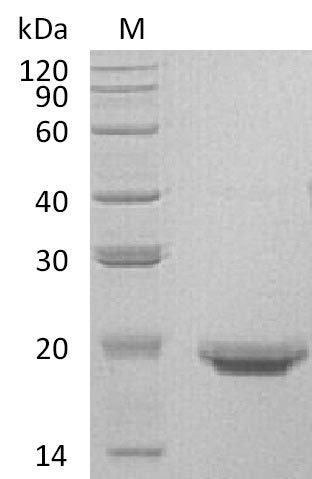
Recombinant Human Interleukin-17F (IL17F) is produced in a mammalian expression system and represents a full-length mature protein with a C-terminal 6xHis tag. The product shows purity greater than 95% as determined by SDS-PAGE analysis. Biological activity appears confirmed through binding ability in a functional ELISA. Endotoxin levels remain below 1.0 EU/µg, which likely makes it suitable for research applications.
Interleukin-17F (IL17F) is a cytokine that participates in immune responses, mainly produced by activated T cells. It seems to play an important role in inflammatory responses and belongs to the IL-17 family of cytokines, which may be critical for host defense against pathogens. IL17F appears involved in signaling pathways that contribute to inflammation and represents a key area of interest in research related to immune regulation and inflammatory diseases.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. IL-17 Receptor Binding Studies and Interaction Analysis
This recombinant IL-17F is confirmed to be biologically active in binding to IL-17RA (ED₅₀ 47.94 ng/ml) and suitable for receptor interaction studies. However, the C-terminal His-tag may cause steric hindrance near the receptor-binding interface, potentially affecting binding kinetics. While mammalian expression ensures proper folding and glycosylation, researchers should validate binding affinity using tag-free IL-17F for precise measurements. The use of mouse IL-17RA in the validation assay may not fully represent human IL-17RA binding characteristics.
2. Antibody Development and Characterization
The mammalian-expressed IL-17F serves as a good antigen due to proper folding, but the C-terminal His-tag may induce tag-specific antibodies, reducing antibodies against native C-terminal epitopes. Comprehensive validation should include testing against tag-free IL-17F to ensure recognition of physiological forms. The low endotoxin supports cell-based validation, but antibodies should be tested for neutralization of IL-17F biological function.
3. Competitive Binding Assays for IL-17 Family Studies
The protein can be used in competitive binding assays, but the His-tag may alter binding kinetics compared to untagged IL-17 family members, potentially skewing competition results. The relatively high ED₅₀ (47.94 ng/ml) suggests moderate binding affinity; competition studies should include tag-free controls and validate results in cellular assays. Comparisons with IL-17A should account for differences in receptor affinity and signaling potency.
4. Structural and Biochemical Characterization Studies
The protein is challenging for structural studies without tag removal, as the His-tag may impede crystallization or cause heterogeneity. While mammalian glycosylation supports native-like folding, the tag may affect protein packing in crystals. For biophysical studies (e.g., CD, AUC), the tag may alter hydrodynamic properties. Structural studies would require tag cleavage and isolation of the pure IL-17F domain.
5. Cell-Free Biochemical Assays and Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The His-tag facilitates pull-down assays but may increase non-specific binding or mask interaction sites. While useful for initial interaction screens, identified binding partners should be validated with tag-free IL-17F. The mammalian expression ensures proper folding, but the tag may interfere with interactions involving the C-terminal region. Low endotoxin minimizes false positives in cell-based validation.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This mammalian-expressed human IL-17F with a C-terminal His-tag is a valuable tool for binding and interaction studies, but the tag necessitates careful experimental design. For immediate use: 1) In binding studies, employ the ED₅₀ (≈50 ng/ml) as a starting point but validate kinetics with tag-free protein if precise affinity measurements are needed; 2) For antibody development, use this protein for immunization but screen clones against tag-free IL-17F to avoid tag-specific antibodies; 3) In competition assays, include controls for tag-related artifacts and confirm functional relevance in cellular models; 4) For structural work, cleave the His-tag prior to crystallization trials; 5) For interaction screens, use stringent controls (e.g., tag-only) and validate hits with full-length, tag-free protein. The mammalian expression ensures proper glycosylation, which is important for IL-17F's stability and function, but the C-terminal tag may affect interactions near the receptor-binding interface. Always include appropriate controls and consider tag cleavage for applications requiring native protein conformation. For cellular studies, the protein is suitable, but verify that biological activity matches tag-free IL-17F in relevant disease models.