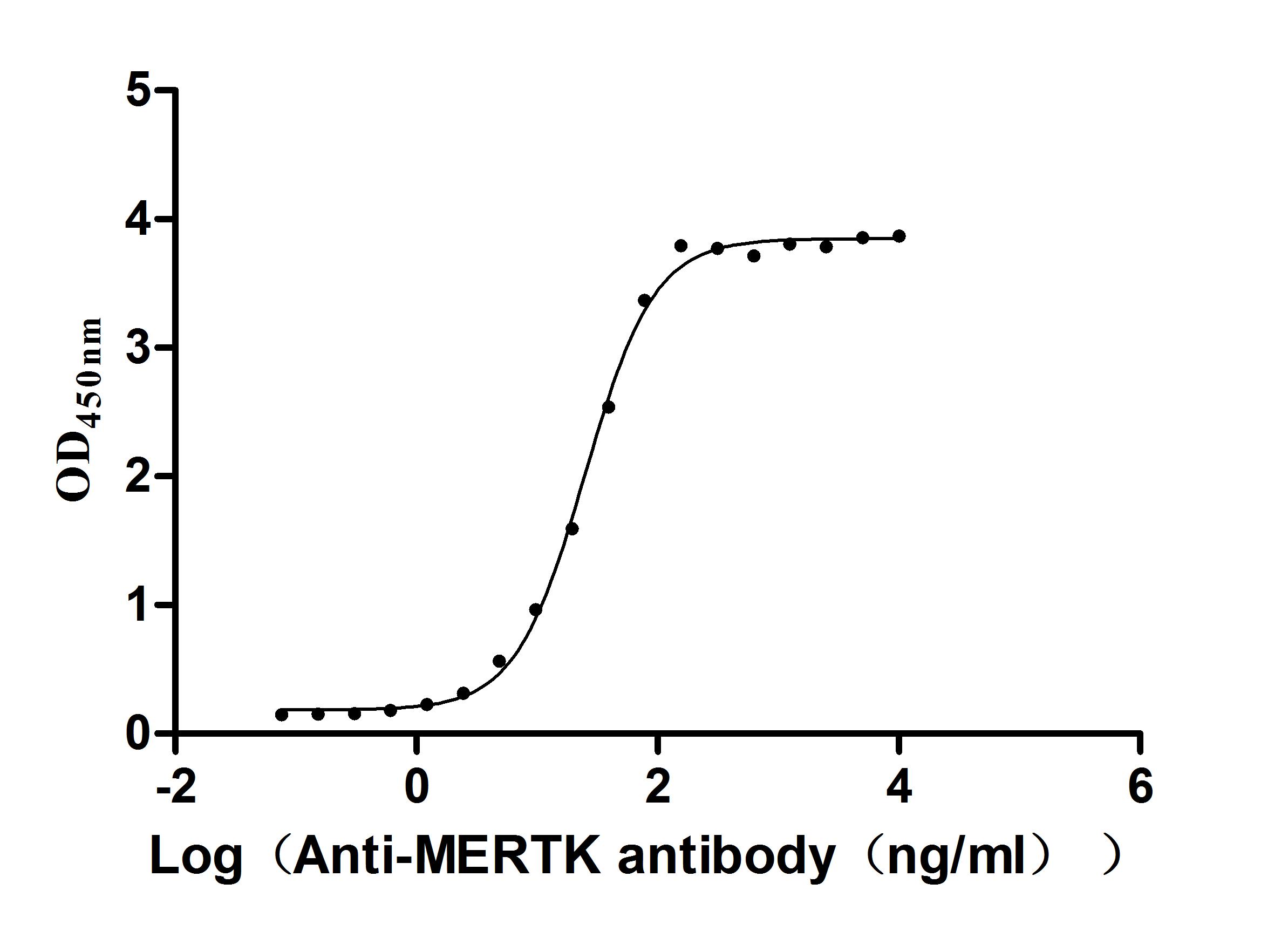
The recombinant Macaca fascicularis MERTK is expressed in mammalian cells. The expression region of the recombinant MERTK protein spans amino acids 23 to 507 of the native protein, ensuring that the functional domains necessary for activity are preserved. Additionally, the protein is tagged with a C-terminal 10xHis tag, which facilitates purification and detection processes, making it easier to isolate the protein for experimental use. The activity of the recombinant MERTK protein is assessed through its binding capability in a functional ELISA. Specifically, immobilized Cynomolgus MERTK at a concentration of 2 μg/mL demonstrates the ability to bind to an anti-MERTK recombinant antibody (CSB-RA621519A1HU). The EC50 for this binding is between 23.48 and 26.59 ng/mL, indicating a high affinity for the antibody, which is essential for its functional applications in research and therapeutic contexts.
The MERTK protein is essential in various physiological processes and plays a significant role in the immune system, with potential implications in diseases. In Macaca fascicularis, commonly known as the cynomolgus monkey, MERTK is involved in immune regulation and homeostasis, particularly in the context of apoptotic cell clearance and macrophage activation.
MERTK functions as a receptor tyrosine kinase that mediates the recognition and clearance of apoptotic cells by phagocytes, a process known as efferocytosis. This mechanism is crucial for maintaining tissue homeostasis and preventing inflammation. Studies indicate that MERTK dampens immune responses following injury or infection, potentially reducing tissue damage and promoting healing [1]. Enhanced expression of MERTK in response to apoptotic signals allows macrophages to transition from an inflammatory to a resolving phenotype, thus facilitating tissue repair [1].
In addition to its apoptotic clearance functions, MERTK is implicated in modulating immune responses. Its overexpression or aberrant signaling can lead to impaired macrophage activation, contributing to chronic inflammatory states or potentially autoimmunity. Research has shown that the regulatory pathways involving MERTK can influence the response to pathogens in non-human primates, such as cynomolgus monkeys, which may be harnessed for vaccine development or therapeutic interventions against diseases like cancer and autoimmunity [2].
Comparative studies across primate species, including Macaca fascicularis, underscore the importance of MERTK in understanding immune responses relevant to human health. This is particularly pertinent in vaccine research, where the immune profiles and responses observed in Macaca fascicularis serve as valuable models for predicting human responses to immunization [3]. The genetic and physiological resemblance between cynomolgus monkeys and humans positions MERTK as a critical focus of study in translational research.
References:
[1] B. Hart, C. Serguera, Y. Kap, & B. Gran. Non-human primates are essential models in the translational research of multiple sclerosis. Drug Discovery Today Disease Models, vol. 23, p. 35-42, 2017. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ddmod.2018.01.001
[2] F. Ling, M. Zhuo, et al. Comprehensive identification of high-frequency and co-occurring mafa-b, mafa-dqb1, and mafa-drb alleles in cynomolgus macaques of vietnamese origin. Human Immunology, vol. 73, no. 5, p. 547-553, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.humimm.2012.02.003
[3] S. Cox, S. Holt, & J. Ebersole. Characteristics of systemic antibody responses of nonhuman primates to cell envelope and cell wall antigens from periodontal pathogens. Oral Microbiology and Immunology, vol. 12, no. 4, p. 204-211, 1997. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1399-302x.1997.tb00380.x