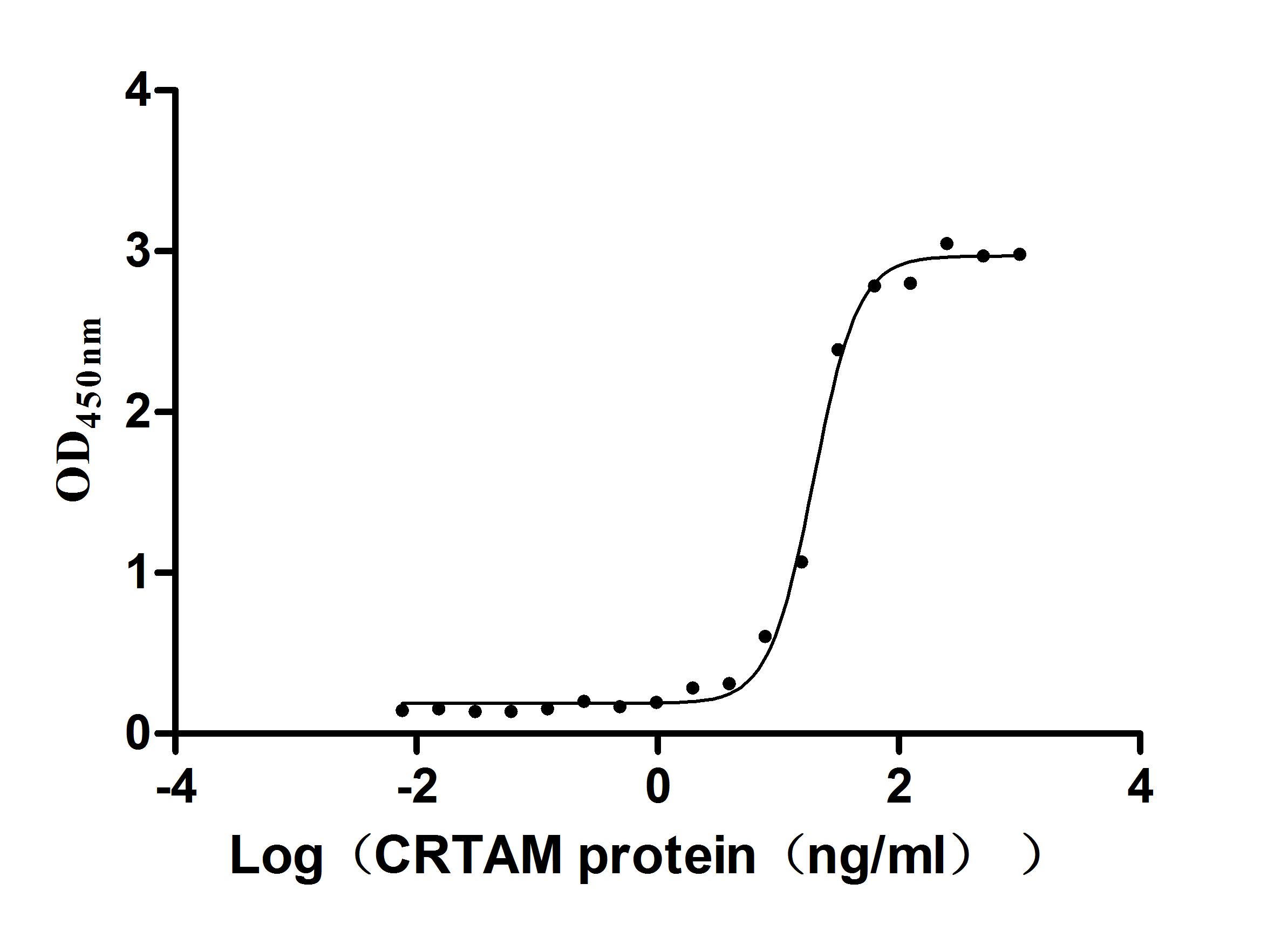
The gene fragment encoding the 45-374aa of the human CADM1 protein is fused with a 10xHis-tag gene at the C-terminus and then inserted into a plasmid vector. The recombinant vector is introduced into mammalian cells, and the transfected mammalian cells are selected and cultured for protein expression. The product is the recombinant human CADM1 protein. Its purity is greater than 95% determined by SDS-PAGE and its endotoxin level is less than 1.0 EU/ug measured by the LAL method. Its bioactivity is validated in a function ELISA. Immobilized human CADM1 at 2 μg/mL can bind human CRTAM (CSB-MP005998HU1), with the EC50 of 17.82-21.71 ng/mL.
CADM1 is expressed in neurons, mast cells, alveolar cells, and pancreatic secretory cells. It is also expressed in fetal and cirrhotic adult bile duct cells, but absent in healthy adult bile ducts. CADM1 mediates cell-cell adhesion through calcium-independent homophilic interactions, contributing to cell interactions and the formation and maintenance of epithelial structures. Overexpression of CADM1 can inhibit epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) induced by growth factors, while loss of CADM1 function can lead to invasion and metastasis of epithelial-derived cancer cells. CADM1 was initially identified as a tumor suppressor gene in human non-small cell lung cancer through functional complementation assays. Currently, a large body of evidence suggests that CADM1 is involved in the formation and development of various human tumors, and downregulation of CADM1 contributes to tumorigenesis in various cancers. Developing stable and active CADM1 proteins can help further investigate the underlying mechanisms and provide new clues for monitoring, diagnosing, and treating tumors.