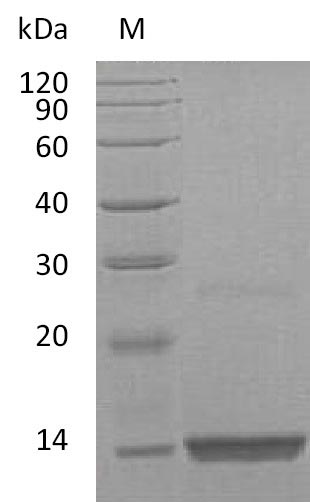
Recombinant Human Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 (FGF9) is produced in E. coli and represents the full-length protein, comprising amino acids 1-208. This tag-free preparation achieves a purity level exceeding 95% as confirmed by SDS-PAGE analysis. The protein demonstrates biological activity, with an effective dose (ED50) ranging from 1 to 5 ng/ml in a cell proliferation assay using Balb/3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells. Endotoxin levels remain below 1.0 EU/µg, as determined by the LAL method.
Fibroblast Growth Factor 9 (FGF9) stands out as an important member of the fibroblast growth factor family. This protein appears to play a significant role in cellular processes such as proliferation and differentiation. FGF9 seems to be involved in various developmental pathways and may be essential for embryonic development, tissue repair, and angiogenesis. Given its apparent importance in these processes, FGF9 has become a key protein of interest in research focused on developmental biology and regenerative medicine.
Potential Applications
Note: The applications listed below are based on what we know about this protein's biological functions, published research, and experience from experts in the field. However, we haven't fully tested all of these applications ourselves yet. We'd recommend running some preliminary tests first to make sure they work for your specific research goals.
1. Cell Proliferation and Growth Factor Signaling Studies
This recombinant FGF9 protein can be used to investigate fibroblast growth factor signaling pathways in various cell types. Its demonstrated biological activity with an ED50 of 1-5 ng/ml in Balb/3T3 mouse embryonic fibroblast cells provides researchers with a reliable tool for studying dose-response relationships, downstream signaling cascades, and receptor binding kinetics in controlled in vitro environments. The high purity (>95%) and low endotoxin levels make it particularly suitable for sensitive cell culture experiments where contamination could easily confound results.
2. FGF Receptor Binding and Interaction Studies
The biologically active FGF9 protein can serve as a ligand in receptor binding assays to characterize interactions with FGF receptors (FGFRs) and co-receptors such as heparan sulfate proteoglycans. Researchers might apply this protein in surface plasmon resonance, isothermal titration calorimetry, or competitive binding assays to determine binding affinities and kinetic parameters. The tag-free nature of this protein eliminates potential interference from fusion tags that could affect native protein-receptor interactions.
3. Antibody Development and Validation
This high-purity, tag-free FGF9 protein can be used as an antigen for generating specific antibodies against human FGF9 or for validating existing antibodies in research applications. The protein may serve as a positive control in immunoassays, Western blotting, and ELISA development to help ensure antibody specificity and sensitivity. The demonstrated biological activity confirms proper protein folding, which appears crucial for generating antibodies that recognize native FGF9 conformations.
4. Comparative Species and Isoform Studies
Researchers can use this human FGF9 protein in comparative studies to examine what seem to be species-specific differences in FGF9 function by testing its activity across different cell lines from various species. Scientists might also apply the protein in structure-function relationship studies when compared with other FGF family members or FGF9 variants. The standardized activity testing method using Balb/3T3 cells provides a consistent benchmark for comparing biological activities across different experimental conditions.
5. Protein Crystallization and Structural Biology Research
The high purity and tag-free nature of this FGF9 protein make it suitable for structural biology applications, including protein crystallization trials and NMR spectroscopy studies. Researchers can use this protein to investigate the three-dimensional structure of FGF9, either alone or in complex with receptors or other binding partners. The confirmed biological activity suggests proper protein folding, which is likely essential for obtaining meaningful structural data that reflects the native protein conformation.