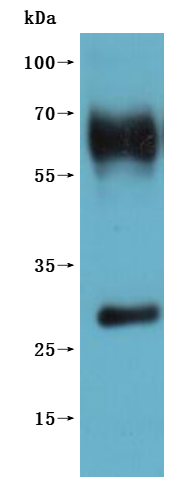
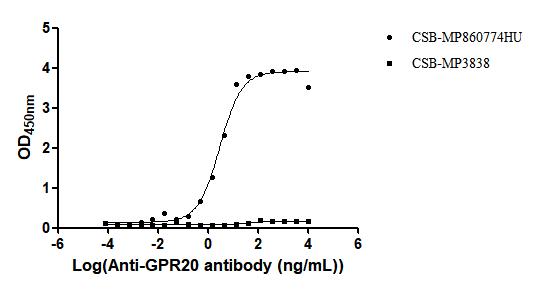
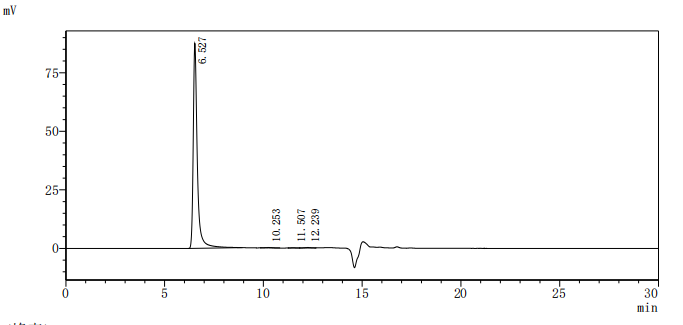
The recombinant human GPR20 protein is presented in the form of virus-like particles (VLPs), allowing for a native-like membrane protein conformation ideal for functional assays. Expressed in mammalian cells to preserve proper folding and post-translational modifications, this recombinant GPR20 protein includes the full-length sequence of human GPR20 (amino acids 1–358) and features a C-terminal 10xHis tag to facilitate purification and detection. It exhibits high purity, greater than 95% as confirmed by SEC-HPLC. Endotoxin levels are controlled below 1.0 EU/μg, validated by the LAL testing. Functional assessment via ELISA demonstrates the GPR20 protein's binding capability. When immobilized at 10 μg/mL, it specifically binds the anti-GPR20 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA860774MA1HU), with an EC50 between 2.431 and 3.239 ng/mL. A VLP (CSB-MP3838) negative control confirms specificity. These characteristics make this GPR20 VLP a robust tool for studying GPCR biology, antibody screening, and drug discovery targeting membrane proteins.
Human GPR20 is a member of the GPCR family, characterized as an orphan receptor due to the absence of identified endogenous ligands. It is encoded by a gene located on chromosome 14 and is of significant interest in physiological and pathological contexts. GPR20 is mainly recognized for its constitutive activity in the absence of a ligand, meaning it can activate intracellular signaling pathways without the need for a specific activating molecule [1]. This distinct feature has implications in various biological processes, including signaling pathways related to neurophysiology and cancer.
Research indicates that GPR20 is expressed in several regions of the human brain, including areas related to motor function and cognition, such as the caudate nuclei and putamen [1]. This widespread expression suggests a potential role in neurophysiological functions and behaviors, as evidenced by studies showing behavioral changes in GPR20-deficient mice [1]. Additionally, the receptor has been implicated in activating inhibitory G-protein signaling, positioning it as a critical player in the modulation of cellular responses [2].
From a pathological perspective, GPR20 has garnered attention in the context of gastrointestinal stromal tumors (GISTs), where it is selectively expressed. Its expression is regulated by key transcription factors related to tumor biology, including FOXF1 and ETV1 [3]. The receptor's exclusive expression in GISTs has led to the development of targeted therapies, such as antibody-drug conjugates specifically designed to recognize GPR20, aiming to improve treatment efficacy for affected patients [3]. Furthermore, its regulation during inflammatory responses has been noted, which can further complicate the understanding of its functional diversity in various tissues.
Beyond its role in cancer, GPR20's association with various signaling pathways, including those related to inflammatory responses, underscores its potential as both a therapeutic target and a biomarker for certain diseases [3]. This receptor has also been associated with neurogenesis and inflammation, indicating its multifaceted roles in human physiology [1].
References:
[1] M. Hase, T. Yokomizo, T. Shimizu, & M. Nakamura. Characterization of an orphan g protein-coupled receptor, gpr20, that constitutively activates gi proteins. Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 283, no. 19, p. 12747-12755, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.m709487200
[2] A. Jobe and R. Vijayan. Orphan g protein-coupled receptors: the ongoing search for a home. Frontiers in Pharmacology, vol. 15, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3389/fphar.2024.1349097
[3] K. Iida, A. Ahmed, et al. Identification and therapeutic targeting of gpr20, selectively expressed in gastrointestinal stromal tumors, with ds-6157a, a first-in-class antibody–drug conjugate. Cancer Discovery, vol. 11, no. 6, p. 1508-1523, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1158/2159-8290.cd-20-1434