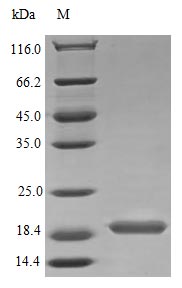
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17B protein (IL17B) gets expressed in E. coli and represents the full mature protein spanning amino acids 21 to 180. This tag-free preparation shows purity greater than 95% when verified by SDS-PAGE. The product appears to demonstrate full biological activity, with an ED50 of less than 1.0 μg/ml in IL-8 secretion assays on human HepG2 cells. This translates to a specific activity of over 1000 IU/mg. Endotoxin levels stay below 1.0 EU/μg according to the LAL method.
Interleukin-17B belongs to the IL-17 cytokine family, which is known for its involvement in immune responses. It likely plays a role in inflammatory pathways and has been studied for its effects on immune cell signaling. The protein is commonly used in research settings to explore mechanisms of inflammation and immune regulation, potentially offering insights into therapeutic targets for inflammatory conditions.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. IL-8 Induction Assays for Inflammatory Response Studies
This recombinant IL-17B protein is validated as biologically active (ED₅₀ < 1.0 μg/ml for IL-8 induction in HepG2 cells) and suitable for studying inflammatory signaling pathways. The high purity (>95%) and low endotoxin levels (<1.0 EU/μg) ensure minimal interference in cell-based assays. Researchers can use this protein to investigate dose-dependent IL-8 secretion and downstream inflammatory mediators with confidence in its functional activity.
2. Receptor Binding and Interaction Studies
The confirmed bioactivity indicates proper folding for receptor engagement, making this IL-17B protein suitable for binding studies. While expressed in E. coli (lacking eukaryotic glycosylation), the demonstrated activity suggests native-like conformation for IL-17RB receptor interaction. Techniques like surface plasmon resonance or competitive binding assays can quantify binding affinity, with the mature protein sequence (21-180aa) representing the physiologically relevant form.
3. Antibody Development and Validation
This protein serves as an excellent immunogen for generating specific antibodies, with high purity and confirmed bioactivity, ensuring recognition of native epitopes. It can be used for antibody screening, ELISA development, and validation assays. The defined specific activity (>1000 IU/mg) provides a quantitative reference for assessing antibody neutralization potency in functional assays.
4. Cytokine Network Analysis in Hepatocyte Models
The demonstrated activity on HepG2 hepatocyte cells validates this IL-17B protein for studying liver-specific inflammatory responses. Researchers can investigate IL-17B's role in hepatic cytokine networks with confidence that observed effects are specifically attributable to IL-17B activity rather than contaminants, given the low endotoxin levels
5. Signal Transduction Pathway Mapping
This biologically active IL-17B protein is ideal for mapping intracellular signaling pathways activated by IL-17B receptor engagement. The defined ED₅₀ enables consistent experimental conditions for studying phosphorylation cascades, transcription factor activation, and gene expression changes. Time-course studies using this protein will reliably elucidate molecular events in IL-17B-mediated cellular responses.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This recombinant Human IL-17B protein is a highly reliable research tool suitable for all proposed applications due to its validated bioactivity, high purity, and low endotoxin levels. For immediate use, prioritize functional assays (IL-8 induction in HepG2 cells) to establish dose-response relationships. For receptor studies, employ SPR or BLI techniques leveraging the protein's confirmed activity. When developing antibodies, use this protein for both immunization and screening, then validate against native IL-17B from human samples. While the E. coli expression system may omit natural glycosylation, the demonstrated biological activity confirms functional competence. Always include appropriate controls (vehicle-only and activity confirmation) in experiments to ensure data quality and reproducibility.