Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP) is a pleiotropic cytokine primarily secreted by epithelial cells in response to environmental stimuli such as allergens, viruses, or pollutants. It plays a pivotal role in immune regulation by initiating downstream inflammatory responses. As a crucial regulatory molecule in immune responses, the function of TSLP in allergic diseases and chronic inflammation has garnered significant attention. In 2010, the team led by Dr. Steven F. Ziegler from the Benaroya Research Institute first elucidated the mechanism by which TSLP promotes the onset of allergic diseases such as asthma through triggering inflammatory cascades. In recent years, notable progress has been made in targeted therapies against TSLP. For instance, in February 2025, tezepelumab, a TSLP monoclonal antibody co-developed by AstraZeneca and Amgen, submitted an application for the marketing authorization of chronic rhinosinusitis with nasal polyps (CRSwNP) in China, further highlighting the clinical translational value of this target.
1. Production and Mechanism of Action of TSLP
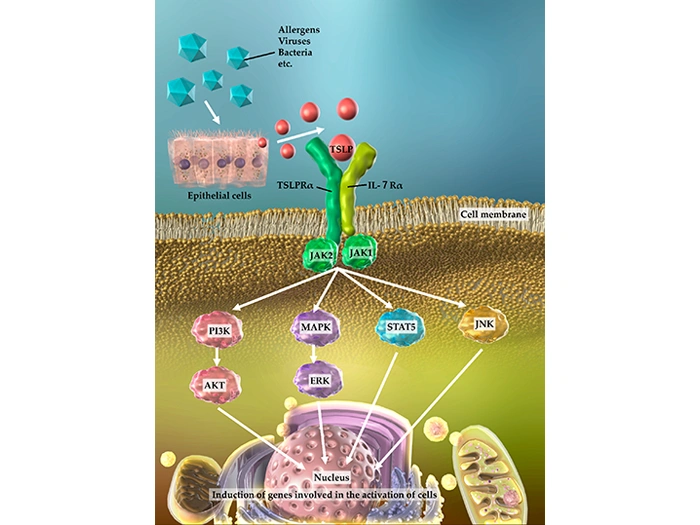
TSLP is produced by airway epithelial cells upon exposure to environmental factors such as allergens and viruses. TSLP binds to and activates the TSLP receptor (a heterodimer composed of TSLPR and IL-7Rα chains) expressed on dendritic cells, leading to the activation of signal transduction and transcription activator (STAT), mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK), phosphatidylinositol 3-kinase (PI3K), c-Jun N-terminal kinase (JNK), and downstream signaling factors. These pathways participate in inducing the expression of genes involved in cell activation, resulting in various types of airway inflammation and contributing to its chronicity and severity (Figure 1) [1].
Figure 1. Production of TSLP, Receptor Structure, and Intracellular Signal Transduction
Figure from:Doi:10.3390/cells11050819
Structure of TSLP
TSLP exists in two isoforms: long-form TSLP (lfTSLP) and short-form TSLP (sfTSLP). lfTSLP is predominantly expressed under inflammatory conditions and exhibits pro-inflammatory functions, while sfTSLP is constitutively expressed and possesses antimicrobial and immunoregulatory properties. The C-terminal region of TSLP contains a 34-amino acid peptide segment (MKK34) with significant antimicrobial activity, capable of disrupting bacterial membrane structures.
Functions of TSLP
Immune Activation: TSLP promotes Th2-type immune responses by activating dendritic cells, mast cells, and T cells.
Antimicrobial Activity: Both sfTSLP and lfTSLP demonstrate potent antimicrobial effects, particularly in defending the skin and mucosal barriers [2].
Metabolic Regulation: TSLP improves obesity and metabolic disorders by inducing excessive sebum secretion, leading to white adipose tissue loss.
2. Research on TSLP-Related Diseases
TSLP plays a critical role in various diseases, including:
● Asthma and Allergic Diseases: TSLP is a key driver of asthma and allergic inflammation. It promotes the release of IL-4, IL-5, and IL-13 by activating Th2-type immune responses, leading to airway inflammation and remodeling [6][7]. Anti-TSLP monoclonal antibodies, such as tezepelumab, have demonstrated significant efficacy in severe asthma and CRSwNP [3][4].
