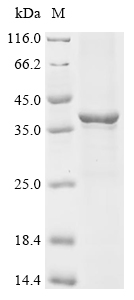
The production of recombinant rat Cxcl13 in E. coli begins with co-cloning the target gene into an expression vector with an N-terminal 6xHis-GST-tag gene, followed by transformation into E. coli cells. These cells are grown under conditions that promote protein expression. Once adequate growth is achieved, the cells are lysed to release the recombinant Cxcl13 protein. Purification involves the affinity chromatography technique. The purity of the recombinant Cxcl13 protein is assessed using SDS-PAGE, reaching over 85%.
Rat Cxcl13 is a chemokine that plays a crucial role in various physiological and pathological processes. Studies have shown that CXCL13 is involved in promoting chronic postsurgical pain and astrocyte activation in rats by targeting NLRP3 [1]. Evidence indicated that inhibiting CXCL13 expression can improve neuropathic pain by modulating the expression of chemokines and inflammatory factors in the spinal cord and interfering with glial cell polarization [2].
Furthermore, CXCL13 is associated with bone marrow mesenchymal stem cell (BMSC) function. It has been demonstrated that CXCL13 can promote osteogenic differentiation of BMSCs by inhibiting miR-23a expression [3]. Research has revealed that CXCL13 enhances the effect of BMSCs on tendon bone healing in rats [4].
In the context of cancer-induced bone pain, CXCL13 attenuates morphine analgesia in rats with cancer-induced bone pain, suggesting a role in pain modulation [5]. Additionally, CXCL13 has been linked to morphine analgesia regulation in bone cancer pain rats through specific signaling pathways [6].
References:
[1] H. Yi, Cxcl13/cxcr5 promote chronic postsurgical pain and astrocyte activation in rats by targeting nlrp3, Neuroreport, vol. 35, no. 6, p. 406-412, 2024. https://doi.org/10.1097/wnr.0000000000002023
[2] T. Zhang, W. Liang, M. Zhang, S. Cui, X. Huang, W. Ouet al., Daphnetin improves neuropathic pain by inhibiting the expression of chemokines and inflammatory factors in the spinal cord and interfering with glial cell polarization, Pharmaceuticals, vol. 16, no. 2, p. 243, 2023. https://doi.org/10.3390/ph16020243
[3] F. Tian, X. Ji, W. Xiao, B. Wang, & F. Wang, Cxcl13 promotes osteogenic differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells by inhibiting mir-23a expression, Stem Cells International, vol. 2015, p. 1-8, 2015. https://doi.org/10.1155/2015/632305
[4] F. Tian, X. Ji, W. Xiao, B. Wang, & F. Wang, Cxcl13 promotes the effect of bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells (mscs) on tendon-bone healing in rats and in c3hiot1/2 cells, International Journal of Molecular Sciences, vol. 16, no. 2, p. 3178-3187, 2015. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms16023178
[5] S. Wang, C. Dong, X. Yang, & J. Yin, Upregulation of (c-x-c motif) ligand 13 (cxcl13) attenuates morphine analgesia in rats with cancer-induced bone pain, Medical Science Monitor, vol. 22, p. 4612-4622, 2016. https://doi.org/10.12659/msm.897702
[6] H. Bu, P. Jiao, X. Fan, Y. Gao, L. Zhang, & H. Guo, The role of botulinum toxin type a related axon transport in neuropathic pain induced by chronic constriction injury, The Korean Journal of Pain, vol. 35, no. 4, p. 391-402, 2022. https://doi.org/10.3344/kjp.2022.35.4.391