|
Drugs
|
Target
|
Mechanism
|
Drug Type
|
Indications
|
Institutes
|
R&D status
|
Ripertamab
Repatumab
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Sinocelltech Group Ltd.
|
Approval for listing
|
|
Mosunetuzumab
|
CD20 | CD3
|
CD20 inhibitor | CD3 inhibitor
|
Bispecific antibodies
|
Follicular lymphoma; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; B-cell lymphoma; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
|
Roche (China) Investment Ltd; Roche Registration GmbH
|
Approval for listing
|
Ocrelizumab
Ocrelizumab
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Multiple sclerosis; chronic progressive multiple sclerosis; relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis; Hashimoto encephalitis
|
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Genentech, Inc.; Roche Holding AG
|
Approval for listing
|
Rituximab/Hyaluronidase
Rituximab/Hyaluronidase
|
CD20 | Hyaluronic acid
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal Antibodies | Enzymes
|
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; follicular lymphoma
|
Roche Holding AG; Genentech, Inc.; Halozyme Therapeutics, Inc.
|
Approval for listing
|
Obinutuzumab
Otuzumab
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Follicular lymphoma; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia; marginal zone B-cell lymphoma; systemic lupus erythematosus; nephropathy; membranous glomerulonephritis; glomerulonephritis; lupus nephritis; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; colorectal cancer; macroglobulinemia; B-cell lymphoma; lymphoplasmacytic lymphoma; graft-versus-host disease; central nervous system tumors; set of cells lymphoma; lymphoma; renal cell carcinoma; solid tumor; nephrotic syndrome
|
Shanghai Roche Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd; Genentech, Inc.; Biogen, Inc.; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co.
|
Approval for listing
|
Ofatumumab
Ofatumumab
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis; multiple sclerosis; lymphocytic leukemia; B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
|
Novartis Pharma AG; GSK Plc; Novartis AG; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corp.; Genmab A/S; Novartis Ireland Ltd.
|
Approval for listing
|
Ibritumomab Tiuxetan
Tiimomab
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Therapeutic radiopharmaceuticals | Radiolabeled antibodies | Monoclonal antibodies
|
Set of cell lymphoma; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Acrotech Biopharma LLC; CASI Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Spectrum Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Mundipharma KK
|
Approval for listing
|
Rituximab
Rituximab
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
lymphocytic leukemia; thrombocytopenic purpura; renal transplant rejection; liver transplant rejection; nephrotic syndrome; vasculitis; polyarteritis nodosa; sarcoidosis with polyangiitis; microscopic polyangiitis; B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia; rheumatoid arthritis; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; aspergillosis; systemic scleroderma; follicular lymphoma; B-cell lymphoma; non-Hodgkin lymphoma; Burkitt's lymphoma; Hodgkin's lymphoma; multiple myeloma
|
Roche Holding AG; Shanghai Roche Pharmaceuticals Ltd.; IDEC Pharmaceuticals Corp.; Chugai Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd.; Genentech, Inc.; Cipla Ltd; Roche Pharma (Schweiz) AG
|
Approval for listing
|
|
304 (3SBio)
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Samson Pharmaceutical Group
|
Application for listing
|
|
Epcoritamab
|
CD20 | CD3
|
CD20-directed cytolysis | CD3 inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor
|
Bispecific antibodies
|
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; large B-cell lymphoma; follicular lymphoma; hematologic neoplasm
|
AbbVie, Inc.; AbbVie Pharmaceutical Trading (Shanghai) Co.
|
Application for listing
|
|
Glofitamab
|
CD20 | CD3
|
Antibody-dependent cytotoxicity | CD3 inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor
|
Bispecific antibodies
|
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; follicular lymphoma; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; lymphoma; B-cell lymphoma
|
Roche Holding AG; F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd.; Roche (China) Investment Ltd.; Genentech, Inc.
