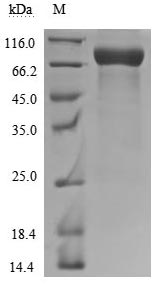
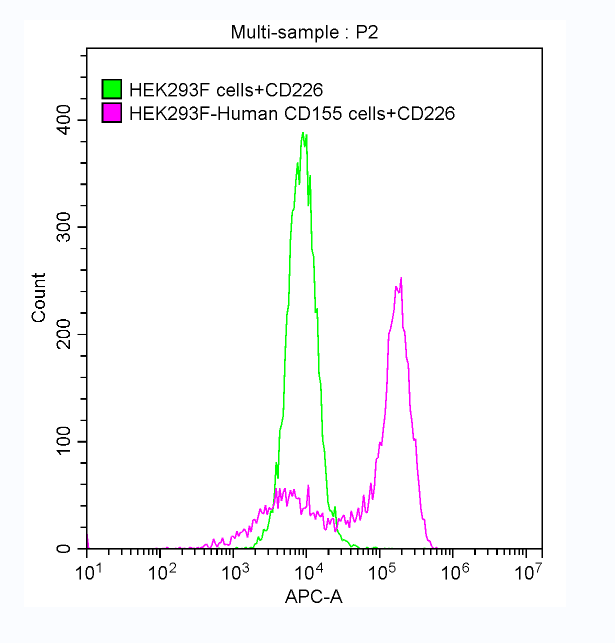
The recombinant human CD226 protein is generated by expressing the plasmid containing the gene fragment encoding amino acids 19-247 of the human CD226 in mammalian cells. The CD226 protein carries a C-terminal hFc-Myc tag. According to SDS-PAGE analysis, the CD226 protein's purity surpasses 90%. Its endotoxin levels are measured below 1.0 EU/μg by the LAL assay. It is validated as an active protein. The FACS assay shows that this human CD226 can bind to 293F cells overexpressing human CD155.
Human CD226 antigen (DNAX-1 or PTA1) is a transmembrane glycoprotein that plays a crucial role in the immune response. It is primarily expressed on various immune cells, including NK cells, T cells (both CD4+ and CD8+), monocytes, and platelets [1][2][3]. CD226 is a member of the immunoglobulin superfamily and is characterized by two immunoglobulin V-like domains, a transmembrane domain, and an intracellular signaling domain [3][4].
CD226 mainly acts as an activating receptor that enhances immune responses. It interacts with its ligands, CD155 (the poliovirus receptor) and CD112, which are expressed on antigen-presenting cells (APCs) and various other cell types [5][6]. This interaction is essential for the activation and proliferation of T cells, particularly in the context of Th1 cell differentiation and the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines such as IL-17 and IFN-γ [7][8]. CD226 signaling is also involved in the cytotoxic activity of NK cells, facilitating their ability to recognize and kill tumor cells [9][10].
Moreover, CD226 plays a significant role in immune checkpoint regulation, particularly in the context of tumor immunity. It competes with inhibitory receptors such as TIGIT and CD96 for binding to CD155 and CD112, thereby modulating the balance between activating and inhibitory signals in T cells [7][10]. This competitive interaction is critical for maintaining effective anti-tumor responses, as evidenced by studies showing that tumor cells can evade immune detection by inducing the degradation of CD226 through CD155 interactions [9][10]. CD226 has also been implicated in various autoimmune diseases and conditions. Genetic variations in the CD226 gene have been associated with susceptibility to multiple sclerosis and type 1 diabetes [11].
References:
[1] Z. Xu, T. Zhang, R. Zhuang, Y. Zhang, W. Jia, C. Song, et al. Increased levels of soluble cd226 in sera accompanied by decreased membrane cd226 expression on peripheral blood mononuclear cells from cancer patients, BMC Immunology, vol. 10, no. 1, 2009. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2172-10-34
[2] L. Bossini‐Castillo, C. Simeón, L. Beretta, J. Broen, M. Vonk, R. Ríos-Fernández, et al. A multicenter study confirms cd226gene association with systemic sclerosis-related pulmonary fibrosis, Arthritis Research & Therapy, vol. 14, no. 2, 2012. https://doi.org/10.1186/ar3809
[3] P. Zhao. Increased proportion of cd226 + cd14 + monocytes correlates with clinical features and laboratory parameters in patients with primary sjögren's syndrome, International Journal of Rheumatic Diseases, vol. 26, no. 12, p. 2460-2469, 2023. https://doi.org/10.1111/1756-185x.14936
[4] K. Shibuya, J. Shirakawa, T. Kameyama, S. Honda, S. Tahara‐Hanaoka, A. Miyamoto, et al. Cd226 (dnam-1) is involved in lymphocyte function–associated antigen 1 costimulatory signal for naive t cell differentiation and proliferation, The Journal of Experimental Medicine, vol. 198, no. 12, p. 1829-1839, 2003. https://doi.org/10.1084/jem.20030958
[5] Z. Liu. Act001 inhibits the proliferation of tumor cells and improves immune function in multiple myeloma.,, 2023. https://doi.org/10.21203/rs.3.rs-3664325/v1
[6] E. Lozano, N. Joller, Y. Cao, V. Kuchroo, & D. Hafler. The cd226/cd155 interaction regulates the proinflammatory (th1/th17)/anti-inflammatory (th2) balance in humans, The Journal of Immunology, vol. 191, no. 7, p. 3673-3680, 2013. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1300945
[7] G. Gaud, R. Roncagalli, K. Chaoui, I. Bernard, J. Familiadès, C. Colacios, et al. The costimulatory molecule cd226 signals through vav1 to amplify tcr signals and promote il-17 production by cd4+ t cells, Science Signaling, vol. 11, no. 538, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1126/scisignal.aar3083
[8] M. Ayano, H. Tsukamoto, K. Kohno, N. Ueda, A. Tanaka, H. Mitoma, et al. Increased cd226 expression on cd8+ t cells is associated with upregulated cytokine production and endothelial cell injury in patients with systemic sclerosis, The Journal of Immunology, vol. 195, no. 3, p. 892-900, 2015. https://doi.org/10.4049/jimmunol.1403046
[9] M. Braun, A. Aguilera, A. Sundarrajan, D. Corvino, K. Stannard, S. Krumeich, et al. Cd155 on tumor cells drives resistance to immunotherapy by inducing the degradation of the activating receptor cd226 in cd8+ t cells, Immunity, vol. 53, no. 4, p. 805-823.e15, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.09.010
[10] M. Philip. Cd226 throttles up cd8+ t cell antitumor activity, Immunity, vol. 53, no. 4, p. 704-706, 2020. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.immuni.2020.09.013
[11] J. Hafler, L. Maier, J. Cooper, V. Plagnol, A. Hinks, M. Simmonds, et al. Cd226 gly307ser association with multiple autoimmune diseases, Genes and Immunity, vol. 10, no. 1, p. 5-10, 2008. https://doi.org/10.1038/gene.2008.82