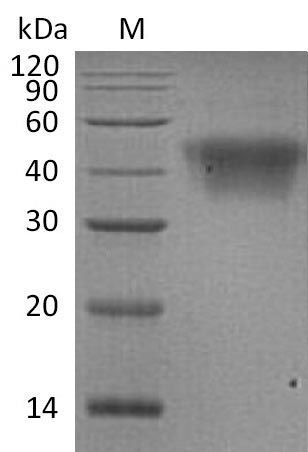
Recombinant Human Low affinity immunoglobulin gamma Fc region receptor III-A (FCGR3A) is produced in mammalian cells, which appears to help ensure proper folding and post-translational modifications. The extracellular domain spans amino acids 17-208 and comes with a C-terminal 6xHis tag for purification. This protein achieves purity levels above 95% when analyzed by SDS-PAGE. Endotoxin levels stay below 1.0 EU/µg. The protein shows biological activity by binding human CD16a-His (V176) with a 0.571 µM affinity constant in BLI assays.
FCGR3A, which researchers also call CD16a, acts as a receptor for the Fc region of immunoglobulin G (IgG). It plays what seems to be a critical role in antibody-dependent cellular cytotoxicity (ADCC). Natural killer (NK) cells express this receptor primarily, though macrophages and some T-cell subsets also show expression. The receptor appears crucial for mediating immune responses. Understanding how FCGR3A works and interacts with other molecules may prove important for research into immunological pathways and therapeutic antibody development.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. IgG-Fc Receptor Binding Affinity Studies
This recombinant FCGR3A extracellular domain is confirmed to bind IgG1 Fc with an affinity of 0.571 μM and is suitable for studying interactions with various IgG subclasses. However, the low affinity (micromolar range) may require sensitive detection methods in binding assays. The mammalian expression ensures proper glycosylation for authentic interactions, but researchers should validate that the C-terminal His-tag does not sterically hinder binding in specific assay formats, such as SPR or BLI.
2. Antibody-Dependent Cellular Cytotoxicity (ADCC) Mechanism Research
The protein is appropriate for studying the initial binding step in ADCC, such as antibody-receptor interactions, but it cannot model full ADCC responses that require cellular signaling via transmembrane and intracellular domains. Researchers can use it in cell-free assays to screen antibodies for Fc binding, but results should be validated in cellular assays with full-length FCGR3A expressed on NK cells.
3. Fc Receptor Competitive Binding Assays
This protein is suitable for competitive binding assays to screen antibody variants or inhibitors. The His-tag facilitates immobilization, and the measured affinity provides a baseline. However, the soluble extracellular domain may exhibit different binding kinetics compared to membrane-bound FCGR3A, and hits should be validated in cellular contexts to ensure physiological relevance.
4. Structural Biology and Protein-Protein Interaction Studies
The extracellular domain is valuable for structural studies, but the C-terminal His-tag may need removal for crystallization to avoid interference. Mammalian glycosylation ensures native-like structure but may complicate crystallization; researchers might consider deglycosylation or tag cleavage. The protein can be used for co-crystallization with IgG Fc to study binding interfaces.
5. Fc Engineering and Antibody Optimization Research
This recombinant FCGR3A is well-suited for Fc engineering studies, providing a standardized, glycosylated domain for testing antibody binding affinity. The known affinity allows comparison of engineered antibodies. However, researchers should validate binding improvements in cellular assays with full-length receptor to confirm enhanced ADCC potential.
Final Recommendation & Action Plan
This mammalian-expressed human FCGR3A extracellular domain with C-terminal His-tag is a validated tool for in vitro Fc binding studies, demonstrating specific interaction with IgG1 Fc at 0.571 μM affinity. Prioritize its use in binding kinetics, competitive assays, and antibody screening, but acknowledge that the soluble domain may not fully replicate membrane-bound receptor behavior. For structural work, consider tag removal to avoid crystallization artifacts. When studying ADCC mechanisms, use this protein for initial binding steps, but complement with cellular models for full validation. Always include controls for tag-related effects and validate key findings in physiological systems expressing full-length FCGR3A. The high purity and low endotoxin support reliable results, but the low affinity requires sensitive detection methods.