● Metabolic Diseases: TSLP improves obesity, glucose metabolism, and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease by inducing excessive sebum secretion and white adipose tissue loss.
● Dermatological Diseases: TSLP plays a significant role in atopic dermatitis, psoriasis, and alopecia. It promotes skin inflammation and pruritus by activating mast cells and dendritic cells . Additionally, TSLP promotes hair follicle stem cell proliferation and hair regeneration after skin injury [5].
● Esophageal Diseases: TSLP promotes Th2-type inflammatory responses in eosinophilic esophagitis (EoE) and reflux esophagitis (RE). TSLP-neutralizing antibodies significantly alleviate esophageal inflammation and pathological damage.
● Systemic Sclerosis and Interstitial Lung Disease: TSLP levels are significantly elevated in the sera of patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) and correlate with the severity of skin fibrosis and interstitial lung disease (ILD).
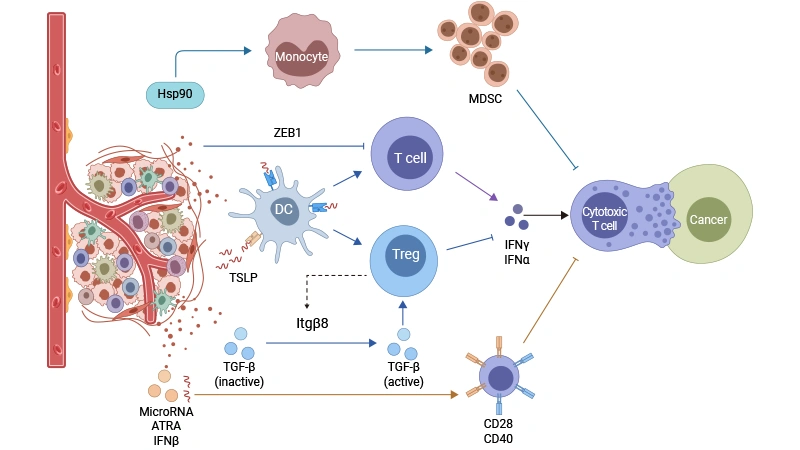
● Cancer and Immunotherapy: TSLP affects the efficacy of immunotherapy by regulating immune cell function in the tumor microenvironment. Inhibiting TSLP may be a potential strategy to enhance the efficacy of immunotherapy (Figure 2) [6].
Figure 2. Mechanisms of resistance to immunotherapy.
Figure from:DOI:10.20517/cdr.2023.150
3. Development Progress in TSLP-Targeted Therapies
Current therapeutic strategies against TSLP include:
● Monoclonal Antibodies: Tezepelumab is the first approved anti-TSLP monoclonal antibody for severe asthma, demonstrating good efficacy and safety.
● Peptide Inhibitors: High-affinity cyclic peptide inhibitors have been developed through structural design and disulfide bond stabilization to competitively block the binding of TSLP to its receptor.
● Small Molecule Compounds: Virtual screening and molecular dynamics simulations have identified certain natural compounds with strong binding affinity to TSLP, which can be used to develop novel drugs.
● Inhalation Therapy: For instance, ecleralimab, which reduces systemic side effects and improves therapeutic efficiency through local administration.
