characterization (e.g., circular dichroism for α-helical content, dynamic light scattering for aggregation state). However, data may not fully reflect native Nefl properties if the protein is misfolded. Use techniques like analytical ultracentrifugation to study oligomerization, but interpret results cautiously.
4. In Vitro Filament Assembly Studies
This application requires proper folding. Neurofilament assembly depends on correct coiled-coil domain formation. If Nefl is misfolded, it will not polymerize correctly. First, validate folding via circular dichroism, then test assembly with other neurofilament subunits using electron microscopy.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Before using this recombinant Nefl for functional studies, validate its folding and assembly capability. Start with circular dichroism spectroscopy to confirm the expected α-helical content characteristic of intermediate filaments. Then test oligomerization state via size-exclusion chromatography with multi-angle light scattering (SEC-MALS). If properly folded, proceed with filament assembly studies by mixing with other neurofilament subunits and examining polymerization by electron microscopy. For antibody production, proceed but validate antibodies against native neurofilaments from mouse brain extracts. Always include appropriate controls with native neurofilament preparations when possible.