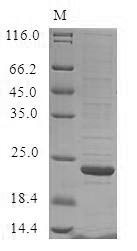
Recombinant Bovine Odorant-binding Protein is expressed in a baculovirus system and includes an N-terminal 10xHis-tag for easy purification. The protein is produced as a full-length sequence from amino acids 1 to 159 and achieves a purity level greater than 85% as determined by SDS-PAGE analysis. This product is designed for research use only and provides reliable performance in various experimental applications.
Odorant-binding proteins from Bos taurus appear to play a critical role in the olfactory system by binding and transporting volatile odor molecules. These proteins seem essential in the initial steps of odor detection and signal transduction. This makes them an intriguing subject of study in olfactory research and the broader field of sensory biology.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
The baculovirus expression system provides proper eukaryotic folding machinery, increasing the likelihood of correct folding for this soluble protein. However, odorant-binding proteins require specific conformational structures for ligand binding activity. While the full-length sequence and eukaryotic expression system suggest favorable folding prospects, the actual folding status and functional capacity for odorant binding cannot be guaranteed without experimental validation. The protein may be correctly folded but still lack activity due to subtle structural variations.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using His-Tag Pull-Down Assays
This application's validity depends entirely on correct protein folding. A properly folded odorant-binding protein could identify physiological interaction partners. However, if misfolded, it may yield non-specific binding or fail to recognize genuine partners, making data interpretation unreliable without independent structural validation.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This recombinant protein serves as an excellent immunogen for antibody production. The full-length sequence ensures comprehensive epitope coverage. Even if misfolded, it will generate antibodies against linear epitopes useful for Western blotting. If correctly folded, it may additionally produce antibodies recognizing conformational epitopes on the native protein.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Stability Studies
This application is essential for determining the protein's physical properties. Techniques like size-exclusion chromatography and circular dichroism can assess oligomeric state, folding quality, and thermal stability, providing critical data on whether the protein is correctly structured. These studies directly address the folding uncertainty and provide fundamental data needed to evaluate the protein's suitability for functional applications.
4. Comparative Protein Analysis Across Species
This protein can serve as a standardized reference for cross-species comparisons. It enables structural comparisons through techniques like Western blotting and immunological cross-reactivity studies, providing insights into evolutionary relationships within the odorant-binding protein family.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
The unknown folding status necessitates a sequential validation approach. The immediate priority should be Application 3 (Biochemical Characterization) to assess protein folding and stability through biophysical methods. If the protein demonstrates proper folding, it may be considered for Application 1 (Interaction Studies) with appropriate controls. Regardless of folding results, Applications 2 and 4 (Antibody Development and Comparative Analysis) can proceed confidently as they don't require functional validation. A functional odorant-binding assay should be conducted after confirming proper folding to fully characterize the protein's capabilities. This systematic approach ensures reliable data interpretation and appropriate resource allocation.