Interleukin-6 (IL-6) is a cytokine with diverse biological activities, involved in immune regulation and inflammatory responses [1]. Research into IL-6's properties and its role in diseases is crucial for developing new treatments. This article covers IL-6's background, mechanisms, signaling pathways, associated diseases, and recent drug research.
1. Sources and Classification of IL-6
Initially identified as a B cell stimulator, IL-6 is now known to affect various immune cells. It belongs to the β-helix cytokine family, with its gene located on human chromosome 7p21, encoding a precursor protein of 184 – 212 amino acids that is cleaved to form the active mature protein.
IL-6 is produced by multiple lymphoid and non-lymphoid cells, such as T and B lymphocytes, macrophages, monocytes, dendritic cells, and mast cells. Additionally, fibroblasts, epithelial cells, keratinocytes, and various tumor cells can produce IL-6. In healthy individuals, blood IL-6 levels are very low (about 1 – 5pg/mL), but during inflammation, levels can surge to μg/mL, as seen in sepsis patients. Elevated IL-6 levels are also found in autoimmune diseases like rheumatoid arthritis (RA), Crohn's disease, and systemic lupus erythematosus.
2. Mechanisms of IL-6
IL-6 gene transcription is activated in response to infections, tissue damage, or immune signals. NF-κB and STAT3 are key transcription factors regulating IL-6 expression and play vital roles in inflammation and stress.
Different cellular sources of IL-6 have distinct functions. Macrophage-derived IL-6 initiates innate immune responses and recruits immune cells to inflamed sites. T lymphocyte-derived IL-6 is more involved in adaptive immune regulation, such as T helper cell differentiation and B cell antibody production. For example, in the early stages of viral infection, macrophage-produced IL-6 activates natural killer cells; as the infection progresses, T lymphocyte-secreted IL-6 promotes Th17 cell differentiation, which recruits neutrophils to eliminate pathogens.
3. IL-6-Related Signaling Pathways
IL-6 exerts its functions by binding to the IL-6 receptor (IL-6R), which has membrane-bound and soluble forms. After IL-6 binds to IL-6R, it forms a complex with gp130 to activate intracellular signaling pathways, including JAK/STAT, MAPK, and PI3K/Akt. These pathways alter gene expression, affecting cell proliferation, differentiation, and survival.
3.1 JAK/STAT3 Pathway
Upon IL-6 activation, STAT3 phosphorylation occurs. Phosphorylated STAT3 enters the nucleus, binds to target gene promoters, and regulates gene expression, influencing cell proliferation and immune responses [2]. In cancer cells, sustained JAK/STAT3 activation promotes proliferation, survival, and immune evasion, facilitating tumor growth and metastasis [3].
3.2 SHP2-MAPK/NF-κB Pathway
Activation of this pathway enhances pro-inflammatory and pro-survival signaling. In immune cells, it increases secretion of inflammatory mediators like TNF-α and IL-1β, amplifying inflammation. In cancer cells, it boosts survival and migration capabilities.
4. IL-6-Related Diseases
4.1 Autoimmune Diseases
IL-6 is linked to various autoimmune diseases. In RA patients, IL-6 activates JAK/STAT and MAPK pathways, promoting synovial inflammation and bone destruction. Elevated soluble IL-6R (sIL-6R) exacerbates trans-signaling and chronic inflammation. IL-6 also promotes osteoclast formation, accelerating joint damage [4]. In Crohn's disease, abnormal IL-6 expression recruits immune cells to the gut, releasing inflammatory mediators and worsening intestinal damage. Inhibiting IL-6 signaling alleviates gut inflammation in animal models. In systemic lupus erythematosus, IL-6 promotes autoantibody production, activates B and T cells, and disrupts Th17/Treg balance, intensifying inflammation. Serum IL-6 levels in patients correlate with disease severity.
4.2 Cancer
IL-6 plays a key role in cancer development. By activating the JAK/STAT3 pathway, it promotes cancer cell proliferation, survival, and immune evasion [5]. In multiple myeloma, IL-6 drives plasma cell proliferation, is associated with advanced disease and poor prognosis, and forms a positive feedback loop with bone marrow microenvironment cells. In ovarian cancer, IL-6 creates a pro-tumor microenvironment via trans-signaling, suppresses chemosensitivity, and regulates cell migration and epithelial-mesenchymal transition, promoting metastasis. Ovarian cancer patients' ascites IL-6 levels correlate with tumor stage and prognosis.