| Drug |
Mechanism of Action |
Drug Type |
Disease Names |
Investigational Institutions |
Highest Development Phase |
| Tezepelumab |
TSLPInhibitor |
Monoclonal Antibody |
Asthma | Severe asthma | Chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) | Nasal polyp | Eosinophilic esophagitis | Churg-Strauss syndrome | Progressive fibrotic interstitial lung disease | Chronic urticaria | Moderate chronic obstructive pulmonary disease | Severe chronic obstructive pulmonary disease |
Amgen, Inc. | AstraZeneca PLC | AstraZeneca AB | AstraZeneca KK | Astrazeneca Korea Ltd. | AstraZeneca Canada, Inc. | AstraZeneca Pty Ltd. | Philipps University Marburg Medical Center | AstraZeneca Investment (China) Co., Ltd. |
Marketed |
| Bosakitug |
TSLPInhibitor |
Monoclonal Antibody |
Asthma | Severe asthma | Eczema | Chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD) | Chronic sinusitis with nasal polyps | Nasal polyp | Moderate Atopic Dermatitis | Severe atopic dermatitis | Atopic dermatitis
|
Shanghai Chia Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Technology Development Co., Ltd. | Shanghai Chia Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. | Chia Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Group Co., Ltd. | Bio - XCell Biotechnology (Nanjing) Co., Ltd. | Nanjing Shunxin Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd., Chia Tai Tianqing Pharmaceutical Group |
Phase III |
| PF-07275315 |
IL-13Inhibitor | IL-4Inhibitor | TSLPInhibitor |
Trispecific Antibody |
Asthma | Moderate Atopic Dermatitis | Severe atopic dermatitis | Moderate asthma | Severe asthma |
Pfizer Inc. |
Phase II |
| Ecleralimab |
