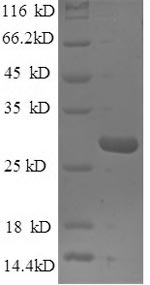
Recombinant Mouse Nidogen-1 (Nid1) is a partial protein expressed in E. coli, covering the 428-665 amino acid region and featuring an N-terminal 6xHis-tag for simplified purification. The product is purified to greater than 90% as determined by SDS-PAGE, ensuring high quality for research applications. This protein is intended for research use only and is not suitable for any clinical or diagnostic purposes.
Nidogen-1 appears to be a crucial component of the extracellular matrix, playing what seems to be a significant role in basement membrane assembly and stability. It acts as a binding link between other matrix proteins—laminins and collagen IV, for instance—and likely proves essential for maintaining tissue architecture. Its apparent importance in structural integrity and cellular signaling makes it a valuable subject in studies related to cell adhesion and tissue development.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
Mouse Nid1 is an extracellular matrix protein that requires complex disulfide bond formation and proper folding for its structural function in basement membrane assembly. The E. coli expression system cannot perform the necessary post-translational modifications (particularly proper disulfide bonding) that are critical for this protein's native conformation. While the protein may be soluble, it is highly unlikely to achieve the correct three-dimensional structure needed for functional activity.
1. Antibody Development and Validation
This recombinant Nid1 fragment serves as an excellent immunogen for generating antibodies against linear epitopes of this specific region. The defined sequence ensures targeted antibody production. The His-tag facilitates purification and immunization procedures. However, antibodies may not efficiently recognize conformational epitopes on the native, properly folded Nid1 in tissues.
2. Biochemical Characterization and Stability Studies
This is the essential first step to assess the protein's physical properties. Techniques like circular dichroism can analyze secondary structure content, while size-exclusion chromatography can determine oligomeric state and homogeneity. These studies provide critical quality control data for understanding this fragment's behavior in solution.
3. Comparative Species Analysis in Extracellular Matrix Research
This protein can be used for sequence-based comparisons and immunological cross-reactivity studies. However, comparative functional studies (e.g., binding affinity comparisons) would be invalid due to the protein's likely misfolded state. The fragment may reveal sequence differences but not functional evolutionary differences.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The E. coli expression system is unsuitable for producing a functionally folded extracellular matrix protein fragment, limiting its applications to non-functional uses. The immediate priority is Application 2 (Biochemical Characterization) to assess the protein's physical properties and folding state. Application 1 (Antibody Development) can proceed confidently for generating linear epitope antibodies. This protein is useful for structural and immunological comparisons but not for functional extracellular matrix studies requiring native protein conformation. For meaningful Nid1 functional studies, use proteins expressed in eukaryotic systems that support proper disulfide bond formation and folding. Extracellular matrix protein interactions are highly dependent on precise three-dimensional conformation. Using a likely misfolded variant makes this application scientifically unsound.