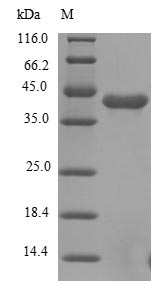
The gene responsible for the Human FGFR1 protein (22-376aa) is incorporated into a plasmid vector, forming recombinant plasmid. The resulting recombinant plasmid is introduced into e.coli cells, from which cells survive in the presence of a specific antibiotic are selected. The selected e.coli cells containing the recombinant plasmid are cultured under conditions that facilitate the expression of the gene of interest. A N-terminal 6xHis tag is linked to the protein. After expression, affinity purification is used to isolate and purify the recombinant Human FGFR1 protein from the cell lysate. Denaturing SDS-PAGE is employed to resolve the resulting recombinant Human FGFR1 protein, revealing a purity greater than 85%.