TSLPInhibitor |
Fab Fragment Antibody |
COPD |
Novartis AG |
Phase II |
| Lunsekimig |
IL-13Inhibitor | TSLPInhibitor |
Nanobody | Bispecific Antibody |
Asthma | Moderate Atopic Dermatitis | Severe Atopic Dermatitis | Moderate Asthma | Severe Asthma |
Sanofi | Vetter GmbH | Sanofi-Aventis Recherche & Développement SA |
Phase II |
| Solrikitug |
TSLPInhibitor |
Monoclonal Antibody |
Eosinophilic Esophagitis | COPD | Asthma |
Uniquity Bio, Inc. |
Phase II |
| HBM-9378 |
TSLPInhibitor |
Monoclonal Antibody |
Asthma | COPD |
Windward Bio AG | Sichuan Kelun-Biotech Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Harbour BioMed (Shanghai) Co., Ltd. |
Phase II |
| CM-326 |
TSLPInhibitor |
Monoclonal Antibody |
CRSwNP | SevereAsthma | Moderate Atopic Dermatitis | SevereAtopic Dermatitis | COPD |
Kangnoah Biomedical Technology (Chengdu) Co., Ltd. | Kangnoah Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd. | CSPC Pharmaceutical Group Ltd. |
Phase II |
| MG-014 |
TSLP Modulator |
Monoclonal Antibody |
SevereAsthma | COPD | Atopic Dermatitis | Sinusitis | Autoimmune Diseases |
Hunan Maiji Biotechnology Co., Ltd. |
Phase II |
| AZD8630 |
TSLPInhibitor |
Immunoglobulin |
Asthma |
AstraZeneca PLC | Amgen, Inc. | AstraZeneca Global R&D (China) Co., Ltd. | AstraZeneca AB |
Phase II |
| SHR-1905 |
TSLPInhibitor |
Monoclonal Antibody |
CRSwNP | Asthma | Respiratory Diseases | COPD | Moderate Asthma | SevereAsthma |
GSK Plc | Guangdong Hengrui Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Shanghai Hengrui Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. | Syneos Health, Inc. | Aiolos Bio, Inc. |
Phase II |
