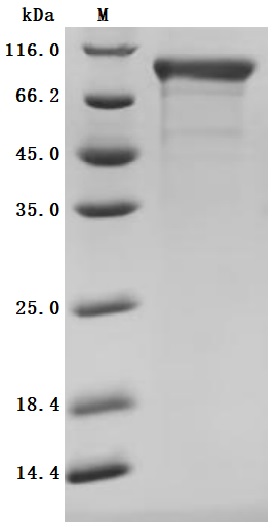
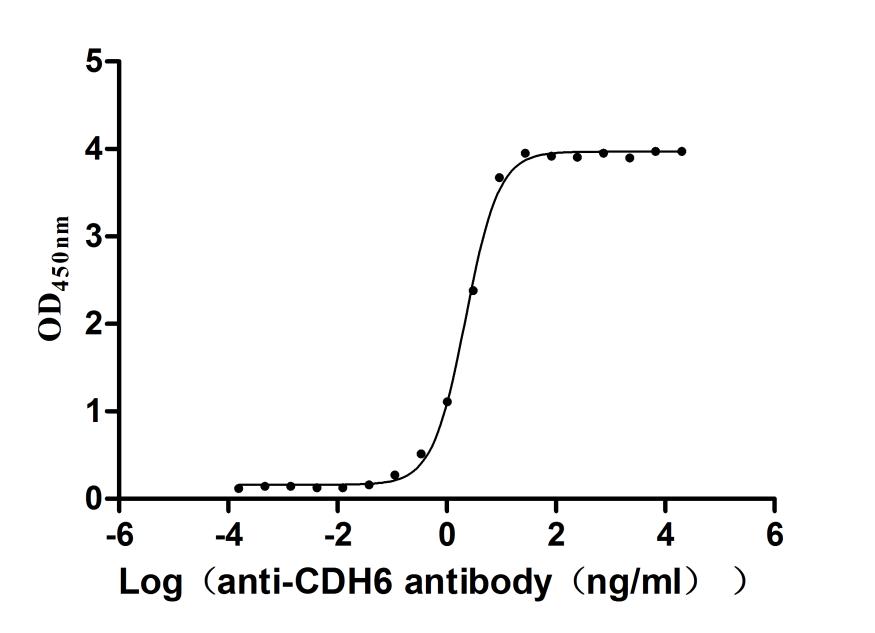
The recombinant Macaca fascicularis CDH6 protein is an active, high-purity product designed for functional studies. It is expressed in mammalian cells, ensuring proper folding and post-translational modifications. The construct includes amino acids 22 to 614 of the native CDH6 protein, with a C-terminal 10xHis tag to aid in purification and detection. This recombinant CDH6 protein is supplied as a lyophilized powder and shows greater than 95% purity, as verified by SEC-HPLC. Endotoxin levels are strictly controlled, measuring below 1.0 EU/µg, confirmed using the LAL assay. Its biological activity is validated through a functional ELISA: when immobilized at 2 μg/mL, it effectively binds the anti-CDH6 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA005055MA1HU), with an EC50 ranging between 2.076 and 2.371 ng/mL, demonstrating reliable binding performance.
The protein CDH6 is a member of the cadherin family that plays a significant role in neural development and tissue architecture. In the context of Macaca fascicularis, also known as the cynomolgus monkey, the exploration of CDH6 addresses its implications in neurogenesis and structural connectivity within the central nervous system.
Cadherins, including CDH6, are crucial for mediating cell-cell adhesion, particularly in the brain, where they facilitate the organization of neural circuits by maintaining synaptic integrity. For instance, the expression of CDH6 has been identified in specific regions of the brain associated with sensory processing, which may reflect its role in the establishment and maintenance of synaptic connections that are vital for proper sensory integration and cognitive functions [1][2]. Specifically, CDH6 expression patterns can indicate its involvement in the architectural configuration of the cerebral cortex and its connections, as observed through investigations into the neuroanatomy of primate species [2][3].
Beyond structural contributions, CDH6 is implicated in the modulation of developmental processes, which may influence behavioral outcomes. Given that Macaca fascicularis serves as a model organism for studying human neurological conditions, understanding CDH6's function may provide insights into the underlying genetic mechanisms linked to neural disorders. Research involving various cadherin family members shows that alterations in their expression can lead to dysregulation in neural development, which is pertinent to both normal and pathological states of neurodevelopment [4][5].
Furthermore, studies into gene expression across species indicate that cadherin genes, including CDH6, undergo evolutionary conservation, highlighting their fundamental role across primate species [6][7]. This reflects a broader trend within primate phylogenomics, where gene flow and adaptive evolutionary traits often underscore the relevance of certain genes in physiological adaptations and constraints [8][9].
References:
[1] L. Ramsay, M. Quillé, et al. Blood transcriptomic biomarker as a surrogate of ischemic brain gene expression. Annals of Clinical and Translational Neurology, vol. 6, no. 9, p. 1681-1695, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1002/acn3.50861
[2] L. Zhuo, M. Wang, et al. Mapbrain: a multi-omics atlas of the primate brain. Nucleic Acids Research, vol. 53, no. D1, p. D1055-D1065, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1093/nar/gkae911
[3] A. Goulas, P. Majka, M. Rosa, & C. Hilgetag. A blueprint of mammalian cortical connectomes. Plos Biology, vol. 17, no. 3, p. e2005346, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.2005346
[4] E. Takahashi, J. Saruwatari, T. Fujimoto, Y. Tanoue, T. Fukuda, & T. Inoue. The effects of exosomes derived from trabecular meshwork cells on schlemm’s canal endothelial cells. Scientific Reports, vol. 11, no. 1, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-021-01450-9
[5] E. Robertson, S. Boehnke, et al. Comparison of cerebrospinal fluid biomarkers relevant to neurodegenerative diseases in healthy cynomolgus and rhesus macaque monkeys. 2021. https://doi.org/10.1101/2021.03.01.433384
[6] N. Galtier. An approximate likelihood method reveals ancient gene flow between human, chimpanzee and gorilla. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1101/2023.07.06.547897
[7] D. Vanderpool, B. Minh, et al. Primate phylogenomics uncovers multiple rapid radiations and ancient interspecific introgression. Plos Biology, vol. 18, no. 12, p. e3000954, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pbio.3000954
[8] S. Seehase, H. Lauenstein, et al. Lps-induced lung inflammation in marmoset monkeys – an acute model for anti-inflammatory drug testing. Plos One, vol. 7, no. 8, p. e43709, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0043709
[9] S. Mariya, F. Dewi, et al. Isolation and characterization of c-c chemokine ligand 7 (ccl7) in cynomolgus macaques. Hayati Journal of Biosciences, vol. 26, no. 3, p. 129, 2019. https://doi.org/10.4308/hjb.26.3.129