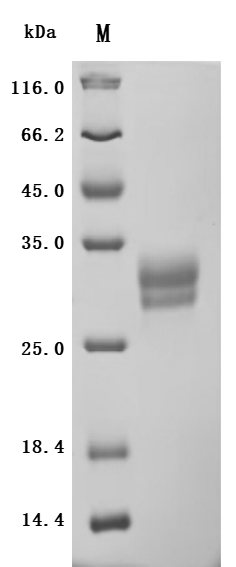
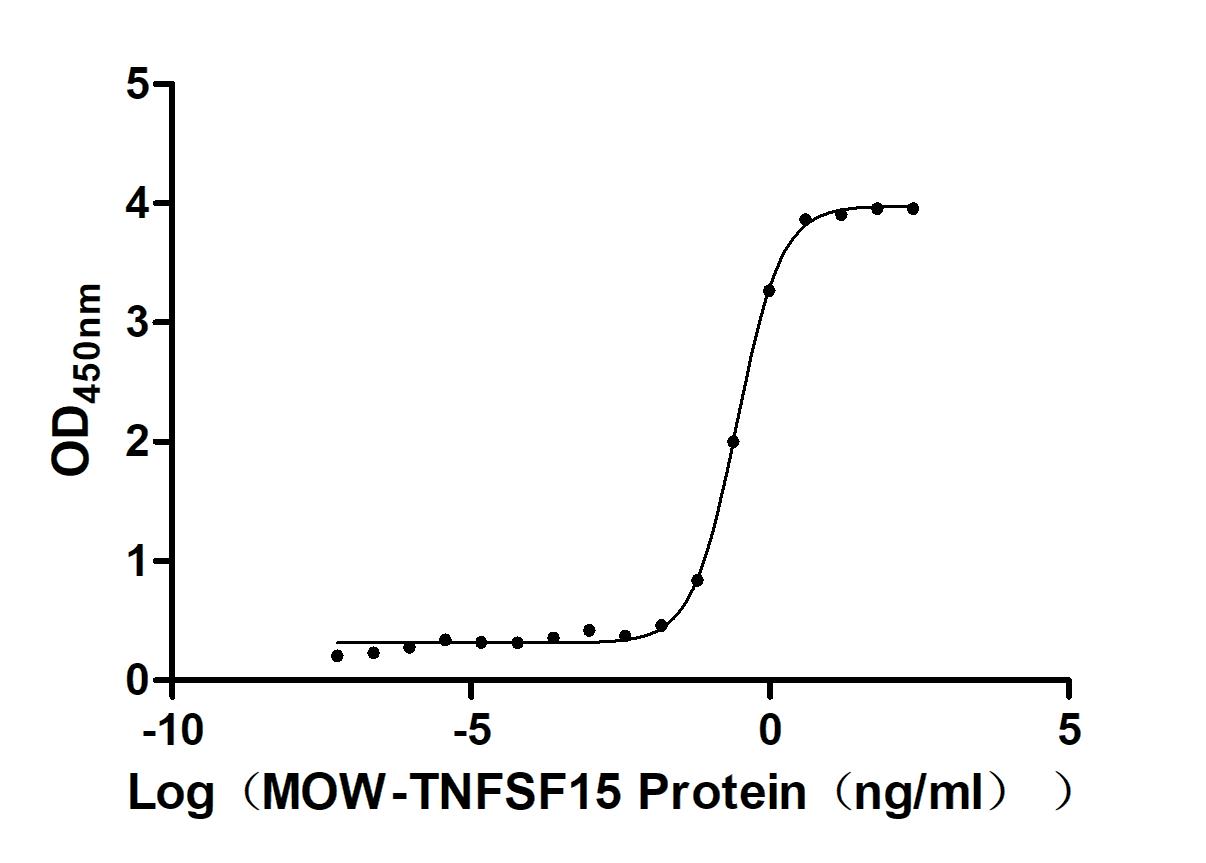
The recombinant Macaca fascicularis TNFSF15 protein is a biologically active, biotinylated construct produced in a mammalian expression system to ensure proper folding and post-translational modification. It consists of amino acids 72 to 251 of the TNFSF15 protein and includes an N-terminal 10xHis-Avi tag to support efficient purification and site-specific biotinylation. Supplied as a lyophilized powder, the recombinant TNFSF15 protein demonstrates high purity, exceeding 95% as confirmed by SDS-PAGE. Endotoxin content is strictly regulated, measuring below 1.0 EU/μg by the LAL assay. Functional validation in a binding ELISA shows that biotinylated TNFSF15 binds specifically to immobilized anti-TNFSF15 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA023992MA1HU) at 2 μg/mL, with an EC50 ranging from 0.2589 to 0.3025 ng/mL. These attributes make it a dependable reagent for studying TNFSF15-related signaling, immune response pathways, and therapeutic antibody interactions.