| Tavo-101 |
TSLPInhibitor | Immunomodulator |
Monoclonal Antibody |
Moderate Atopic Dermatitis | SevereAtopic Dermatitis |
Tavotek Biotherapeutics Co. Ltd. |
Phase II |
| CM512 |
IL - 13 Modulators | TSLP Modulator |
Bispecific Antibody |
COPD | Moderate Atopic Dermatitis | SevereAtopic Dermatitis | Chronic Bronchitis | Asthma | Nasal Polyp | CRSwNP | Bronchiectasis |
Kangnoah Biomedical Technology (Chengdu) Co., Ltd. | Kangnoah Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd. |
Phase II |
| CDX-622 |
TSLPInhibitor | c - Kit Inhibitor |
Bispecific Antibody |
Inflammation |
Celldex Therapeutics, Inc. |
Phase I |
| BSI-502 |
IL-4RαInhibitor | TSLPInhibitor | Helper - Inducer T - lymphocyte Modulators |
Bispecific Antibody |
Autoimmune Diseases |
Aclaris Therapeutics, Inc. | Bio - XCell Biotechnology (Nanjing) Co., Ltd. |
Phase I |
| GR-2002 |
TSLPInhibitor |
Bispecific Antibody |
Moderate Atopic Dermatitis | SevereAtopic Dermatitis | Asthma | CRSwNP |
Chongqing ZhiXiang JinTai Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd. |
Phase I |
| GB-0895 |
TSLPInhibitor |
Monoclonal Antibody |
COPD | SevereAsthma |
Generate Biomedicines, Inc. |
Phase I |
| STSA-1201 |
TSLPInhibitor |
Monoclonal Antibody |
Asthma |
Staidson (Beijing) Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd. |
Phase I |
| IBI-3002 |
IL - 4Rα Modulator | TSLP Modulator |
Bispecific Antibody |
Atopic Dermatitis | Asthma |
Innovent Biologics (Suzhou) Co., Ltd. |
Phase I |
| APG333 |
TSLPInhibitor |
Monoclonal Antibody |
Asthma | COPD |
Paragon Therapeutics, Inc. | Apogee Therapeutics, Inc. |
Phase I |
| QX-008N |
TSLPInhibitor |
Monoclonal Antibody |
