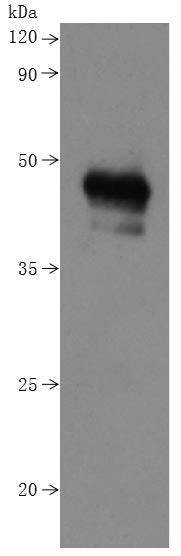
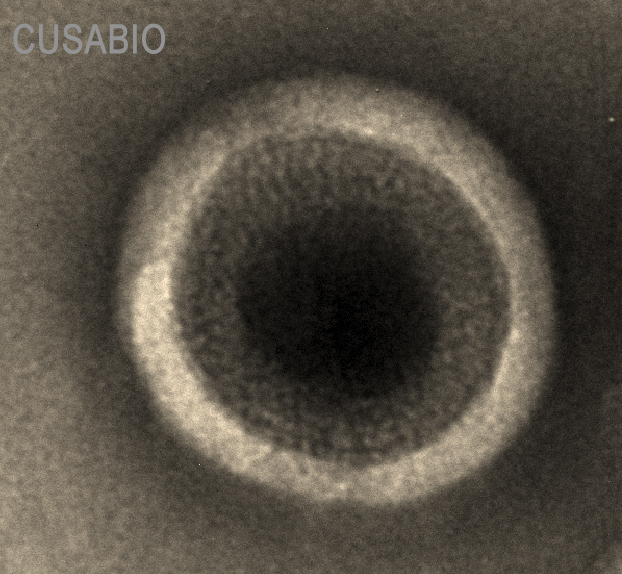
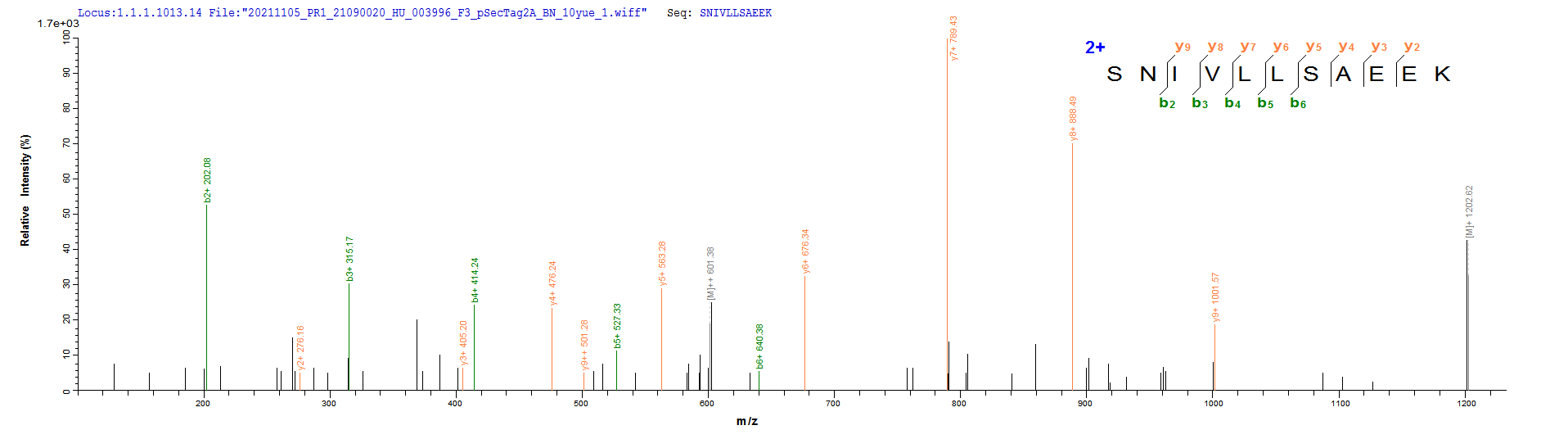
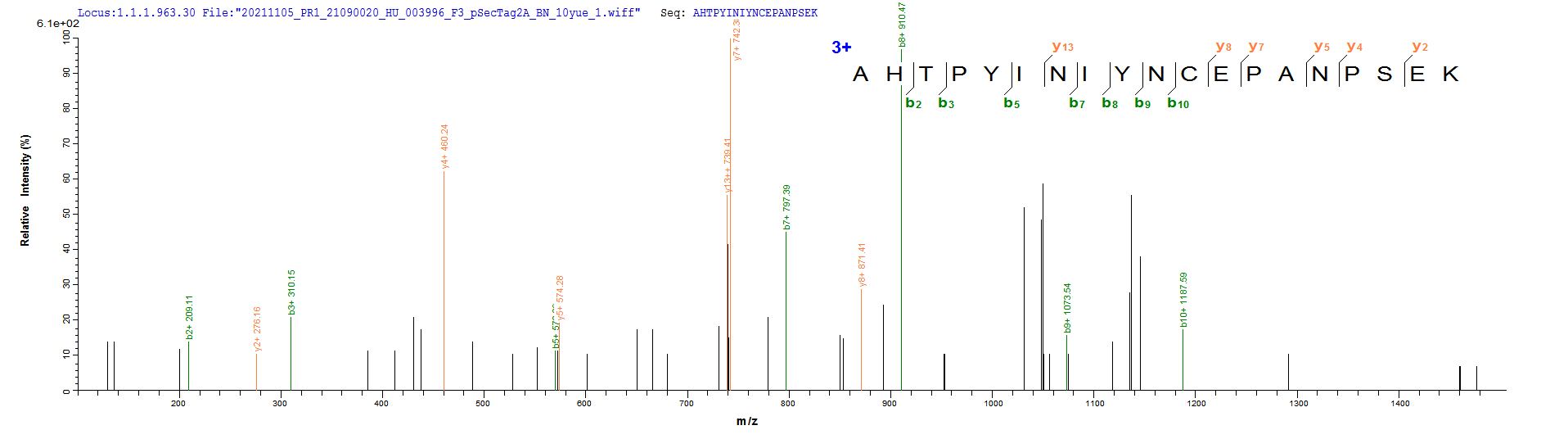
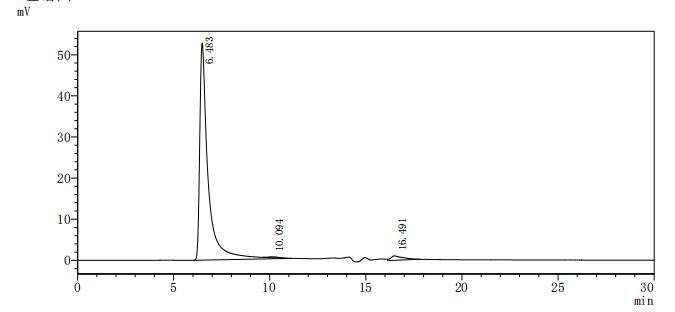
This recombinant human CD20 (MS4A1) protein is produced as a virus-like particle (VLP) in mammalian cells, encompassing the full-length (amino acids 1-297) with a C-terminal 10×His tag for enhanced purification and detection. The VLP formulation mimics native membrane presentation while maintaining excellent purity (>90% by SDS-PAGE) and low endotoxin levels (<1.0 EU/μg, LAL method).
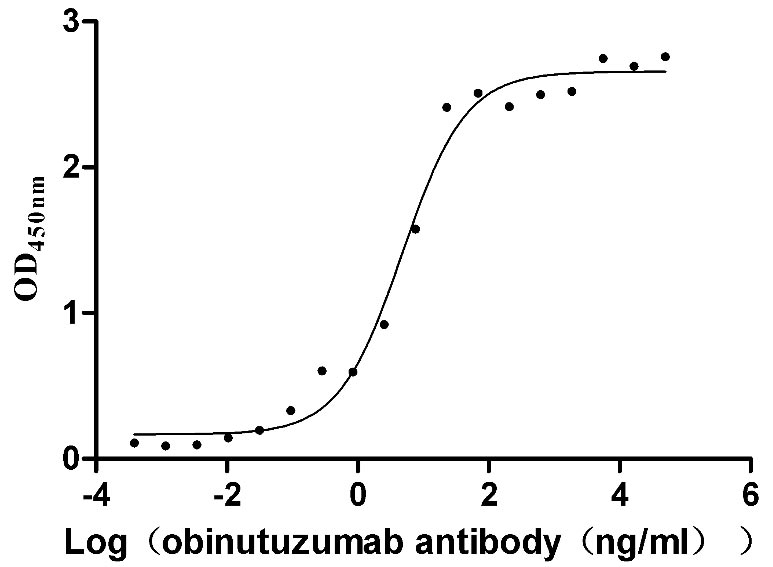
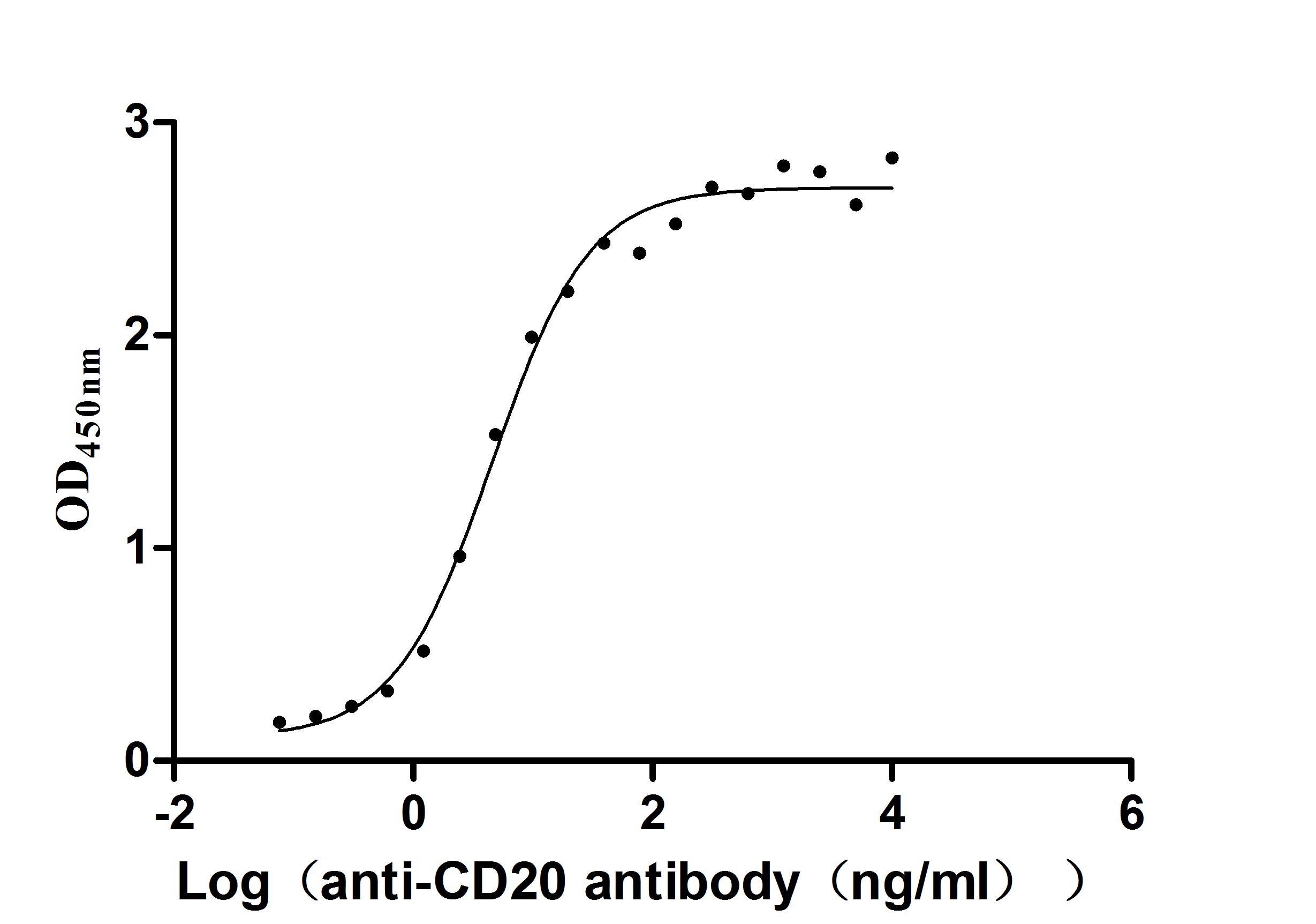
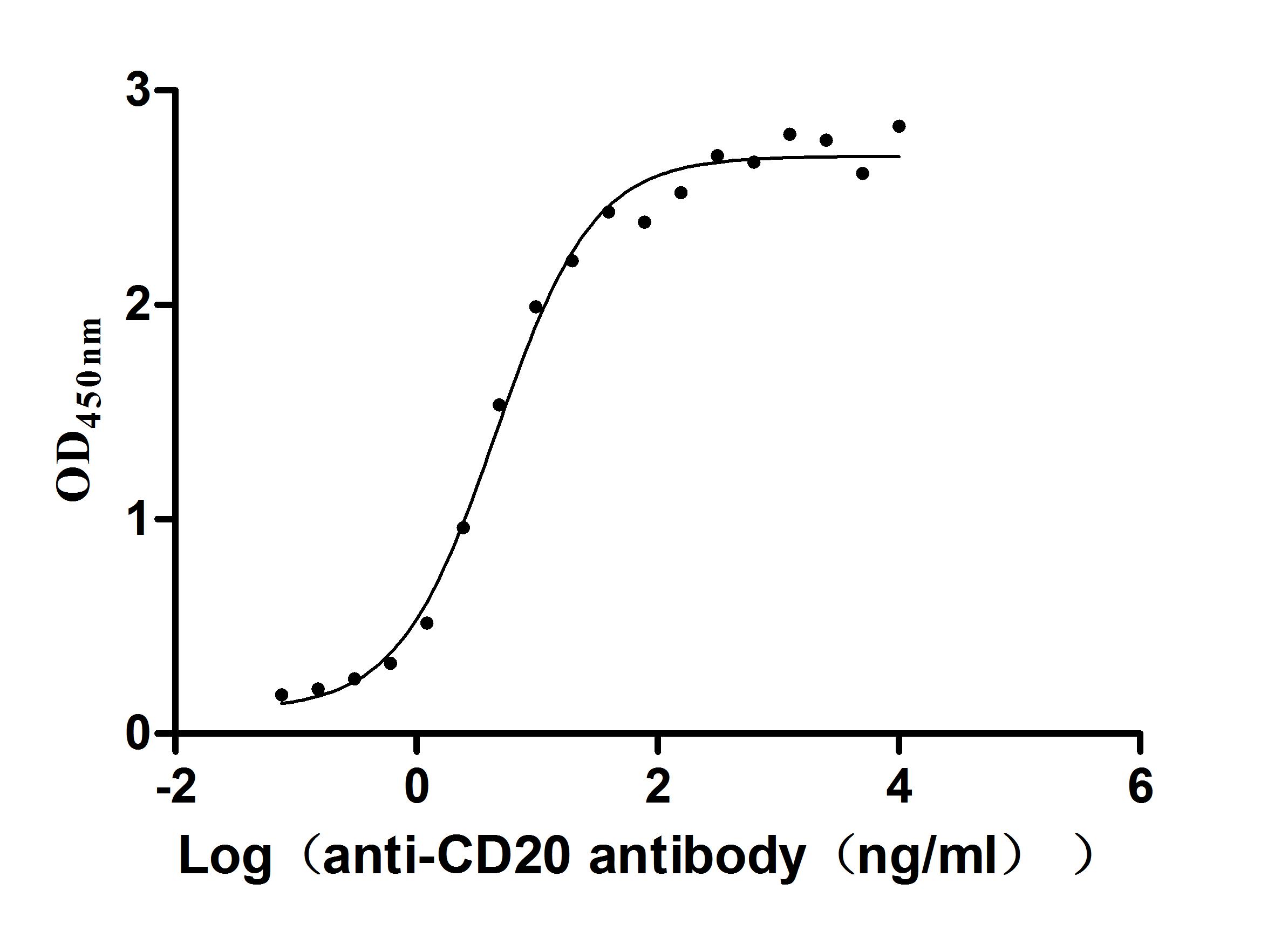