|
Application for listing
|
|
Ublituximab
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Relapsing-remitting multiple sclerosis; multiple sclerosis; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; follicular lymphoma; set of cell lymphoma; marginal zone B-cell lymphoma; B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; optic neuromyelitis optica; autoimmune disease; tumor
|
TG Therapeutics, Inc.; Ildong Pharmaceutical Co.
|
Application for listing
|
Zebituzumab
Zebituzumab
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; thrombocytopenia; idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
|
Zhejiang Borui Biopharmaceutical Co.
|
Application for listing
|
|
Divozilimab
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Multiple Sclerosis
|
Biocad CJSC
|
Clinical Phase 3
|
|
MB-CART2019.1
|
CD20 | CD19
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD19 inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
|
Miltenyi Biomedicine GmbH; Miltenyi GmbH; Miltenyi Biotec, Inc.
|
Clinical Phase 3
|
Recombinant chimeric anti-CD20 antibody(Shanghai Institute of Biological Products Co., Ltd.)
Recombinant chimeric anti-CD20 monoclonal antibody (Shanghai Institute of Biological Products)
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
|
Shanghai Institute of Biological Products Co.
|
Clinical Phase 3
|
Recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody MIL62
Recombinant humanized monoclonal antibody MIL62
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Follicular lymphoma; marginal zone B-cell lymphoma; B-cell lymphoma; systemic lupus erythematosus; myasthenia gravis; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; optic neuromyelitis optica
|
Jiangsu Hengrui Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd; Beijing Tianguang Shi Biotechnology Co.
|
Clinical Phase 3
|
|
4SCAR-T cell therapy (Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute)
|
CD20 | CD22 | CD38
|
CD20 inhibitor | CD22 modulator | CD38 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Tumors
|
Shenzhen Institute of Immunogene Therapy
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
Anti-CD19 and anti-CD20 CAR-T cell therapy (The Medical College of Wisconsin, Inc.)
|
CD20 | CD19
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD19 inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Tumors
|
The Medical College of Wisconsin, Inc.
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
Anti-CD20 CAR T-cell therapy(Shanghai Longyao Biotech Co., Ltd.)
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
|
Shanghai Longyao Biotech Co., Ltd.
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
Anti-CD20 CART-transduced T cells (Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital)
Anti-CD20 CART-transduced T cells (Chinese People's Liberation Army General Hospital)
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
B-cell lymphoma; leukemia; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Cellular Biomedicine Group, Inc.; General Hospital of the Chinese People's Liberation Army
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
Autologous Anti-CD19/CD20 CAR T-cell Therapy (Kite Pharma, Inc)
|
CD20 | CD19
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD19 inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Tumor; B-cell lymphoma; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma
|
Kite Pharma, Inc.
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
BVX20-CD20 antibody(Biocon Ltd.)
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; multiple sclerosis
|
Vaccinex, Inc.; Biocon Ltd.
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
CD20 monoclonal antibody(The First Affiliated Hospital of Soochow University)
|
CD20
|
CD20 modulator
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Aplastic anemia
|
The First Hospital of Soochow University
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
CPO-107
|
CD20 | CD47
|
CD47 inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor
|
Fusion proteins
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Conjupro Bioerapecitics, Inc.
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
DI-Leu16-IL2
|
CD20 | IL2R
|
CD20 inhibitor | IL2R agonist
|
Fusion proteins
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Alopexx Oncology, LLC; Merck Serono SA; Provenance Biopharmaceuticals Corp.
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
MRG001
|
CD20 | Tubulin
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
ADC | Monoclonal Antibodies
|
Novel coronavirus pneumonia; adult respiratory distress syndrome; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Lepu Biopharma Co., Ltd.; MedRegen LLC; Shanghai Mayak Biotechnology Co.
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
MT-3724
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Antibody-coupled toxins
|
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia; B-cell lymphoma; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; hematologic neoplasm
|
Molecular Templates, Inc.
