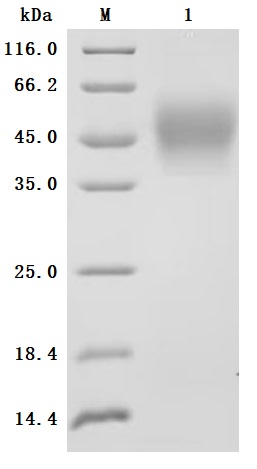
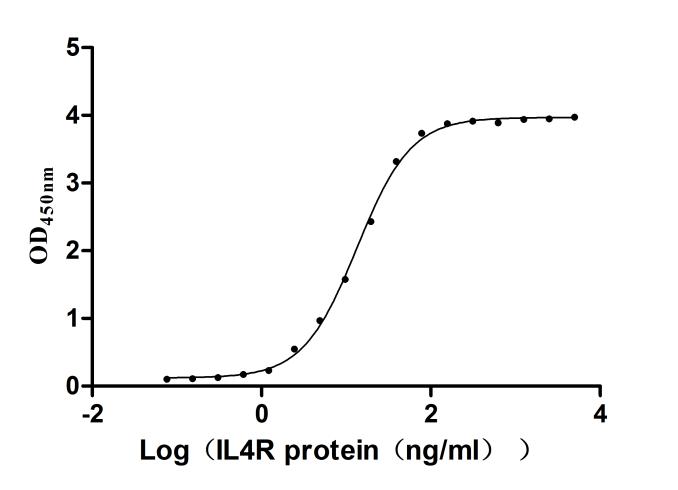
This recombinant human interleukin-4 receptor subunit alpha (IL4R) is expressed in mammalian cells with a C-terminal 10×His-Avi tag and site-specific biotinylation, ensuring optimal functionality for ligand-binding studies. Its expression region corresponds to the 26-232aa of human IL4RA. The protein demonstrates high purity (>95% by SDS-PAGE) and ultra-low endotoxin levels (<1.0 EU/μg, LAL method). Its bioactivity has been validated through functional ELISA, showing specific interaction with immobilized human IL4 (CSB-MP011659HU) (EC50: 12.68–14.23 ng/mL at 2 μg/mL). Mammalian expression preserves native glycosylation and structural integrity critical for IL4R's role in Th2 immune responses and allergic inflammation pathways. The Avi tag enables controlled biotinylation for streptavidin-based assays, while the His tag facilitates purification. Lyophilized for stability, this biotinylated recombinant IL4R protein is ideal for therapeutic antibody development targeting IL4/IL13 signaling in asthma, atopic dermatitis, and oncology research.
The human IL4RA (IL4R) is a significant component of the IL4 signaling pathway, which plays a critical role in mediating immune responses, particularly within the context of allergic diseases and T-helper 2 (Th2) type immunity. IL4RA, in conjunction with its binding partner IL13Rα1, forms a receptor complex that allows for the transduction of signals initiated by IL4 and IL13, cytokines that are crucial in regulating Th2 cell differentiation, activation, and the resultant immune response [1][2].
Upon binding of IL4 to its receptor, IL4RA activates the JAK/STAT pathway, specifically leading to the phosphorylation and activation of the transcription factor STAT6 [1][3]. This activation promotes the transcription of various genes integral to the Th2 response, including those involved in B-cell class switching to immunoglobulin E (IgE), which is particularly relevant in allergic reactions [4][5]. Indeed, studies have shown that STAT6 is essential for M2 macrophage polarization, a process linked to the resolution of inflammation and enhancement of fibrotic responses in various tissues [3][6].
Moreover, research indicates that IL4RA expression is not only essential for standard Th2 responses but also plays a complex role across various immune pathways, including protective immunity against parasites and in regulating autoimmune processes [7][8]. This complexity underscores the potential for ongoing research in understanding the wider implications of IL4RA signaling in both health and disease, alongside the prospect of novel therapeutic avenues targeting this pathway.
References:
[1] H. Harb and T. Chatila. Mechanisms of dupilumab. Clinical & Experimental Allergy, vol. 50, no. 1, p. 5-14, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/cea.13491
[2] K. Barry and D. Gorelik. Dupilumab (dupixent) for asthma. Jama, vol. 321, no. 10, p. 1000, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1001/jama.2019.0080
[3] H. Sadoun, M. Burgess, K. Hentges, & K. Mace. Enforced expression of hoxa3 inhibits classical and promotes alternative activation of macrophages in vitro and in vivo. The Journal of Immunology, vol. 197, no. 3, p. 872-884, 2016. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1501944
[4] N. Kim, S. Ramon, T. Thatcher, C. Woeller, P. Sime, & R. Phipps. Specialized proresolving mediators (spms) inhibit human b‐cell ige production. European Journal of Immunology, vol. 46, no. 1, p. 81-91, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/eji.201545673
[5] S. Hong, J. Ku, et al. Oral administration of cervus nippon mantchuricus extract suppresses 2,4-dinitrochlorobenzene-induced atopic dermatitis in balb/c mice and inflammatory effects in mast cells. International Journal of Molecular Medicine, 2018. https://doi.org/10.3892/ijmm.2018.3856
[6] M. Bartoli, X. Gu, et al. Vascular endothelial growth factor activates stat proteins in aortic endothelial cells. Journal of Biological Chemistry, vol. 275, no. 43, p. 33189-33192, 2000. https://doi.org/10.1074/jbc.c000318200
[7] T. Yi, Y. Chen, et al. Reciprocal differentiation and tissue-specific pathogenesis of th1, th2, and th17 cells in graft-versus-host disease. Blood, vol. 114, no. 14, p. 3101-3112, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2009-05-219402
[8] J. Zamorano, M. Rivas, A. Garcia-Trinidad, C. Qu, & A. Keegan. Phosphatidylcholine-specific phospholipase c activity is necessary for the activation of stat6. The Journal of Immunology, vol. 171, no. 8, p. 4203-4209, 2003. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.171.8.4203