The TNFSF15 protein plays a significant role in various biological processes in Macaca fascicularis, specifically concerning angiogenesis, immune modulation, and cellular apoptosis. TNFSF15 is primarily expressed by endothelial cells and functions as a crucial regulator of vascular homeostasis and inflammatory responses.
One of the key functions of TNFSF15 is its ability to modulate angiogenesis. Studies have shown that TNFSF15 acts as an endogenous inhibitor of neovascularization, thus maintaining vascular stability. This is particularly important in conditions where abnormal vascular growth could be harmful, such as in tumors or diabetic retinopathy [1][2]. For instance, TNFSF15 inhibits the proliferation of endothelial cells while inducing apoptosis in rapidly proliferating cells, a mechanism essential for proper vascular remodeling during angiogenesis [1][2]. Furthermore, TNFSF15 facilitates the differentiation and polarization of macrophages towards the M1 phenotype, enhancing their capacity to inhibit tumor growth and modulate immune responses [3].
Additionally, TNFSF15 has been implicated in the regulation of lymphangiogenesis by upregulating VEGFR3 gene expression in lymphatic endothelial cells [4]. The interaction of TNFSF15 with various signaling pathways, including those mediated by STAT transcription factors, highlights its relevance in both promoting inflammatory responses and acting as a tumor suppressor [5]. LITAF, in particular, is recognized for its role in the pro-inflammatory signaling cascade and has been noted to exert inhibitory effects on tumor growth in conjunction with TNFSF15 [5].
Moreover, TNFSF15 demonstrates protective qualities against conditions such as diabetic retinopathy by inhibiting breakdown of the blood-retinal barrier, which is critical for maintaining retinal health. This protective mechanism involves the preservation of tight junction proteins within retinal endothelial cells, showcasing TNFSF15's potential as a therapeutic target in diabetic conditions [6].
In terms of its genetic underpinnings, the variability within the TNFSF15 gene, particularly polymorphisms like rs4979462, has been linked to altered expression levels and susceptibility to various diseases, including inflammatory bowel diseases and certain cancers, indicating its influence on the immune system [7][8]. The expression and function of TNFSF15 thus exemplify its multifaceted role in modulating both local and systemic responses in health and disease within Macaca fascicularis and possibly across other species.
References:
[1] W. Deng, X. Gu, et al. Down-modulation of tnfsf15 in ovarian cancer by vegf and mcp-1 is a pre-requisite for tumor neovascularization. Angiogenesis, vol. 15, no. 1, p. 71-85, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10456-011-9244-y
[2] Z. Zhang and L. Li. Tnfsf15 modulates neovascularization and inflammation. Cancer Microenvironment, vol. 5, no. 3, p. 237-247, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12307-012-0117-8
[3] C. Zhao, Q. Han, et al. Tnfsf15 facilitates differentiation and polarization of macrophages toward m1 phenotype to inhibit tumor growth. Oncoimmunology, vol. 11, no. 1, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1080/2162402x.2022.2032918
[4] T. Qin, G. Xu, et al. Tumour necrosis factor superfamily member 15 (tnfsf15) facilitates lymphangiogenesis via up‐regulation of vegfr3 gene expression in lymphatic endothelial cells. The Journal of Pathology, vol. 237, no. 3, p. 307-318, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1002/path.4577
[5] J. Zhou, Y. Zhang, et al. Litaf and tnfsf15, two downstream targets of ampk, exert inhibitory effects on tumor growth. Oncogene, vol. 30, no. 16, p. 1892-1900, 2011. https://doi.org/10.1038/onc.2010.575
[6] F. Jiang, Q. Chen, et al. Tnfsf15 inhibits blood retinal barrier breakdown induced by diabetes. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 17, no. 5, p. 615, 2016. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms17050615
[7] K. Jia and J. Shen. Transcriptome-wide association studies associated with crohn’s disease: challenges and perspectives. Cell & Bioscience, vol. 14, no. 1, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13578-024-01204-w
[8] A. Al-Danakh, M. Safi, et al. Aging-related biomarker discovery in the era of immune checkpoint inhibitors for cancer patients. Frontiers in Immunology, vol. 15, 2024. https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2024.1348189