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
Odronextamab
|
CD20 | CD3
|
CD20-directed cytolysis | CD3 inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor
|
Bispecific antibodies
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; Follicular lymphoma; Lymphoma; B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia; B-cell lymphoma; Lymphocytic leukemia
|
Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Inc.; Redding Pharmaceuticals (Shanghai) Co.
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
Plamotamab
Paramotumab
|
CD20 | CD3
|
CD20-directed cytolysis | CD3 inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor
|
Bispecific Antibodies | Monoclonal Antibodies
|
Primary generalized cutaneous diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; B-cell lymphoma
|
Xencor, Inc.; Novartis Pharma AG
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
Veltuzumab
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura
|
Immunomedics, Inc.
|
Clinical Phase 2
|
|
4SCAR20 (Shenzhen Geno-Immune Medical Institute)
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
B-cell leukemia; B-cell lymphoma; tumor; primary central nervous system lymphoma; drug-resistant cancer
|
Shenzhen Institute of Immunogene Therapy
|
Clinical Phase 1/2
|
|
Anti-CD19/CD20 CAR-T cell therapy (Shanghai Longyao Biotechnology)
|
CD20 | CD19
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD20 inhibitor | CD19 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
B-cell lymphoma
|
Shanghai Longyao Biotech Co., Ltd.; Xuzhou Medical University; Shanghai Jiao Tong University
|
Clinical Phase 1/2
|
|
CD20-targeted CAR T cell therapy (Mustang Bio)
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia; refractory B-cell lymphoma; follicular lymphoma; relapsed set of cell lymphoma; refractory set of cell lymphoma; small lymphocytic lymphoma; relapsed macroglobulinemia; refractory Walden's macroglobulinemia
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Mustang Bio, Inc.; Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center
|
Clinical Phase 1/2
|
|
CMG1A46
|
CD20 | CD3 | CD19
|
CD3 modulators | CD19 inhibitors | CD20 inhibitors
|
Tri-Specific Antibodies
|
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; tumor
|
Chengdu Enmu Biotechnology Co., Ltd; Zhejiang Borui Bio Pharmaceutical Co.
|
Clinical Phase 1/2
|
|
IMM-0306
|
CD20 | CD47
|
CD47 inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor
|
Bispecific antibodies
|
B-cell lymphoma; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Yiming Onco Biomedical Technology (Shanghai) Co.
|
Clinical Phase 1/2
|
|
JMT-601
|
CD20 | SIRPA
|
SIRPA inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor
|
Fusion Proteins | Bispecific Antibodies
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Conjupro Biotherapeutics, Inc.; Shanghai Zimantec Biotechnology Co.
|
Clinical Phase 1/2
|
|
Tandem CAR19/20 engineered T cells (Chinese PLA General Hospital)
|
CD20 | CD19
|
CD20 inhibitor | CD19 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Attack; B-cell lymphoma; lymphoma; tumor; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
General Hospital of the Chinese People's Liberation Army
|
Clinical Phase 1/2
|
|
UCART 20x22
|
CD20 | CD22
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD20 inhibitor | CD22 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; precursor B-cell adult lymphocytic leukemia lymphoma
|
Cellectis SA
|
Clinical Phase 1/2
|
|
ACE-1831
|
CD20
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD20 inhibitor
|
Gene Therapy
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; hematologic neoplasm
|
Acepodia Biotech, Inc.
|
Clinical Phase 1
|
|
Anti-CD19 anti-CD20 CAR-T cell therapy (PersonGen BioTherapeutics)
|
CD20 | CD19
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD20 inhibitor | CD19 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Hematologic tumors; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Boshengji Pharmaceutical Technology (Suzhou) Co.
