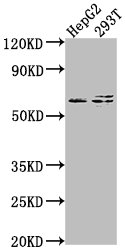
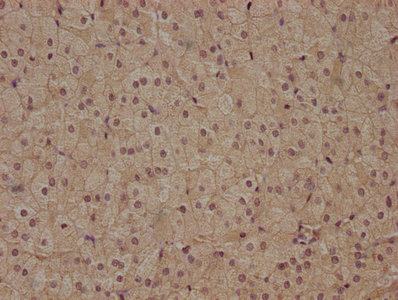
Receptor for Wnt proteins. Most frizzled receptors are coupled to the beta-catenin canonical signaling pathway, which leads to the activation of disheveled proteins, inhibition of GSK-3 kinase, nuclear accumulation of beta-catenin and activation of Wnt target genes. A second signaling pathway involving PKC and calcium fluxes has been seen for some family members, but it is not yet clear if it represents a distinct pathway or if it can be integrated in the canonical pathway, as PKC seems to be required for Wnt-mediated inactivation of GSK-3 kinase. Both pathways seem to involve interactions with G-proteins. Activation by WNT8 induces expression of beta-catenin target genes. Following ligand activation, binds to CCDC88C/DAPLE which displaces DVL1 from FZD7 and leads to inhibition of canonical Wnt signaling, activation of G-proteins by CCDC88C and triggering of non-canonical Wnt responses. May be involved in transduction and intercellular transmission of polarity information during tissue morphogenesis and/or in differentiated tissues.; (Microbial infection) Acts as a receptor for C.difficile toxin TcdB in the colonic epithelium.