Functional analysis demonstrates that the recombinant MS4A1 protein specifically binds to the anti-CD20 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA015007A1HU) in ELISA format (EC50: 3.243-7.085 ng/mL), validating its structural integrity and biological relevance. The VLP structure provides multiple CD20 epitopes in their native conformation, making this preparation particularly valuable for the development and evaluation of CD20-targeting therapeutics, vaccine research against B-cell malignancies, structural studies of antibody-CD20 interactions, and B-cell immunology research.
The mammalian expression system ensures proper post-translational modifications, while the lyophilized form offers convenient storage and handling. This MS4A1 VLP represents an advanced tool for cancer research, particularly in studies of B-cell lymphomas and therapeutic antibody development, combining the benefits of recombinant protein technology with native-like membrane presentation.
Human CD20 protein, also known as MS4A1, is a transmembrane protein predominantly expressed on B-lymphocytes. It has significant implications in both normal immune function and pathological conditions, particularly in hematological malignancies such as lymphomas. Structurally, CD20 is composed of four hydrophobic transmembrane domains, with both N- and C-termini located in the cytoplasm, which is critical for its role in cellular signaling and receptor organization on the B-cell surface [1][2][3].
CD20 functions primarily as a regulator of B-cell activation, influencing processes such as cell proliferation, differentiation, and immunoglobulin secretion. Unlike many surface proteins, CD20 does not have a known natural ligand, suggesting its function is primarily cell-intrinsic [3][4]. It has been identified as a calcium-permeable cation channel that plays a vital role in calcium signaling, essential for B-cell activation [5][6]. The involvement of CD20 in calcium mobilization indicates its crucial role in initial B-cell activation, which subsequently regulates various downstream signaling pathways essential for immune responses [4][7].
