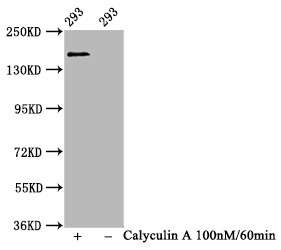
CUSABIO put the phospho-SMC1A (S957) monoclonal antibody DNA sequence into the plasmid, which was subsequently transfected into the cell line for expression. Immunizing mice with the phosphopeptide corresponding to residues surrounding Ser 957 of human SMC1A produced the phospho-SMC1A (S957) monoclonal antibody. The recombinant phospho-SMC1A (S957) monoclonal antibody was obtained after the product was purified using affinity chromatography. It's a rabbit IgG antibody. This phospho-SMC1A (S957) antibody has undergone ELISA and WB quality testing. It can bind to the pS957-SMC1A in human samples.
SMC1A is a subunit of the evolutionarily conserved four-subunit complex cohesion. SMC1A plays an important role in genome integrity, chromosomal function, gene control, and double-stranded DNA repair, among other functions. It is phosphorylated by both ATR and ATM protein kinases and is involved in the G2/M checkpoint. SMC1A has been linked to the formation of tumors in various types of human malignancies. SMC1A promotes prostate cancer development and migration in vitro and in vivo, according to the finding of Xiu-Wu Pan et al.