|
Clinical Phase 1
|
|
Anti-CD19/CD20/CD22 CAR T-Cells (Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Centerc)
|
CD20 | CD19 | CD22
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD19 inhibitor | CD20 inhibitor | CD22 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Acute lymphoblastic leukemia; B-cell lymphoblastic leukemia; high-grade B-cell lymphoma; relapsed B acute lymphoblastic leukemia; relapsed inert non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; relapsed non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; relapsed transformed chronic lymphocytic leukemia; refractory B acute lymphoblastic leukemia; refractory pre-B-cell lymphocytic leukemia; refractory inert non-Hodgkin's lymphoma. Refractory transformed chronic lymphocytic leukemia
|
Ohio State University Comprehensive Cancer Center
|
Clinical Phase 1
|
|
Anti-CD20 B9E9 scFv-Streptavidin Fusion Protein (Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center)
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Fusion proteins
|
Burkitt's lymphoma; diffuse large B-cell lymphoma; set cell lymphoma; non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Fred Hutchinson Cancer Research Center; National Cancer Institute
|
Clinical Phase 1
|
|
Anti-CD20/CD22 CAR-T cell therapy (Yake Biotechnology)
|
CD20 | CD22
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD20 inhibitor | CD22 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Hematologic Tumors
|
Shanghai Artech Biotechnology Co.
|
Clinical Phase 1
|
|
B-001
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma; B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia
|
Shanghai Pharmaceutical Group Co.
|
Clinical Phase 1
|
|
BAT-4406F
|
CD20
|
CD20 inhibitor
|
Monoclonal antibodies
|
Optic neuromyelitis optica; multiple sclerosis
|
Biotest Biopharmaceutical Co.
|
Clinical Phase 1
|
|
C-CAR039
|
CD20 | CD19
|
CD20 inhibitor | CD19 inhibitor
|
Autologous CAR-T
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Cellular Biomedicine Group, Inc.
|
Clinical Phase 1
|
|
CD 20 CAR-T cell therapy (Shanghai Longyao Biotechnology)
|
CD20
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD20 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Non-Hodgkin's lymphoma
