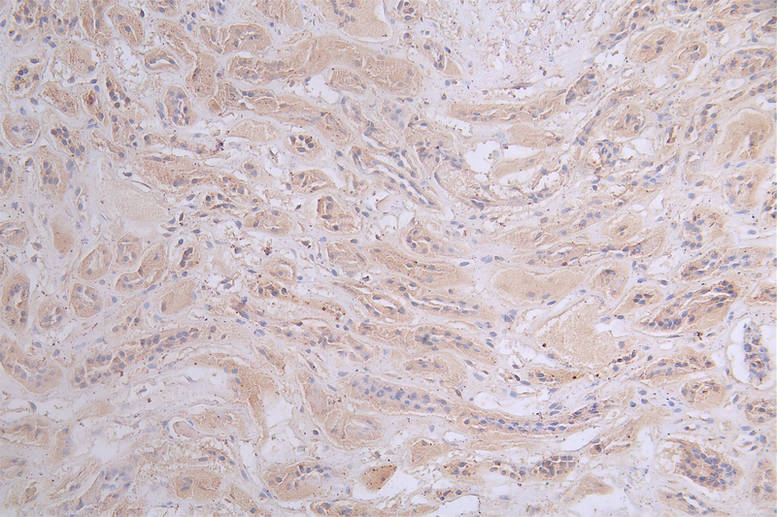
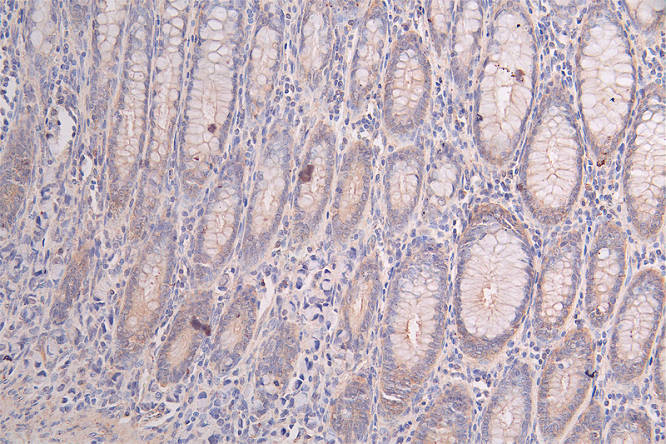
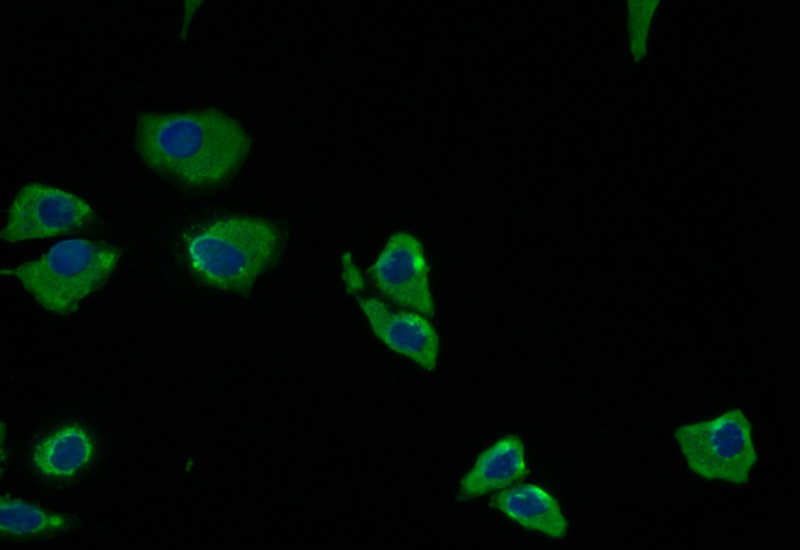
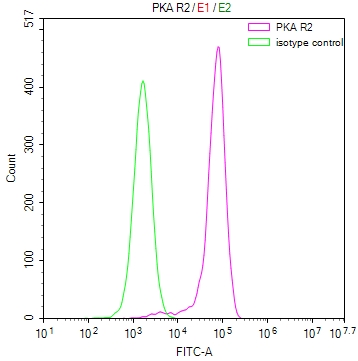
The PRKAR2A recombinant monoclonal antibody is created using in vitro expression systems, which are established by cloning the DNA sequences of PRKAR2A antibodies obtained from immunoreactive rabbits. The immunogen used in this process is a synthesized peptide derived from the human PRKAR2A protein. Subsequently, the genes encoding the PRKAR2A antibodies are inserted into plasmid vectors, and these recombinant plasmid vectors are transfected into host cells to facilitate antibody expression. The PRKAR2A recombinant monoclonal antibody then undergoes affinity-chromatography purification and is thoroughly tested for functionality in ELISA, IHC, IF, and FC applications, confirming its reactivity with the human PRKAR2A protein.
PRKAR2A is a regulatory subunit of PKA, a key enzyme involved in the cAMP signaling pathway. Through its role in regulating PKA activity, PRKAR2A influences a wide range of cellular processes, including metabolism, cell signaling, gene expression, and neurotransmitter release.