4.3 Other Diseases
IL-6 is involved in many diseases. In cardiovascular diseases, elevated IL-6 levels are associated with poor outcomes like acute myocardial infarction and atherosclerosis [6]. In neurodegenerative diseases, Alzheimer's and Parkinson's patients have increased brain IL-6, which activates microglia and加剧s neuroinflammation and neuron damage. In viral infections, IL-6 participates in immune responses but may trigger cytokine storms in severe COVID-19 cases [7]. IL-6 also contributes to obesity and diabetes by regulating immune cell functions and inflammation.
5. Drug Development Targeting IL-6
IL-6 and its signaling pathways are major drug development targets. Siltuximab is used for multicentric Castleman disease and is being explored for multiple myeloma and cytokine release syndrome prevention. Olokizumab shows promise in early rheumatoid arthritis trials, with Phase III results indicating efficacy and safety comparable to adalimumab, and is now in the approval process. Small-molecule JAK inhibitors suppress downstream IL-6 signaling, offering anti-inflammatory and anti-tumor effects. New drug strategies, such as RNA interference and microRNA regulation, are under investigation. The indications for IL-6 inhibitors are expanding, with combination therapies like "immunotherapy + cytokine regulation" emerging and drug delivery methods being optimized.
Below is a summary of some IL-6 monoclonal antibody pipelines as of April 23, 2025:
| Drug |
Target |
Indication |
Organization |
Highest Development Phase |
| Stuximab |
IL6 |
Multicentric Castleman disease | Chronic pain | Schwannomatosis | Immunoglobulin light chain amyloidosis | Multiple myeloma | Metastatic pancreatic cancer | Metastatic pancreatic adenocarcinoma | Mental disorders | Schizophrenia | Large granular lymphocytic leukemia |
Recordati AG | Augusta University Research Institute | Janssen Scientific Affairs LLC | Novartis AG | Recordati Rare Diseases | EUSA Pharma, Inc. | Recordati SpA | Recordati |
Approved for listing |
| Olokizumab |
IL6 |
Rheumatoid arthritis | Novel Coronavirus Infection | Progressive fibrosis and interstitial lung disease |
R-Pharm International, LLC | R-Pharm JSC | R-Pharm Overseas, Inc. |
Application for listing |
| RO-7200220 |
IL6 |
Uveitis macular edema | Diabetic macular edema |
F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. | Genentech, Inc. | Roche (China) Investment Co., Ltd | Hoffmann-La Roche, Inc. | Roche Holding AG |
Phase 3 clinical trial |
| Ziltivekimab |
IL6 |
Acute myocardial infarction | Acute decompensated heart failure | Chronic heart failure | Chronic kidney disease | Inflammation | Peripheral arterial disease | Rheumatoid arthritis | Kidney disease | Stroke |
Novo Nordisk A/S | Novo Nordisk Pharmaceuticals Pty Ltd. | Novo Nordisk (China) Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd |
Phase 3 clinical trial |
| Clazakizumab |
IL6 |
Myocardial infarction | Atherosclerosis | End-stage renal disease |
CSL Behring LLC |
Phase 2/3 clinical trial |
| FB-704A |
IL6 |
Severe asthma | Asthma | Chronic kidney disease |
Hop Biotech Co., Ltd. | Zhongtian (Shanghai) Biotechnology Co., Ltd |