|
Shanghai Longyao Biotech Co., Ltd.
|
Clinical Phase 1
|
CD19/CD20 bispecific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy(Shanghai Cellular Biopharmaceutical Group)
Anti-CD19/CD20 chimeric antigen receptor autologous T cells (Shanghai Cellular Biopharmaceutical Group)
|
CD20 | CD19
|
CD20 inhibitor | CD19 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
Large B-cell lymphoma
|
Shanghai Saibiman Biotechnology Co.
|
Clinical Phase 1
|
CD19/CD20 bispecific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy (University of California)
CD19/CD20 bispecific chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)-T cell therapy (University of California)
|
CD20 | CD19
|
T-lymphocyte replacement | CD20 inhibitor | CD19 inhibitor
|
CAR-T
|
B-cell chronic lymphocytic leukemia; B-cell lymphoma
|
University of California
|
Clinical Phase 1
|


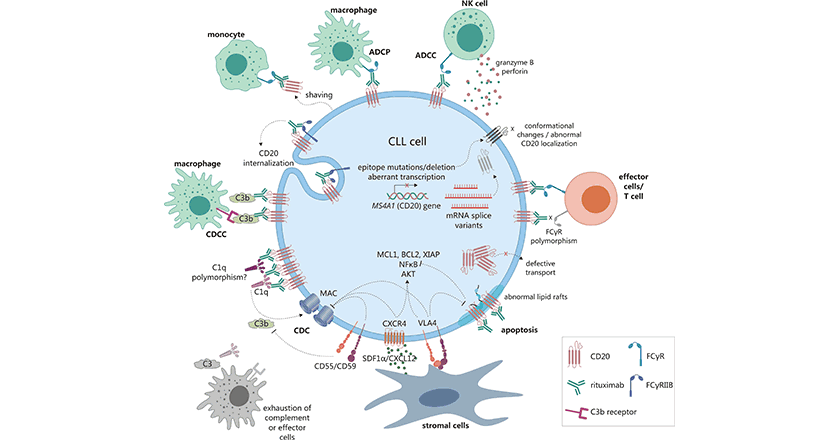
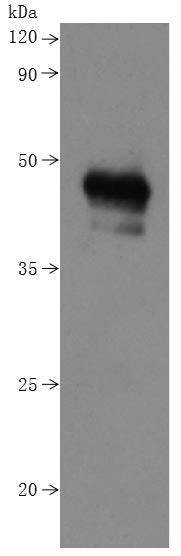
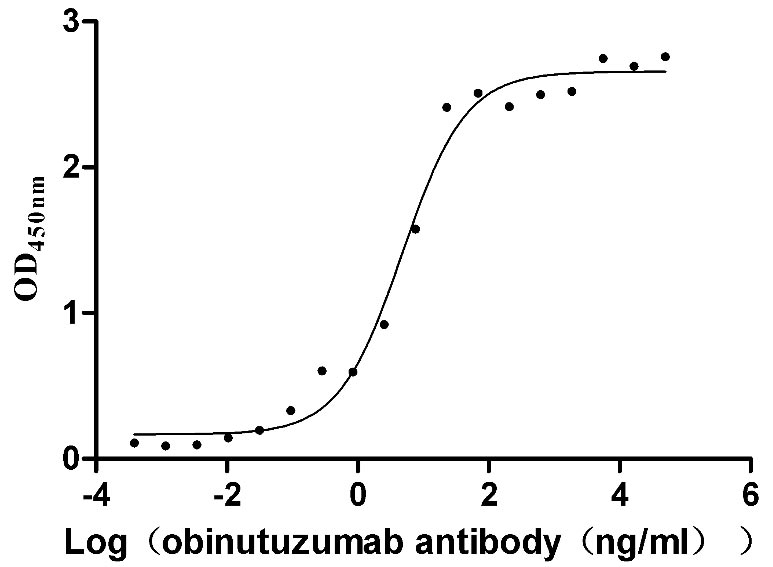
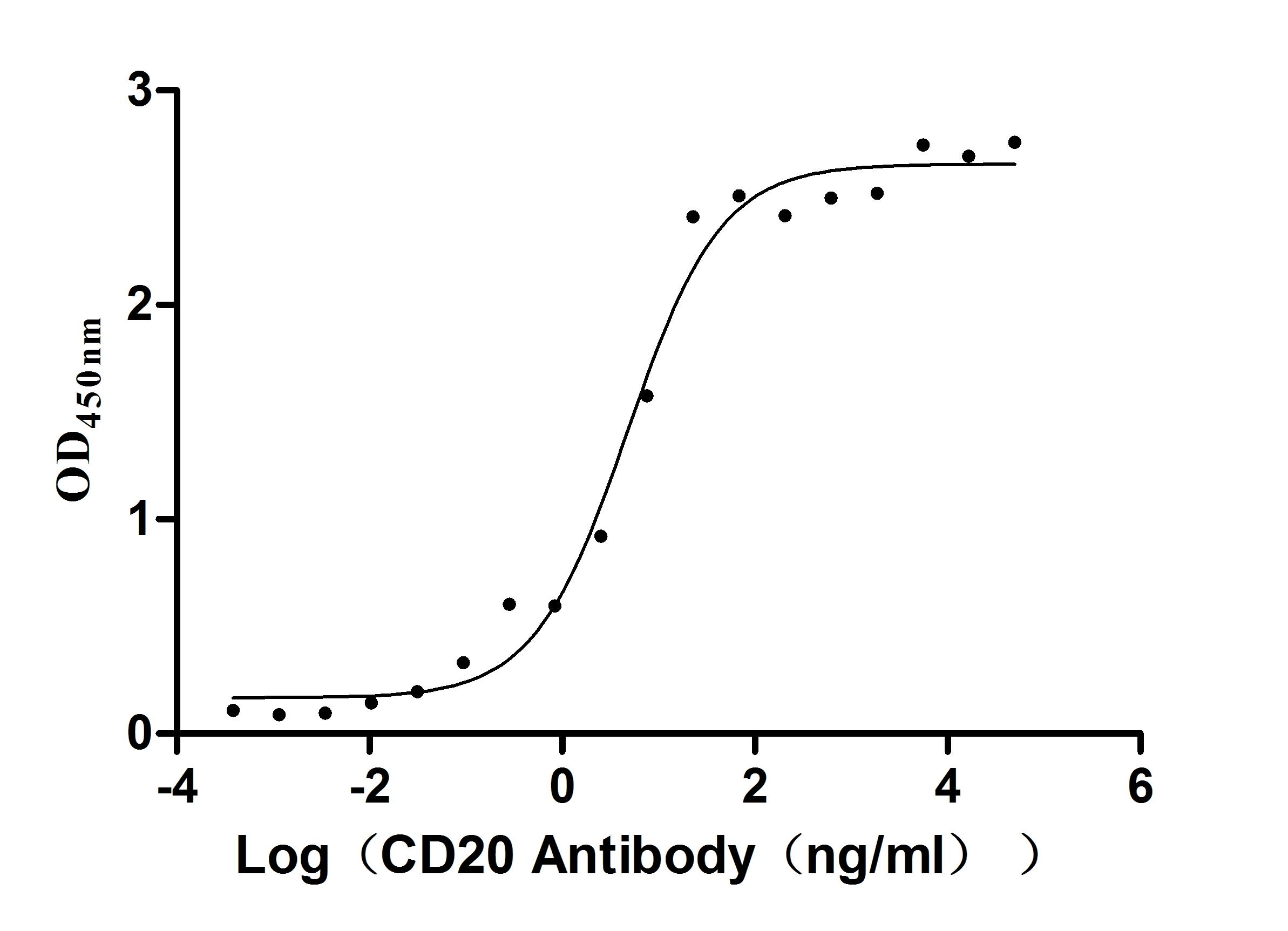
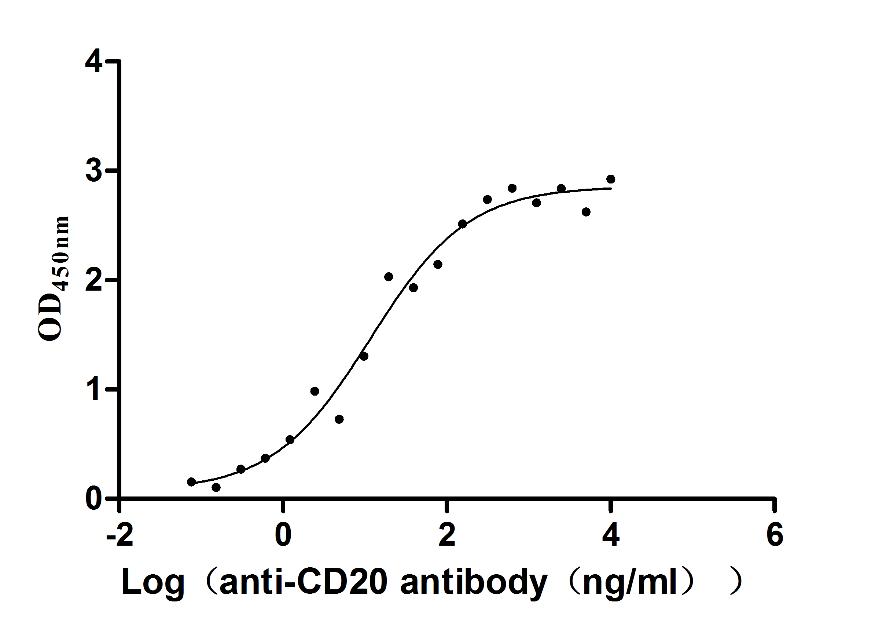



Comments
Leave a Comment