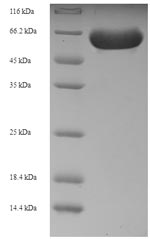
Like all recombinant proteins, this Recombinant Human RIPK2 protein was encoded by recombinant DNA. The recombinant DNA was introduced to a plasmid in which the gene of RIPK2 was cloned downstream of a promoter region. When the plasmid was introduced to the cells of E.coli, the E.coli’s own protein synthesis pathways would then result in the expression of the RIPK2 protein. And the next step was protein purification. The purity of this recombinant protein is 90%+ determined by SDS-PAGE.
Receptor-interacting serine/threonine kinase 2 (RIPK2), also known as receptor-interacting protein 2 (RIP2), is a signaling molecule downstream of NOD2 and ATG16L1. Recent studies have provided evidence that excessive activation of RIPK2 is involved in the development of experimental and human bowel diseases. RIPK2 is expressed in antigen-presenting cells, such as dendritic cells and macrophages. Recognition of microbe-associated molecular patterns by NOD1, NOD2, and TLRs leads to the interaction between RIPK2 and these innate immune receptors, followed by the release of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-12/23p40 through the activation of nuclear factor kappa B and mitogen-activated protein kinases. Thus, activation of RIPK2 plays a critical role in host defense against microbial infections. Recent experimental and clinical studies have provided evidence that activation of RIPK2 is involved in the development of autoimmune diseases, especially bowel diseases. In addition, the colonic mucosa of patients with bowel diseases exhibits enhanced expression of RIPK2 and associated signaling molecules. Furthermore, the blockage of RIPK2 activation ameliorates the development of experimental murine colitis. Thus, activation of RIPK2 underlies bowel diseases immunopathogenesis.