Phase 2 clinical trial |
| Pacibekitug |
IL6 |
Chronic kidney disease | Graves' ophthalmopathy | Atherosclerosis | Abdominal aortic aneurysm |
Tourmaline Bio, Inc. |
Phase 2 clinical trial |
| Gerilimzumab |
IL6 |
Rheumatoid arthritis | inflammation |
argenx SE | arGENX BV | Genor Biopharma Company Limited |
Phase 2 clinical trial |
| EBI-031 |
IL6 |
Diabetic macular edema | uveitis |
Sesen Bio, Inc. | F. Hoffmann-La Roche Ltd. |
Phase 1 clinical trial |
| MEDI-5117 |
IL6 |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
WuXi Likang Biopharmaceutical Co., Ltd |
Phase 1 clinical trial |
| C14mab |
IL6 |
Autoimmune diseases |
National Taiwan University |
Preclinical |
| HZ-0408b |
IL6 |
Rheumatoid arthritis |
Huizhi Heyuan Biotechnology (Suzhou) Co., Ltd |
Preclinical |
6. Related Product Recommendations
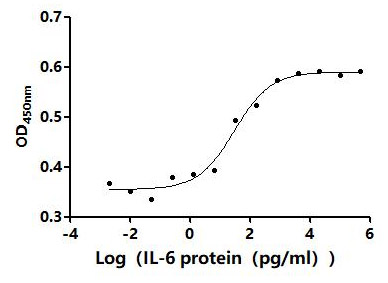
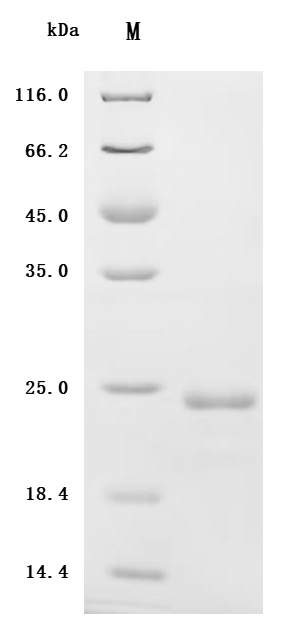
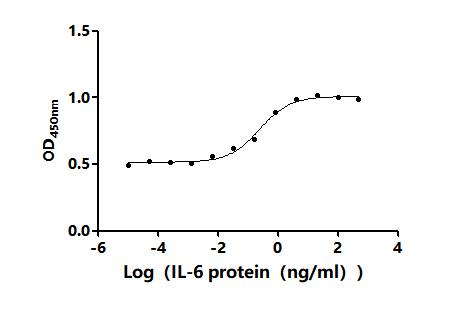
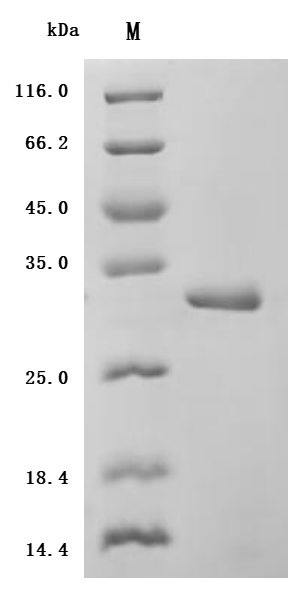
IL-6 plays a key role in immune regulation, inflammatory response, and disease progression as a multifunctional cytokine. A better understanding of the biology of IL-6 and its mechanism of action in diseases is of great significance for the development of new therapeutic strategies and drugs. CUSABIO has launched a variety of highly active IL6 recombinant protein products, and provides IL6 antibody and ELISA kit products to help you research the IL6 mechanism or explore its potential clinical value.
● IL6 Recombinant Proteins
References
[1] Kawai, Taro, and Shizuo Akira. et al. The Innate Immune System and Adjuvant Action of Toll-like Receptors. Journal of Immunology, vol. 184, no. 6, 2010, pp. 3163-3168.
[2] Yu Jin1, Yalin Kang, Wei Wang. et al. Targeting Polarized Phenotype of Microglia via IL6/JAK2/STAT3 Signaling to Reduce NSCLC Brain Metastasis. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2022.
[3] Siersbæk, R., Scabia, V., Nagarajan, S., et al. IL6/STAT3 Signaling Hijacks Estrogen Receptor α Enhancers to Drive Breast Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Cell, 2020, 38(3), 412–423.e9.
[4] S. A. Habib1 , M. M. Kamal1 , M. Senousy. et al. Exendin-4 enhances osteogenic differentiation of adipose tissue mesenchymal stem cells through the receptor activator of nuclear factor-kappa B and osteoprotegerin signaling pathway. 2022.
[5] Zhang, X., Wang, Y., Liu, Q., et al. IL6 pretreatment overcomes chemoresistance in lung adenocarcinoma by promoting quiescent cancer stem cells to enter the cell cycle. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research, 40(1), 1-12.
[6] Ziegler, L., Wallen, H., Aspberg, S.et al. IL6 trans-signalling associates with atherothrombotic but not with cardioembolic stroke. European Heart Journal, 41(Supplement_2), ehaa946.
[7] Juni RP, Phelp PG, Bink DI, et al. COVID-19 Impairs Cardiac Function via Endothelial H19 and IL6 Signaling. Circulation Research. 2023;132(6):648-651.
CUSABIO team. IL-6: A Central Factor in Cytokine Storms and a Health Alert for Infections and Diseases. https://www.cusabio.com/c-21218.html




Comments
Leave a Comment