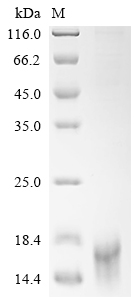
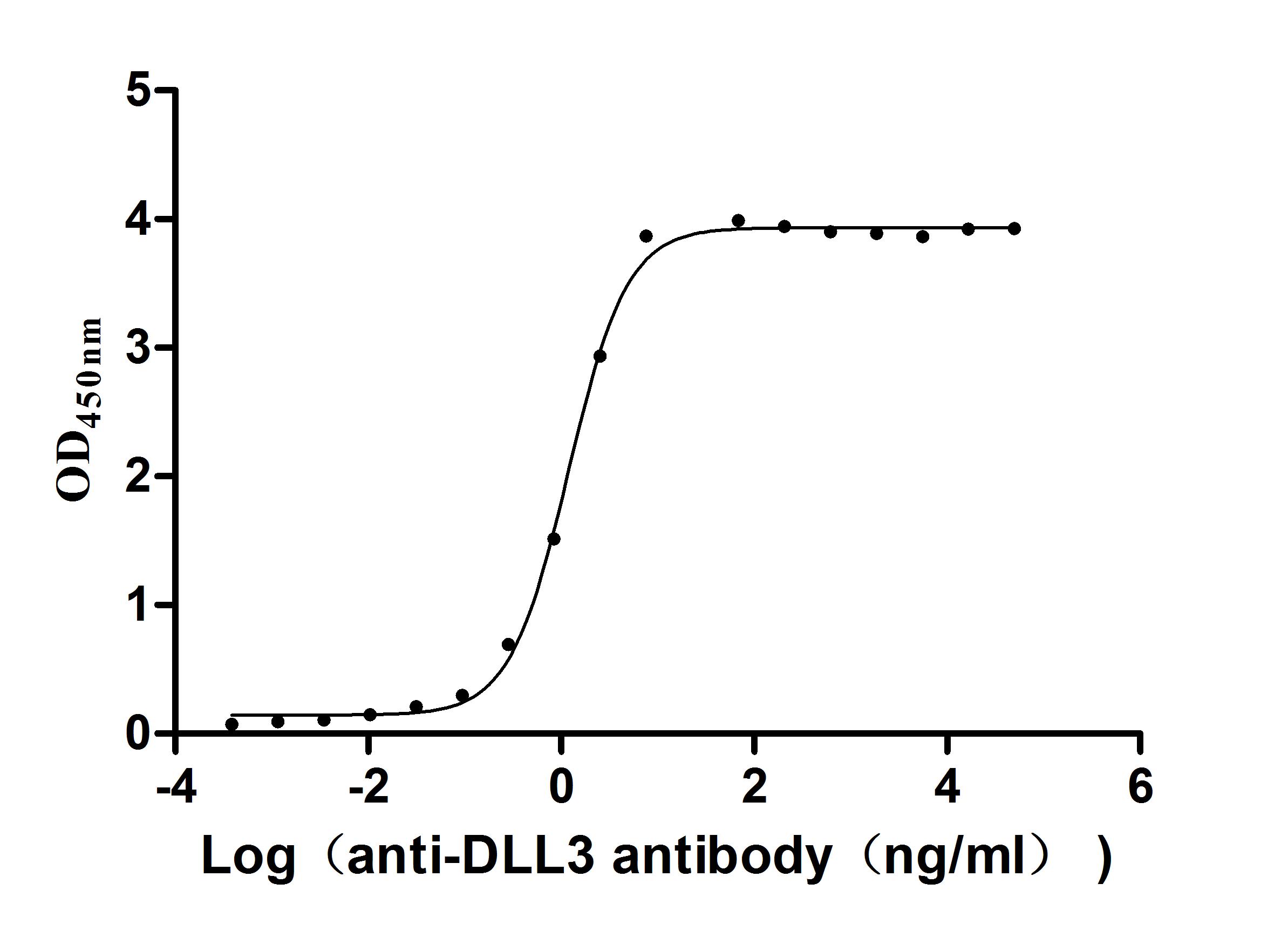
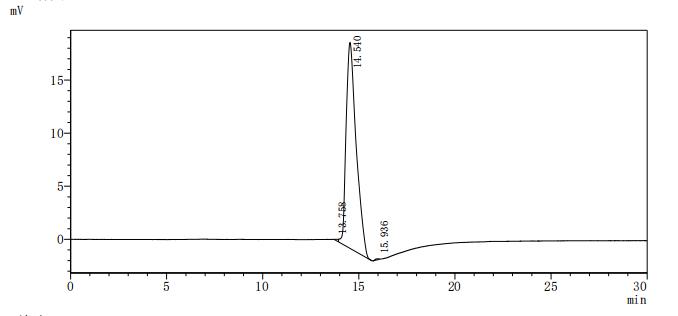
The recombinant human DLL3 protein is an active protein generated in mammalian cells. Its expression region corresponds to the 391-492aa of the human DLL3. The target gene is co-expressed with the C-terminal 10xHis-tag gene through a plasmid. The resulting DLL3 protein's purity is over 95% as measured by SDS-PAGE. In a functional ELISA, this human DLL3 protein can bind to the DLL3 recombinant antibody (CSB-RA882142MA2HU), with the EC50 of 1.107-1.282 ng/mL.
