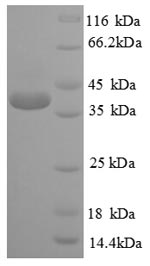
The recombinant Human CREB1 was expressed with the amino acid range of 1-341. The expected molecular weight for the CREB1 protein is calculated to be 40.7 kDa. This CREB1 recombinant protein is manufactured in e.coli. The CREB1 gene fragment has been modified by fusing the N-terminal 6xHis tag, providing convenience in detecting and purifying the recombinant CREB1 protein during the following stages.
Human cyclic AMP-responsive element-binding protein 1 (CREB1) is a transcription factor that plays a crucial role in various cellular processes. Upon activation by signaling pathways such as cAMP-dependent pathways, CREB1 undergoes phosphorylation, leading to its binding to cAMP response elements (CREs) in target gene promoters. CREB1 regulates the transcription of genes involved in cell growth, differentiation, survival, and memory formation. Its diverse functions contribute to cellular responses in the nervous system, immune system, and other tissues. Research on CREB1 spans areas such as neurobiology, cancer, metabolism, and circadian rhythms. Understanding CREB1's intricate regulatory role provides insights into fundamental cellular processes and potential therapeutic targets for various diseases.