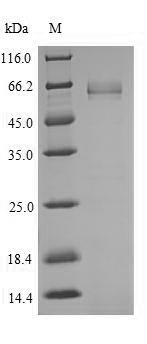
Recombinant Human Transcription factor 7-like 2 (TCF7L2) is produced in an E.coli expression system, covering amino acids 1-456 of the protein. This partial length protein carries an N-terminal 6xHis-tag for easier purification and detection. The product reaches greater than 90% purity as confirmed by SDS-PAGE, which appears to ensure reliable research applications. Endotoxin levels are kept low to support sensitive experimental conditions.
TCF7L2 represents a crucial transcription factor in the Wnt signaling pathway. It plays a significant role in regulating gene expression tied to cell proliferation and differentiation. Research interest in this protein stems largely from its function in modulating various biological processes. As a key component in cellular signaling, TCF7L2 is often studied to understand how it influences development and disease progression.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
The human TCF7L2 is a transcription factor that requires proper folding of its DNA-binding domain (HMG box) and β-catenin interaction domains for functionality. While the expressed region (1-456aa) contains the N-terminal β-catenin binding domain, it may lack critical C-terminal regulatory regions. E. coli expression often fails to properly fold complex eukaryotic transcription factors due to the absence of chaperones and post-translational modifications. His tag may cause relatively minor interference. Still, without experimental validation (e.g., electrophoretic mobility shift assays for DNA binding or β-catenin interaction assays), the protein cannot be assumed to be correctly folded or bioactive.
1. Protein-Protein Interaction Studies Using His-Tag Pull-Down Assays
The His tag enables pull-down assays to screen for binding partners like β-catenin. However, if TCF7L2 is misfolded, interactions may be non-physiological. The partial sequence (1-456aa) lacks the C-terminal domain, which may affect interactions with some co-regulators. Validate any identified interactions using full-length TCF7L2 from eukaryotic expression systems.
2. Antibody Development and Validation
This application is suitable. The recombinant protein can serve as an immunogen for generating antibodies against linear epitopes within the 1-456aa region. The high purity supports consistent immunization. However, antibodies may not recognize conformational epitopes of full-length, properly folded TCF7L2. Validate antibody specificity against endogenous TCF7L2 in human cell lysates.
3. Biochemical Characterization and Stability Studies
This recombinant human TCF7L2 is suitable for basic biophysical analysis (e.g., circular dichroism for secondary structure, dynamic light scattering for aggregation state). However, data may not reflect full-length TCF7L2 properties due to the truncated sequence and potential misfolding. Use the protein for stability studies, but interpret results in the context of the partial sequence.
4. In Vitro Transcriptional Complex Assembly Studies
This application is not recommended without confirmed bioactivity. The partial TCF7L2 (1-456aa) may lack domains needed for full transcriptional complex assembly. If misfolded, it will not bind DNA or β-catenin properly. Use full-length, functionally validated TCF7L2 for transcriptional studies.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
Before using this recombinant TCF7L2 for functional studies, validate its folding and DNA-binding capability. Start with electrophoretic mobility shift assays (EMSA) using a known TCF7L2 DNA target sequence. If DNA binding is confirmed, test β-catenin interaction via co-immunoprecipitation. If active, proceed with limited interaction studies; if inactive, reserve for antibody production or biochemical characterization. For reliable transcriptional studies, use full-length TCF7L2 expressed in eukaryotic systems. Always include appropriate controls (e.g., full-length protein) when possible.