Function
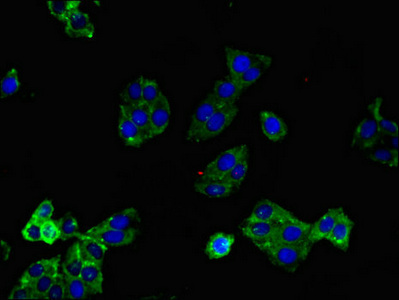
Receptor for lysophosphatidic acid (LPA). Plays a role in the reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton, cell migration, differentiation and proliferation, and thereby contributes to the responses to tissue damage and infectious agents. Activates downstream signaling cascades via the G(i)/G(o), G(12)/G(13), and G(q) families of heteromeric G proteins. Signaling inhibits adenylyl cyclase activity and decreases cellular cAMP levels. Signaling triggers an increase of cytoplasmic Ca(2+) levels. Activates RALA; this leads to the activation of phospholipase C (PLC) and the formation of inositol 1,4,5-trisphosphate. Signaling mediates activation of down-stream MAP kinases. Contributes to the regulation of cell shape. Promotes Rho-dependent reorganization of the actin cytoskeleton in neuronal cells and neurite retraction. Promotes the activation of Rho and the formation of actin stress fibers. Promotes formation of lamellipodia at the leading edge of migrating cells via activation of RAC1. Through its function as lysophosphatidic acid receptor, plays a role in chemotaxis and cell migration, including responses to injury and wounding. Plays a role in triggering inflammation in response to bacterial lipopolysaccharide (LPS) via its interaction with CD14. Promotes cell proliferation in response to lysophosphatidic acid. Required for normal skeleton development. May play a role in osteoblast differentiation. Required for normal brain development. Required for normal proliferation, survival and maturation of newly formed neurons in the adult dentate gyrus. Plays a role in pain perception and in the initiation of neuropathic pain.
Tissue Specificity
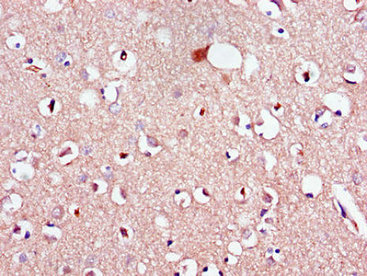
Expressed in many adult organs, including brain, heart, colon, small intestine, placenta, prostate, ovary, pancreas, testes, spleen, skeletal muscle, and kidney. Little or no expression in liver, lung, thymus, or peripheral blood leukocytes. Detected in l