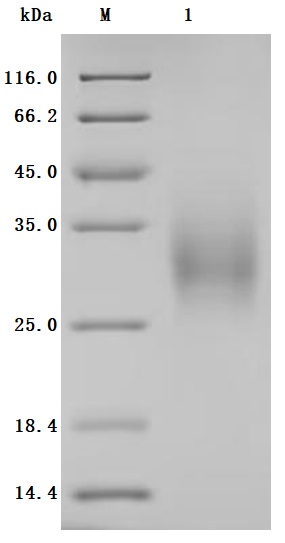
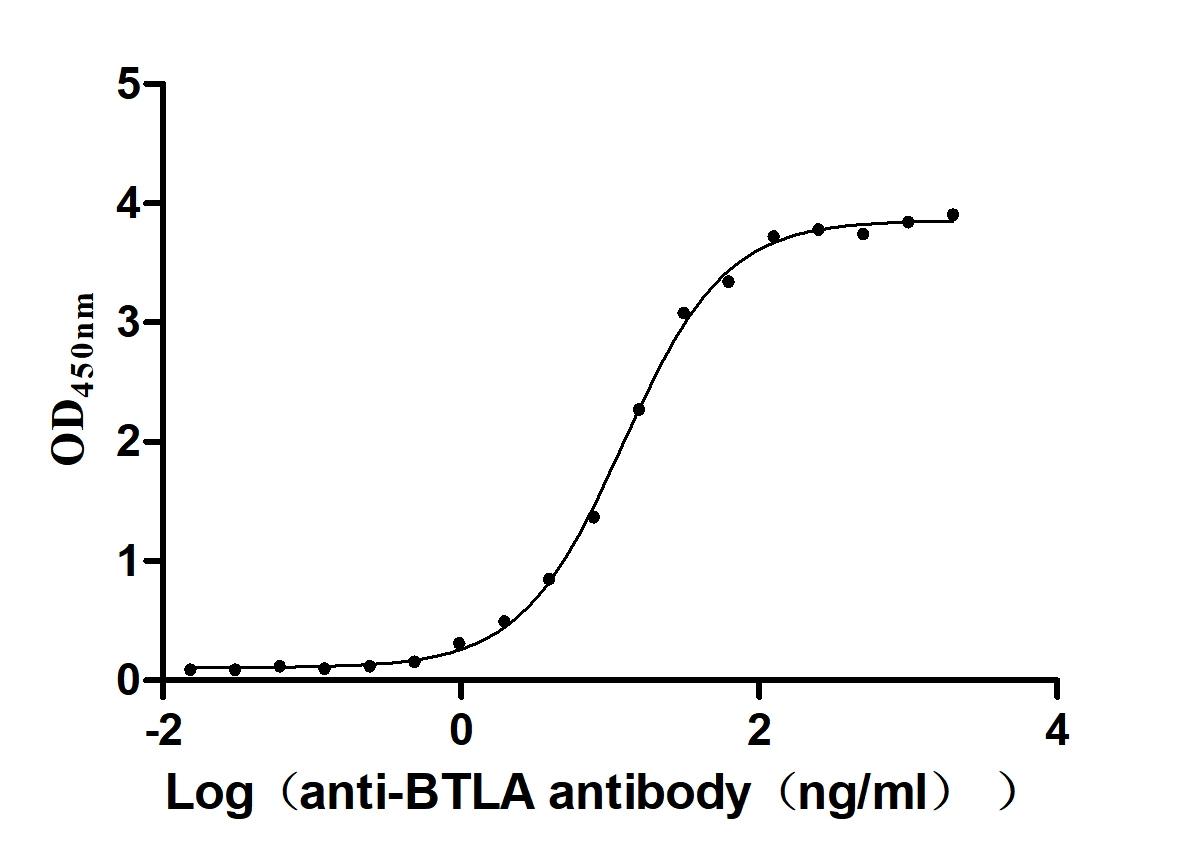
To produce the recombinant human BTLA protein, a plasmid carrying the gene sequence for residues 31-157 of the human BTLA is expressed in mammalian cells. The target gene fragment is co-expressed with a C-terminal 10xHis-tag gene. SDS-PAGE confirms the BTLA protein purity exceeds 95%, and endotoxin content, measured using the LAL assay, remains below 1.0 EU/μg. ELISA testing validates the BTLA protein's functionality, with specific BTLA recombinant antibody(CSB-RA773799MAIHU) binding and an EC50 range of 11.56-13.00 ng/mL.
Human BTLA is an important co-inhibitory receptor that plays a significant role in regulating immune responses. BTLA is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and is primarily expressed on various immune cells, including T cells, B cells, NK cells, and dendritic cells (DCs) [1][2]. It negatively regulates immune activation, thereby maintaining immune homeostasis and preventing excessive immune responses that could lead to autoimmunity or tissue damage [1][3].
The binding of BTLA to the herpes virus entry mediator (HVEM) inhibits T cell and B cell activation, leading to reduced cytokine production and proliferation [4][5]. Specifically, BTLA engagement has been shown to decrease phosphorylation of key signaling molecules in T cells, such as CD3ζ, and in B cells, including Syk and PLCγ2, thereby dampening their activation [6][7]. This inhibitory signaling pathway is crucial for the regulation of immune responses, particularly in the context of chronic infections and cancer, where BTLA expression is often upregulated [8][9].
In the context of cancer, BTLA has been implicated in creating a protumor microenvironment by promoting immune evasion mechanisms [4][10]. Studies have demonstrated that high levels of BTLA expression correlate with poor outcomes in various cancers, including chronic lymphocytic leukemia and melanoma [10][11]. The blockade of BTLA signaling has been proposed as a potential therapeutic strategy to enhance anti-tumor immunity by reinvigorating T cell responses [8][12].
