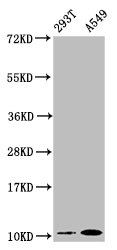
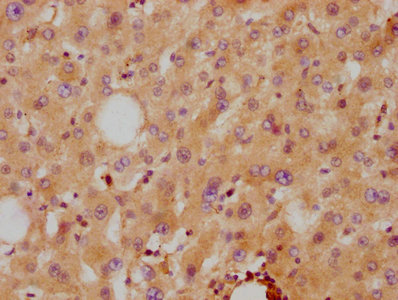
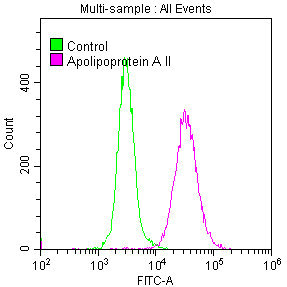
This is an APOA2 recombinant monoclonal antibody produced in vitro expression system. The clones constructed by the human APOA2 DNA gene and vector were transfected into the cell line for production. This APOA2 antibody is purified using affinity-chromatography. It is recommended for applications, including ELISA, WB, IHC, and FC.
APOA2 is a major constituent of high-density lipoprotein (HDL) mainly produced in the liver and small intestine. It appears to promote insulin secretion and play a role in protection against the development of the metabolic syndrome. Defects in the APOA2 gene may result in apolipoprotein A-II deficiency or hypercholesterolemia.