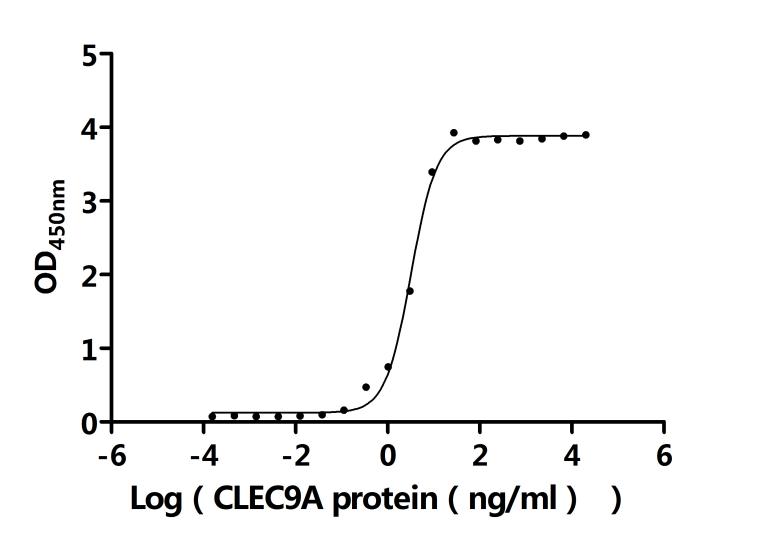
The recombinant human CLEC9A protein is a biologically active, biotinylated molecule expressed in mammalian cells to ensure native folding and post-translational modifications. It comprises amino acids 57 to 241 of the CLEC9A sequence, representing its extracellular domain. The recombinant CLEC9A protein is engineered with an N-terminal hFc-Avi tag, allowing site-specific biotinylation and compatibility with avidin-based assays. Supplied as a lyophilized powder, this CLEC9A protein maintains a purity greater than 90% as verified by SDS-PAGE, and its endotoxin content is controlled to be below 1.0 EU/μg, as assessed by the LAL method. Functional ELISA testing confirms its activity. The anti-CLEC9A recombinant antibody (CSB-RA740922MA1HU) can bind to this biotinylated CLEC9A, with an EC50 between 2.915 and 3.520 ng/mL. These features make it a dependable reagent for use in receptor-ligand binding studies, antibody screening, and dendritic cell research.
Human CLEC9A is a significant receptor predominantly expressed on dendritic cells (DCs), particularly on BDCA3+ myeloid dendritic cells. This protein plays a crucial role in the immune system, specifically in antigen uptake and cross-presentation, which are essential for initiating immune responses against pathogens and tumors.
CLEC9A is known for its ability to recognize and bind necrotic or apoptotic cellular material, which aids in antigen processing [1]. This functionality is conserved across species, indicating evolutionary importance in immune responses [1]. When targeted appropriately, CLEC9A enhances the activation of both CD4+ and CD8+ T cells, further contributing to the adaptive immune response. Specifically, activation of CLEC9A primes T follicular helper cells, which are vital for inducing robust antibody responses even in the absence of adjuvants [2]. Such unique capabilities render CLEC9A an attractive target for cancer immunotherapy, as its engagement can lead to enhanced antitumor immunity [1][3].
The mechanisms of CLEC9A's action involve the uptake of antigens and their subsequent cross-presentation on major histocompatibility complex (MHC) molecules, a process critical for T cell activation [3]. The receptor is particularly noted for its role in improving both class I and class II MHC presentations, making it instrumental in inducing diverse T cell responses [2][3]. In the context of dendritic cells, CLEC9A is typically expressed at higher levels on immature dendritic cells, while its expression is downregulated during maturation, suggesting a sophisticated regulatory mechanism that guides immune activation [3].
References:
[1] I. Caminschi, E. Maraskovsky, & W. Heath. Targeting dendritic cells in vivo for cancer therapy. Frontiers in Immunology, vol. 3, 2012. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2012.00013
[2] K. Tullett, P. Tan, et al. Rnf41 regulates the damage recognition receptor clec9a and antigen cross-presentation in mouse dendritic cells. Elife, vol. 9, 2020. https://doi.org/10.7554/elife.63452
[3] G. Schreibelt, L. Klinkenberg, et al. The c-type lectin receptor clec9a mediates antigen uptake and (cross-)presentation by human blood bdca3+ myeloid dendritic cells. Blood, vol. 119, no. 10, p. 2284-2292, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1182/blood-2011-08-373944