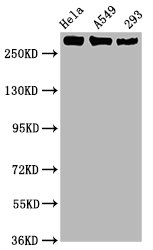
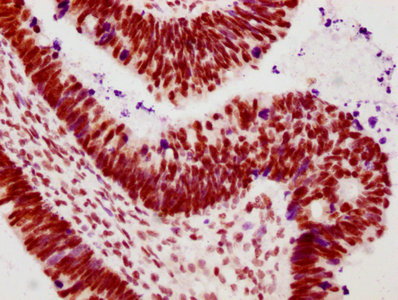
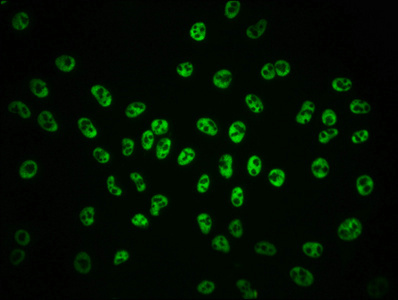
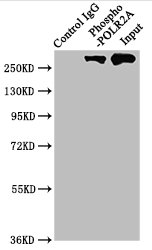
The vectors expressing anti-POLR2A antibody were constructed as follows: immunizing an animal with a synthesized peptide derived from human Phospho-POLR2A (S2), isolating the positive splenocyte and extracting RNA, obtaining DNA by reverse transcription, sequencing and screening POLR2A antibody gene, and amplifying heavy and light chain sequence by PCR and cloning them into plasma vectors. After that, the vector clones were transfected into the mammalian cells for production. The product is the recombinant POLR2A antibody. Recombinant POLR2A antibody in the culture medium was purified using affinity-chromatography. It can react with POLR2A protein from Human and is used in the ELISA, WB, IHC, IF, IP.
POLR2A encodes the largest subunit of RNA polymerase II, the polymerase responsible for the synthesis of eukaryotic messenger RNA. The product of POLR2A contains a carboxy-terminal domain consisting of heptapeptide repeats that is essential for polymerase activity. According to some studies, POLR2A may have the following characteristics.
Potential for pH-responsive nanoparticles and precise targeting of POLR2A in TNBC harboring common TP53 genomic alterations. The clinical consequences of a potentially pathogenic variant in POLR2A depend on its effect on pol-II-mediated transcription, as POLR2A variants predicted to cause loss of RPB1 protein are more tolerated than missense variants. BCAR1 promotes proliferation and cell growth, likely through upregulation of POLR2A and subsequent enhancement of catalytic and transferase activity. Humanized monoclonal antibody-induced nuclear localization of CD26 inhibits tumor cell growth by regulating POLR2A transcription.