Moreover, BTLA is involved in the regulation of immune tolerance and the maintenance of homeostasis within the immune system. It plays a role in the differentiation of Tregs and the modulation of dendritic cell functions, which are essential for inducing tolerance to self-antigens and preventing autoimmune diseases [13][14]. The dual role of BTLA in promoting both immune suppression and tolerance highlights its complexity as an immune checkpoint molecule [15][16].
References:
[1] L. Gherardi. Targeting b and t lymphocyte attenuator regulates lupus disease development in nzb/w mice,, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1101/2024.05.28.596218
[2] J. Tang, J. Fei, C. Gu, W. Liu, M. Li, & C. Zhou. The influence of b and t lymphocyte attenuator genetic variants on susceptibility to chronic hepatitis b virus infection, Cellular Physiology and Biochemistry, vol. 45, no. 6, p. 2540-2547, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1159/000488272
[3] N. Shubin, S. Monaghan, D. Heffernan, C. Chung, & A. Ayala. B and t lymphocyte attenuator expression on cd4+ t-cells associates with sepsis and subsequent infections in icu patients, Critical Care, vol. 17, no. 6, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1186/cc13131
[4] S. Oguro, Y. Ino, K. Shimada, Y. Hatanaka, Y. Matsuno, M. Esaki, et al. Clinical significance of tumor‐infiltrating immune cells focusing on btla and cbl‐b in patients with gallbladder cancer, Cancer Science, vol. 106, no. 12, p. 1750-1760, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.12825
[5] X. Jiang, J. He, Y. WANG, J. LIU, X. LI, X. HE, et al. A pan-cancer analysis of the biological function and clinical value of btla in tumors, Biocell, vol. 47, no. 2, p. 351-366, 2023. https://doi.org/10.32604/biocell.2023.025157
[6] J. Šedý, R. Bjordahl, V. Bekiaris, M. Macauley, B. Ware, P. Norris, et al. Cd160 activation by herpesvirus entry mediator augments inflammatory cytokine production and cytolytic function by nk cells, The Journal of Immunology, vol. 191, no. 2, p. 828-836, 2013. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1300894
[7] Y. Sakoda, J. Park, Y. Zhao, A. Kuramasu, D. Geng, Y. Liu, et al. Dichotomous regulation of gvhd through bidirectional functions of the btla-hvem pathway, Blood, vol. 117, no. 8, p. 2506-2514, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2010-08-301325
[8] X. Dong, J. Song, B. Chen, Y. Qi, W. Jiang, H. Li, et al. Exploration of the prognostic and immunotherapeutic value of b and t lymphocyte attenuator in skin cutaneous melanoma, Frontiers in Oncology, vol. 10, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2020.592811
[9] J. Fourcade, Z. Sun, O. Pagliano, P. Guillaume, I. Luescher, C. Sander, et al. Cd8+ t cells specific for tumor antigens can be rendered dysfunctional by the tumor microenvironment through upregulation of the inhibitory receptors btla and pd-1, Cancer Research, vol. 72, no. 4, p. 887-896, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1158/0008-5472.can-11-2637
[10] C. Sordo‐Bahamonde, S. Lorenzo‐Herrero, A. González-Rodríguez, Á. Payer, E. González-García, A. López‐Soto, et al. Btla/hvem axis induces nk cell immunosuppression and poor outcome in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Cancers, vol. 13, no. 8, p. 1766, 2021. https://doi.org/10.3390/cancers13081766
[11] C. Sordo‐Bahamonde, S. Lorenzo‐Herrero, A. Martínez‐Pérez, A. González-Rodríguez, Á. Payer, E. González-García, et al. Btla dysregulation correlates with poor outcome and diminished t cell-mediated antitumor responses in chronic lymphocytic leukemia, Cancer Immunology Immunotherapy, vol. 72, no. 7, p. 2529-2539, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00262-023-03435-1
[12] W. Hobo, W. Norde, N. Schaap, H. Fredrix, F. Maas, K. Schellenset al., B and t lymphocyte attenuator mediates inhibition of tumor-reactive cd8+ t cells in patients after allogeneic stem cell transplantation, The Journal of Immunology, vol. 189, no. 1, p. 39-49, 2012. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1102807
[13] A. Jones, J. Bourque, L. Kuehm, A. Opejin, R. Teague, C. Gross, et al. Immunomodulatory functions of btla and hvem govern induction of extrathymic regulatory t cells and tolerance by dendritic cells, Immunity, vol. 45, no. 5, p. 1066-1077, 2016. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2016.10.008
[14] J. Zhang, Y. Lu, W. Wang, G. Liu, C. Chen, L. Shen, et al. Btla-expressing dendritic cells in patients with tuberculosis exhibit reduced production of il-12/ifn-α and increased production of il-4 and tgf-β, favoring th2 and foxp3+ treg polarization, Frontiers in Immunology, vol. 11, 2020. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2020.00518
[15] V. Bekiaris, J. Šedý, M. Macauley, A. Rhode-Kurnow, & C. Ware. The inhibitory receptor btla controls γδ t cell homeostasis and inflammatory responses, Immunity, vol. 39, no. 6, p. 1082-1094, 2013. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2013.10.017
[16] P. Diefenhardt. Stimulation of immune checkpoint molecule b and t-lymphocyte attenuator alleviates experimental crescentic glomerulonephritis, Journal of the American Society of Nephrology, vol. 34, no. 8, p. 1366-1380, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1681/asn.0000000000000159