The presence of CD20 on B cells makes it an important target for therapeutic interventions, particularly in the form of monoclonal antibodies like rituximab. The binding of these antibodies to CD20 induces the death of B cells through mechanisms such as complement-dependent cytotoxicity (CDC) and antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC) [8][9]. These effects are particularly relevant in the context of treatments for B-cell malignancies, where anti-CD20 therapies have shown significant efficacy [10][11]. For instance, studies have shown that anti-CD20 antibodies can profoundly impact the clinical outcomes in B-cell neoplasms by depleting CD20-positive cells, leading to therapeutic remission in many patients [12][10].
Furthermore, CD20 expression is relatively restricted, absent in terminally differentiated plasma cells and expressed at various stages of B-cell development, including pre-B, immature, mature, and activated B cells [1][13]. This selective expression pattern makes CD20 a useful biomarker for identifying B-cell populations in clinical diagnostics and research settings. Understanding the functional implications of CD20's activity and its interaction with therapeutic antibodies continues to drive research aimed at improving outcomes in B-cell-related diseases [14].
References:
[1] T. Kuijpers, R. Bende, et al. Cd20 deficiency in humans results in impaired t cell–independent antibody responses. Journal of Clinical Investigation, vol. 120, no. 1, p. 214-222, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1172/jci40231
[2] C. Adra, J. Lélias, et al. Cloning of the cdna for a hematopoietic cell-specific protein related to cd20 and the beta subunit of the high-affinity ige receptor: evidence for a family of proteins with four membrane-spanning regions. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 91, no. 21, p. 10178-10182, 1994. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.91.21.10178
[3] M. Cragg, C. Walshe, А. Иванов, & M. Glennie. The biology of cd20 and its potential as a target for mab therapy. p. 140-174, 2004. https://doi.org/10.1159/000082102
[4] F. Förster, A. Singla, S. Arora, R. Schmidt, & R. Jacobs. Cd20+ t cell numbers are decreased in untreated hiv-1 patients and recover after haart. Immunology Letters, vol. 146, no. 1-2, p. 74-78, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.imlet.2012.05.004
[5] H. Li, L. Ayer, J. Lytton, & J. Deans. Store-operated cation entry mediated by cd20 in membrane rafts. Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 278, no. 43, p. 42427-42434, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m308802200
[6] M. Kanzaki, L. Nie, H. Shibata, & I. Kojima. Activation of a calcium-permeable cation channel cd20 expressed in balb/c 3t3 cells by insulin-like growth factor-i. Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 272, no. 8, p. 4964-4969, 1997. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.272.8.4964
[7] K. Kläsener, J. Jellusova, et al. Cd20 as a gatekeeper of the resting state of human b cells. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, vol. 118, no. 7, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2021342118
[8] K. Yoshinaga, M. Araki, et al. Low‐dose rituximab induction therapy is effective in immunological high‐risk renal transplantation without increasing cytomegalovirus infection. International Journal of Urology, vol. 27, no. 12, p. 1136-1142, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1111/iju.14382
[9] J. Teeling, W. Mackus, et al. The biological activity of human cd20 monoclonal antibodies is linked to unique epitopes on cd20. The Journal of Immunology, vol. 177, no. 1, p. 362-371, 2006. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.177.1.362
[10] E. Wilk, T. Witte, et al. Depletion of functionally active cd20+ t cells by rituximab treatment. Arthritis & Rheumatism, vol. 60, no. 12, p. 3563-3571, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1002/art.24998
[11] M. Cragg, S. Morgan, et al. Complement-mediated lysis by anti-cd20 mab correlates with segregation into lipid rafts. Blood, vol. 101, no. 3, p. 1045-1052, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2002-06-1761
[12] M. Weber, T. Prod’homme, et al. B‐cell activation influences t‐cell polarization and outcome of anti‐cd20 b‐cell depletion in central nervous system autoimmunity. Annals of Neurology, vol. 68, no. 3, p. 369-383, 2010. https://doi.org/10.1002/ana.22081
[13] W. Sun, N. Zhang, Y. Zhang, Z. Shao, L. Gong, & W. Wei. Immunophenotypes and clinical features of lymphocytes in the labial gland of primary sjogren's syndrome patients. Journal of Clinical Laboratory Analysis, vol. 32, no. 9, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1002/jcla.22585
[14] A. Pröbstel and S. Hauser. Multiple sclerosis: b cells take center stage. Journal of Neuro-Ophthalmology, vol. 38, no. 2, p. 251-258, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1097/wno.0000000000000642