DLL3 is a Notch ligand that plays a crucial role in various cellular processes, particularly in the development and progression of certain types of cancer [1-6]. DLL3 is primarily localized in the Golgi apparatus and is rarely expressed on the cell surface [7][8]. Unlike other Notch ligands, DLL3 does not activate Notch receptors on neighboring cells. Instead, it can suppress the Notch signaling in a cell-autonomous manner by targeting newly synthesized Notch1 or DLL1 for endosomal/lysosomal degradation [8][9].
DLL3 is highly expressed in various types of cancer, particularly in small cell lung cancer (SCLC), neuroendocrine tumors, and some other neuroendocrine-like cancers [1-6]. High DLL3 expression is often associated with tumor growth, invasion, and metastasis, as well as poor patient prognosis [1][3][5][6]. DLL3 has been shown to regulate the conversion between mesenchymal and epithelial states, which is a crucial process in cancer metastasis [1].
DLL3 may interact with immune-related proteins, such as LG3BP and HSPA8, which regulate immune response [9]. However, the exact mechanisms by which DLL3 modulates the immune system are not yet fully understood. Due to its specific expression in certain types of cancer, DLL3 has emerged as a promising therapeutic target. Several DLL3-targeted therapies, including antibody-drug conjugates, bispecific T-cell engagers, and chimeric antigen receptor T cells, are currently under development and investigation for the treatment of DLL3-positive cancers [2][6][10][11].
References:
[1] C. Zhu. The predictive value of delta-like3 and serum nse in evaluating chemotherapy response and prognosis in patients with advanced small cell lung carcinoma: an observational study, Medicine, vol. 103, no. 23, p. e38487, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1097/md.0000000000038487
[2] L. Saunders, A. Bankovich, W. Anderson, M. Aujay, S. Bheddah, K. Black, et al. A dll3-targeted antibody-drug conjugate eradicates high-grade pulmonary neuroendocrine tumor-initiating cells in vivo, Science Translational Medicine, vol. 7, no. 302, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1126/scitranslmed.aac9459
[3] L. Yang, G. Wang, H. Shi, S. Jia, J. Ruan, R. Cui, et al. Methylation-driven gene dll3 is a potential prognostic biomarker in ocular melanoma correlating with metastasis, Frontiers in Oncology, vol. 12, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3389/fonc.2022.964902
[4] M. Furuta, J. Sakakibara‐Konishi, H. Kikuchi, H. Yokouchi, H. Nishihara, H. Minemura, et al. Analysis of dll3 and ascl1 in surgically resected small cell lung cancer (hot1702), The Oncologist, vol. 24, no. 11, p. e1172-e1179, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1634/theoncologist.2018-0676
[5] M. Furuta, H. Kikuchi, T. Shoji, Y. Takashima, E. Kikuchi, J. Kikuchi, et al. dll3 regulates the migration and invasion of small cell lung cancer by modulating snail, Cancer Science, vol. 110, no. 5, p. 1599-1608, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1111/cas.13997
[6] V. Koshkin, J. García, J. Reynolds, P. Elson, C. Magi‐Galluzzi, J. McKenney, et al. Transcriptomic and protein analysis of small-cell bladder cancer (scbc) identifies prognostic biomarkers and dll3 as a relevant therapeutic target, Clinical Cancer Research, vol. 25, no. 1, p. 210-221, 2019. https://doi.org/10.1158/1078-0432.ccr-18-1278
[7] H. Hamamoto, K. Maemura, K. Matsuo, K. Taniguchi, Y. Tanaka, S. Futaki, et al. Delta-like 3 is silenced by hbx via histone acetylation in hbv-associated hccs, Scientific Reports, vol. 8, no. 1, 2018. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-018-23318-1
[8] Y. Mizuno, K. Maemura, Y. Tanaka, A. Hirata, S. Futaki, H. Hamamoto, et al. Expression of delta-like 3 is downregulated by aberrant dna methylation and histone modification in hepatocellular carcinoma, Oncology Reports, 2018. https://doi.org/10.3892/or.2018.6293
[9] J. Ye, J. Wen, D. Wu, B. Hu, M. Luo, Y. Lin, et al. Elevated dll3 in stomach cancer by tumor-associated macrophages enhances cancer-cell proliferation and cytokine secretion of macrophages, Gastroenterology Report, vol. 10, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1093/gastro/goab052
[10] K. Krytska, C. Casey, J. Pogoriler, D. Martı́nez, K. Rathi, A. Farrel, et al. Evaluation of the dll3-targeting antibody–drug conjugate rovalpituzumab tesirine in preclinical models of neuroblastoma, Cancer Research Communications, vol. 2, no. 7, p. 616-623, 2022. https://doi.org/10.1158/2767-9764.crc-22-0137
[11] B. Rath, A. Plangger, D. Krenbek, M. Hochmair, S. Stickler, V. Tretter, et al. Rovalpituzumab tesirine resistance: analysis of a corresponding small cell lung cancer and circulating tumor cell line pair, Anti-Cancer Drugs, vol. 33, no. 3, p. 300-307, 2021. https://doi.org/10.1097/cad.0000000000001267