ModerateAsthma | SevereAsthma | Asthma | COPD |
Jiangsu Quanxin Biomedical Co., Ltd. |
Phase I |
| HB0056 |
IL - 11 Modulators | TSLP Modulator |
Bispecific Antibody |
ModerateAsthma | SevereAsthma | Asthma |
Shanghai Huaotai Bio - Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. |
Phase I |
| LQ043H Single-Domain Antibody |
TSLP Modulator |
Nanobody |
Asthma | COPD |
Shanghai Luoqi Biomedical Technology Co., Ltd. |
Phase I |
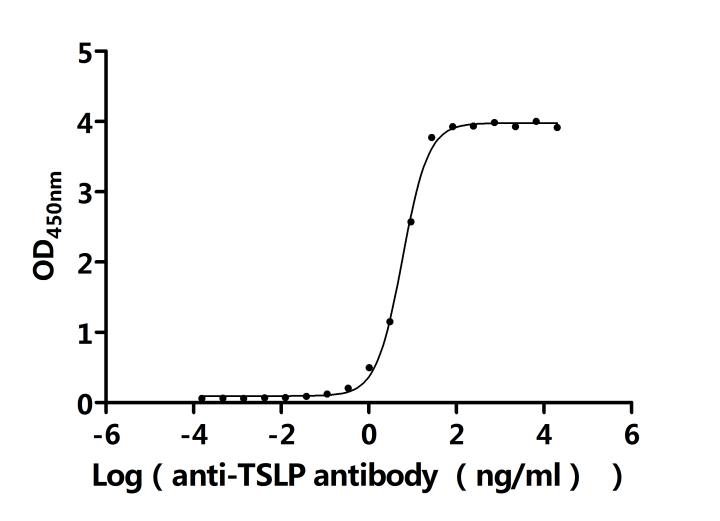
4. CUSABIO's TSLP-related Products
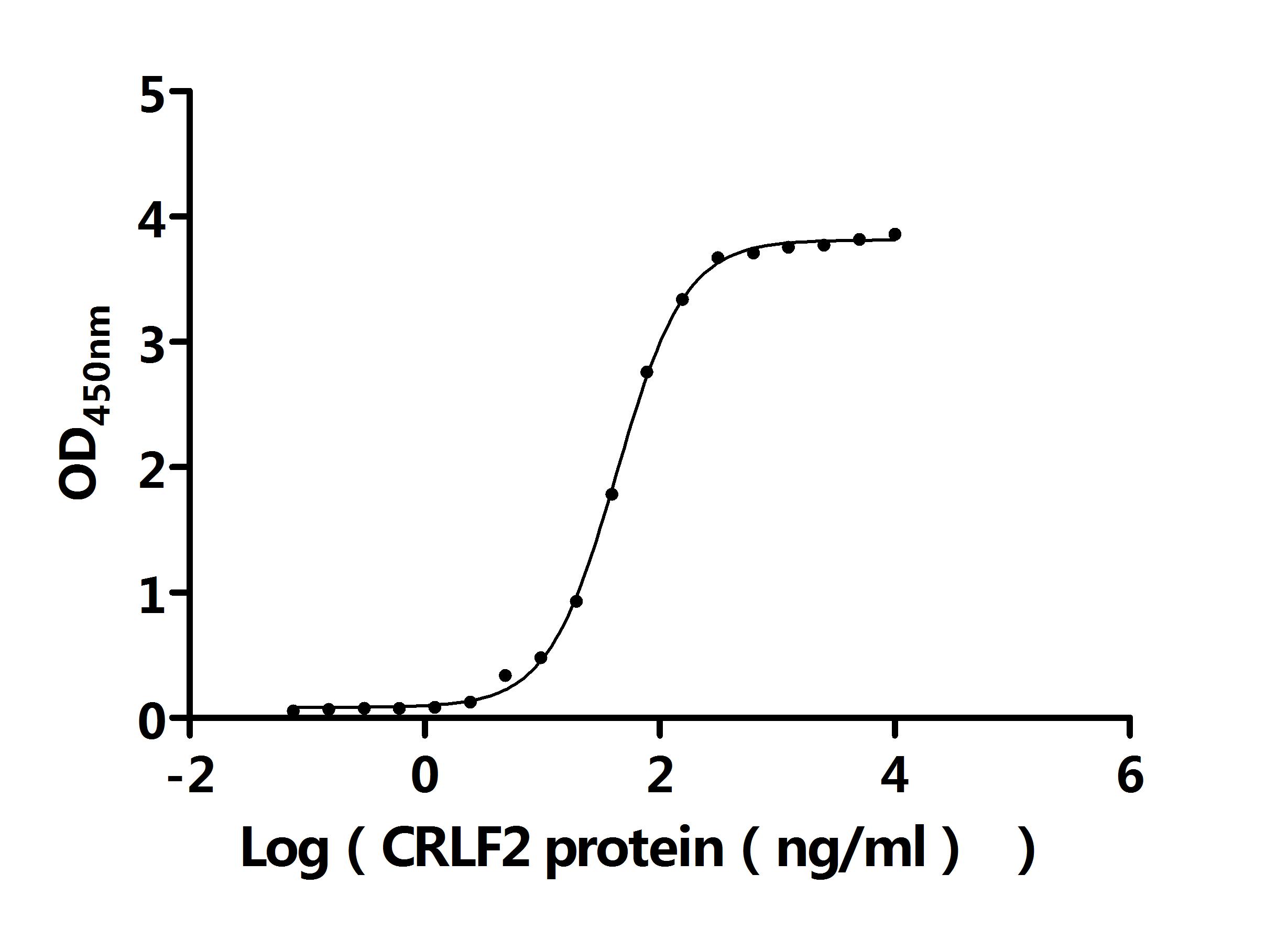
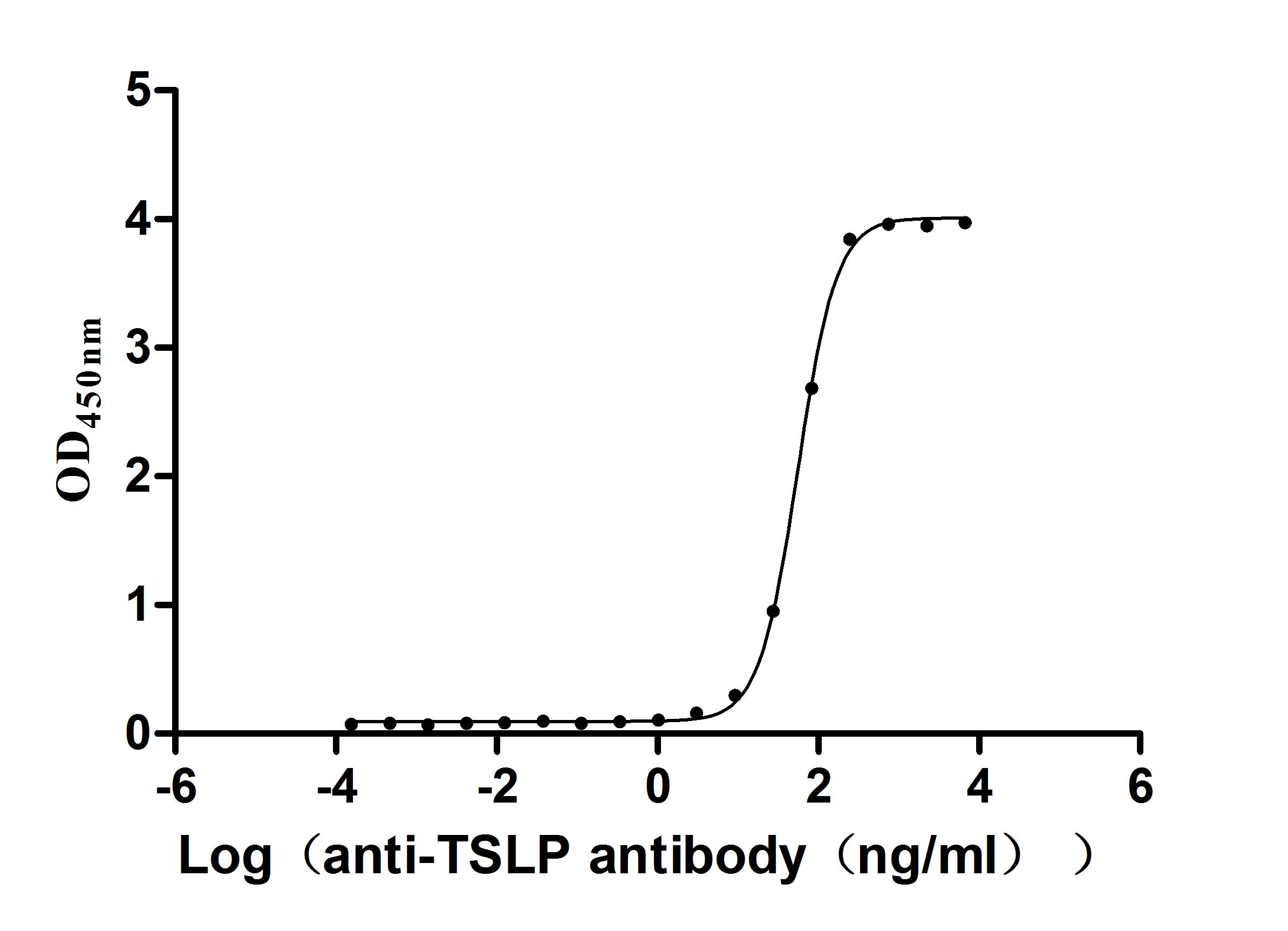
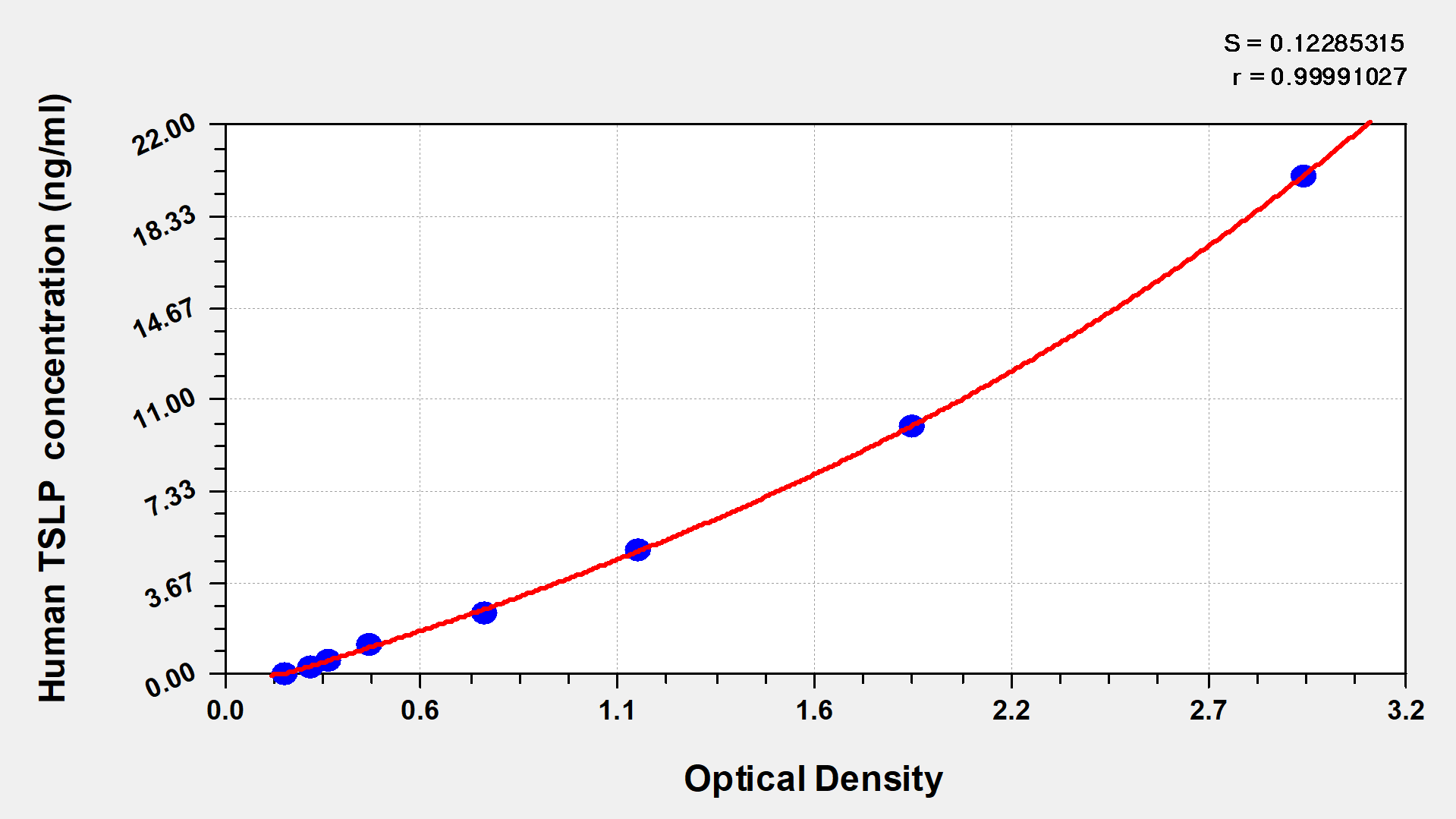
Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP), as a pleiotropic cytokine, plays a crucial role in immune regulation, inflammatory responses, and metabolic homeostasis. It regulates immune and inflammatory responses as well as metabolic homeostasis through signaling pathways such as JAK/STAT, MAPK, and PI3K/AKT. Its dysfunction is closely associated with Th2-type diseases such as asthma and atopic dermatitis. In recent years, monoclonal antibodies against TSLP, such as tezepelumab, have demonstrated significant efficacy in clinical trials, highlighting the therapeutic potential of this target. To facilitate in-depth understanding of TSLP's molecular mechanisms and drug development, highly specific and active recombinant proteins and antibody tools are essential. CUSABIO offers a variety of TSLP recombinant proteins, antibodies, and ELISA-related products to support receptor-binding experiments, cellular functional studies, and antibody drug screening, thereby accelerating TSLP-related translational medical research.
► Click here to view all products related to TSLP
References
[1] Ando K,Fukuda Y,Tanaka A, et al. Comparative Efficacy and Safety of Tezepelumab and Other Biologics in Patients with Inadequately Controlled Asthma According to Thresholds of Type 2 Inflammatory Biomarkers: A Systematic Review and Network Meta-Analysis. Cells. 2022;11 (5):. doi:10.3390/cells11050819.
[2] Bjerkan L,Sonesson A,Schenck K. Multiple Functions of the New Cytokine-Based Antimicrobial Peptide Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP). Pharmaceuticals (Basel). 2016;9 (3):null. doi:10.3390/ph9030041.
[3] De Corso E,Hellings PW,Fokkens WJ, et al. Thymic Stromal Lymphopoietin (TSLP): Evidence in Respiratory Epithelial-driven Diseases Including Chronic Rhinosinusitis with Nasal Polyps. Curr Allergy Asthma Rep. 2024;25 (1):7. doi:10.1007/s11882-024-01186-2.
[4] Yu G,Zhang Y,Wang X, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin (TSLP) and Toluene-diisocyanate-induced airway inflammation: Alleviation by TSLP neutralizing antibody. Toxicol Lett. 2019;317:59-67. doi:10.1016/j.toxlet.2019.09.021.
[5] Shannon JL,Corcoran DL,Murray JC, et al. Thymic stromal lymphopoietin controls hair growth. Stem Cell Reports. 2022;17 (3):649-663. doi:10.1016/j.stemcr.2022.01.017.
[6] Song L,Yang Y,Tian X. Current knowledge about immunotherapy resistance for melanoma and potential predictive and prognostic biomarkers. Cancer Drug Resist. 2024;7:17. doi:10.20517/cdr.2023.150.
CUSABIO team. TSLP: A Key Target in Allergic and Inflammatory Diseases. https://www.cusabio.com/c-21247.html



Comments
Leave a Comment